Rigid Body Dynamics - UCSD Computer Graphics Lab
... We treat a rigid body as a system of particles, where the distance between any two particles is fixed We will assume that internal forces are generated to hold the relative positions fixed. These internal forces are all balanced out with Newton’s third law, so that they all cancel out and have no ef ...
... We treat a rigid body as a system of particles, where the distance between any two particles is fixed We will assume that internal forces are generated to hold the relative positions fixed. These internal forces are all balanced out with Newton’s third law, so that they all cancel out and have no ef ...
Lecture 2 Quantum mechanics in one dimension
... We have seen that even a weak potential can lead to the formation of a bound state. However, for such a confining potential, we expect high energy states to remain unbound. Curiously, and counter-intuitively, in 1d a weak extended disorder potential always leads to the exponential localization of al ...
... We have seen that even a weak potential can lead to the formation of a bound state. However, for such a confining potential, we expect high energy states to remain unbound. Curiously, and counter-intuitively, in 1d a weak extended disorder potential always leads to the exponential localization of al ...
N2(g)
... -values different – e.g. ∆Hc\ for hydrogen is small but very high per unit mass for rocket fuels ‘specific enthalpy’ of fuel (energy per mass) much more important H2 + ½O2 ...
... -values different – e.g. ∆Hc\ for hydrogen is small but very high per unit mass for rocket fuels ‘specific enthalpy’ of fuel (energy per mass) much more important H2 + ½O2 ...
15. The Kinetic Theory of Gases
... The ideal gas model assumes that gas molecules have no collisions with one another. The only collisions the gas molecules have are with the walls of the container and this produces the gas pressure. Nonetheless, there are phenomena, like diffusion, that depend upon the molecules colliding among them ...
... The ideal gas model assumes that gas molecules have no collisions with one another. The only collisions the gas molecules have are with the walls of the container and this produces the gas pressure. Nonetheless, there are phenomena, like diffusion, that depend upon the molecules colliding among them ...
Chemistry Unit Notes Organizing the Periodic Table All the elements
... 3. A subscript outside a bracket multiplies to all the element inside the brackets. Examples: Mg3(PO4)2 : 3 atoms of Mg 1*2 = 2 atoms of P 4*2 = 8 atoms of O Ca4(SO4)3: 4 atoms of Ca 1*3 = 3 atoms of S 4*3 = 12 atoms of O 4. A coefficient is a number written in front of a chemical formula. The coeff ...
... 3. A subscript outside a bracket multiplies to all the element inside the brackets. Examples: Mg3(PO4)2 : 3 atoms of Mg 1*2 = 2 atoms of P 4*2 = 8 atoms of O Ca4(SO4)3: 4 atoms of Ca 1*3 = 3 atoms of S 4*3 = 12 atoms of O 4. A coefficient is a number written in front of a chemical formula. The coeff ...
Exam 1 Solutions – 100 points
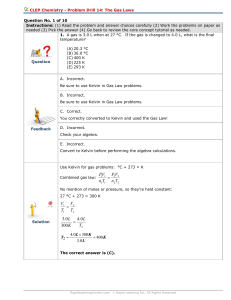
... The region of negative deviation for a real gas typically occurs at low pressure. This is a result of intermolecular interactions. At low pressure, the atoms or molecules of a real gas interact with one another and "stick together". This results in a pressure that is lower than expected, and therefo ...
... The region of negative deviation for a real gas typically occurs at low pressure. This is a result of intermolecular interactions. At low pressure, the atoms or molecules of a real gas interact with one another and "stick together". This results in a pressure that is lower than expected, and therefo ...