Geometry A - Arkansas Department of Education
... Content Standard 2. Students will identify and describe types of triangles and their special segments. They will use logic to apply the properties of congruence, similarity, and inequalities. The students will apply the Pythagorean Theorem and trigonometric ratios to solve problems in real world sit ...
... Content Standard 2. Students will identify and describe types of triangles and their special segments. They will use logic to apply the properties of congruence, similarity, and inequalities. The students will apply the Pythagorean Theorem and trigonometric ratios to solve problems in real world sit ...
Geometry A Course
... Content Standard 2. Students will identify and describe types of triangles and their special segments. They will use logic to apply the properties of congruence, similarity, and inequalities. The students will apply the Pythagorean Theorem and trigonometric ratios to solve problems in real world sit ...
... Content Standard 2. Students will identify and describe types of triangles and their special segments. They will use logic to apply the properties of congruence, similarity, and inequalities. The students will apply the Pythagorean Theorem and trigonometric ratios to solve problems in real world sit ...
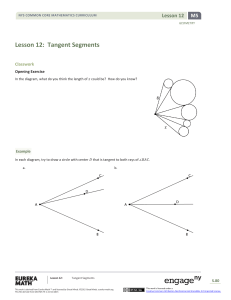
Tangents and Normals
... In this Workbook you will learn to apply your knowledge of differentiation to solve some basic problems connected with curves. First you will learn how to obtain the equation of the tangent line and the normal line to any point of interest on a curve. Secondly, you will learn how to find the positio ...
... In this Workbook you will learn to apply your knowledge of differentiation to solve some basic problems connected with curves. First you will learn how to obtain the equation of the tangent line and the normal line to any point of interest on a curve. Secondly, you will learn how to find the positio ...
329homework7 - WordPress.com
... geometry, the fourth angle would be a right angle and follow the definition of a quadrilateral as we know it. In non-Euclidean geometries, the angle can be acute. My perception of these quadrilaterals is different now that we have analyzed other types of geometries. The existence of these figures is ...
... geometry, the fourth angle would be a right angle and follow the definition of a quadrilateral as we know it. In non-Euclidean geometries, the angle can be acute. My perception of these quadrilaterals is different now that we have analyzed other types of geometries. The existence of these figures is ...
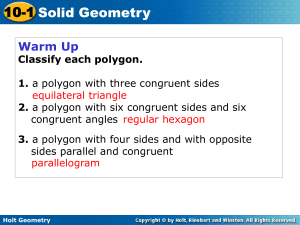
1.5 glenco geometry.notebook - Milton
... Intersect to form four right angles Perpendicular lines intersect to form congruent adjacent angles Segments and rays can be perpendicular to lines or other line segments and rays The right angle symbol in the figure indicates that the lines are perpendicular ...
... Intersect to form four right angles Perpendicular lines intersect to form congruent adjacent angles Segments and rays can be perpendicular to lines or other line segments and rays The right angle symbol in the figure indicates that the lines are perpendicular ...
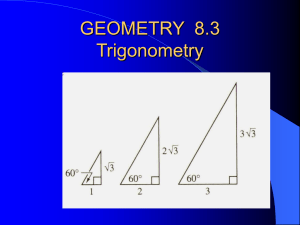
Example 6 page 146
... Check it out with the formula. In Euclidean Geometry we can chat casually about the Pythagorean Theorem and how the 3 – 4 – 5 right triangle illustrates it. In Taxicab Geometry, the Pythagorean Theorem is NOT TRUE; it’s not a theorem at all. The Pythagorean Theorem is a Euclideanspecific theorem. We ...
... Check it out with the formula. In Euclidean Geometry we can chat casually about the Pythagorean Theorem and how the 3 – 4 – 5 right triangle illustrates it. In Taxicab Geometry, the Pythagorean Theorem is NOT TRUE; it’s not a theorem at all. The Pythagorean Theorem is a Euclideanspecific theorem. We ...