FDMF6704V - XS DrMOS FD M
... The high-side driver (GH) is designed to drive a floating N-channel MOSFET. The bias voltage for the high-side driver is developed by a bootstrap supply circuit, consisting of the internal BOOT diode and an external bootstrap capacitor (CBOOT). During start-up, VSWH is held at PGND, allowing CBOOT t ...
... The high-side driver (GH) is designed to drive a floating N-channel MOSFET. The bias voltage for the high-side driver is developed by a bootstrap supply circuit, consisting of the internal BOOT diode and an external bootstrap capacitor (CBOOT). During start-up, VSWH is held at PGND, allowing CBOOT t ...
Chapter 5 Signal Encoding Techniques
... —Conversion of analog data into digital data —Digital data can then be transmitted using NRZ-L —Digital data can then be transmitted using code other than NRZ-L —Digital data can then be converted to analog signal —Analog to digital conversion done using a codec —Pulse code modulation —Delta modulat ...
... —Conversion of analog data into digital data —Digital data can then be transmitted using NRZ-L —Digital data can then be transmitted using code other than NRZ-L —Digital data can then be converted to analog signal —Analog to digital conversion done using a codec —Pulse code modulation —Delta modulat ...
Micro Power Systems™ - Dynapower Energy Storage Systems
... In the Grid-Tied mode, the MPS controls the AC output real power (P) and reactive power (Q). In Stand-Alone mode, the MPS controls the AC output voltage (U) and frequency (F). The system can be started in either mode and the transfer between modes is done dynamically. The transition between operatin ...
... In the Grid-Tied mode, the MPS controls the AC output real power (P) and reactive power (Q). In Stand-Alone mode, the MPS controls the AC output voltage (U) and frequency (F). The system can be started in either mode and the transfer between modes is done dynamically. The transition between operatin ...
Sorensen XBT 32-3FTP 15–32 V 3–5 A 222 W
... there is one 0-32V/0-6A output and one 0-15V/0-5A/30W output; in series mode, there is one 0-64V/0-3A output and one 0-15V/0-5A/30W output. Safety of devices under test is paramount. The XBT series of power supplies provides superior device protection. Each output is fully isolated with voltage/curr ...
... there is one 0-32V/0-6A output and one 0-15V/0-5A/30W output; in series mode, there is one 0-64V/0-3A output and one 0-15V/0-5A/30W output. Safety of devices under test is paramount. The XBT series of power supplies provides superior device protection. Each output is fully isolated with voltage/curr ...
J047015963
... suitability of MLC’s for high voltage and high power applications. The general structure of the multilevel converter is to synthesize a sinusoidal voltage from several levels of voltages. The so-called “multilevel” starts from three levels. A three-level converter, also known as a “neutral-clamped” ...
... suitability of MLC’s for high voltage and high power applications. The general structure of the multilevel converter is to synthesize a sinusoidal voltage from several levels of voltages. The so-called “multilevel” starts from three levels. A three-level converter, also known as a “neutral-clamped” ...
ISSCC 2011 / SESSION 22 / DC/DC CONVERTERS / 22.7
... transferred energy by buck/boost conversion; S4 and S5 distribute the energy stored in the inductor to both outputs. All switches are controlled by PWM signals which are generated in two control loops. The converter is specified for two outputs from 1 to 5V with the maximum total power of 2.5W and s ...
... transferred energy by buck/boost conversion; S4 and S5 distribute the energy stored in the inductor to both outputs. All switches are controlled by PWM signals which are generated in two control loops. The converter is specified for two outputs from 1 to 5V with the maximum total power of 2.5W and s ...
presentation final copy
... P = number of poles It is important that no matter the number you get you must round down to the next integer. If its 12.6 then Ys = 12. If its 10 then Ys = 10. ...
... P = number of poles It is important that no matter the number you get you must round down to the next integer. If its 12.6 then Ys = 12. If its 10 then Ys = 10. ...
Control Systems Elements of a control system
... * The output of the machine/plant/process can be arranged to provide an electrical signal ...
... * The output of the machine/plant/process can be arranged to provide an electrical signal ...
EE 4BD4 Lecture 28
... • (1) Use a DC-DC converter to give high voltage source to drive circuit Fig 3.8 slide 21 • (2) Replace load in Fig 3.8 by the input coil of a pulse transformer • If output current to electrodes is to be e.g. 40 ma, the input current must be 480 ma if transformer ratio is 1:12 • May then replace tra ...
... • (1) Use a DC-DC converter to give high voltage source to drive circuit Fig 3.8 slide 21 • (2) Replace load in Fig 3.8 by the input coil of a pulse transformer • If output current to electrodes is to be e.g. 40 ma, the input current must be 480 ma if transformer ratio is 1:12 • May then replace tra ...
Desing of power sources, converters
... Power semiconductor converters • Equipment for changing quality of electrical energy (voltage, current, frequency, no. of phases, impedance, etc.) • Conversion of energy „nearly“ without power losses • The most often converters: – rectifiers (diodes, not controlled), – frequency converters (non-dir ...
... Power semiconductor converters • Equipment for changing quality of electrical energy (voltage, current, frequency, no. of phases, impedance, etc.) • Conversion of energy „nearly“ without power losses • The most often converters: – rectifiers (diodes, not controlled), – frequency converters (non-dir ...
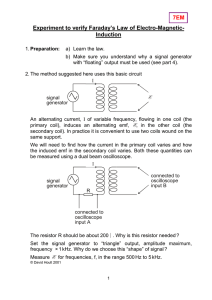
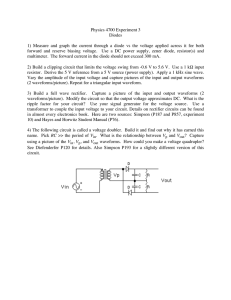
Physics 4700 Experiment 3 Diodes
... Diodes 1) Measure and graph the current through a diode vs the voltage applied across it for both forward and reserve biasing voltage. Use a DC power supply, zener diode, resistor(s) and multimeter. The forward current in the diode should not exceed 300 mA. 2) Build a clipping circuit that limits th ...
... Diodes 1) Measure and graph the current through a diode vs the voltage applied across it for both forward and reserve biasing voltage. Use a DC power supply, zener diode, resistor(s) and multimeter. The forward current in the diode should not exceed 300 mA. 2) Build a clipping circuit that limits th ...
Design Options for High Efficiency Linear Handset Power Amplifiers
... series resistance increases with stacking, so that increasing device width is needed at the same time. The stacking principle has been applied with success for RF switches, such as needed next to the antenna for TX/RX and band selection, where voltage levels can be very high (handling 15V is require ...
... series resistance increases with stacking, so that increasing device width is needed at the same time. The stacking principle has been applied with success for RF switches, such as needed next to the antenna for TX/RX and band selection, where voltage levels can be very high (handling 15V is require ...
Pulse-width modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), or pulse-duration modulation (PDM), is a modulation technique used to encode a message into a pulsing signal. Although this modulation technique can be used to encode information for transmission, its main use is to allow the control of the power supplied to electrical devices, especially to inertial loads such as motors. In addition, PWM is one of the two principal algorithms used in photovoltaic solar battery chargers, the other being MPPT.The average value of voltage (and current) fed to the load is controlled by turning the switch between supply and load on and off at a fast rate. The longer the switch is on compared to the off periods, the higher the total power supplied to the load.The PWM switching frequency has to be much higher than what would affect the load (the device that uses the power), which is to say that the resultant waveform perceived by the load must be as smooth as possible. Typically switching has to be done several times a minute in an electric stove, 120 Hz in a lamp dimmer, from few kilohertz (kHz) to tens of kHz for a motor drive and well into the tens or hundreds of kHz in audio amplifiers and computer power supplies.The term duty cycle describes the proportion of 'on' time to the regular interval or 'period' of time; a low duty cycle corresponds to low power, because the power is off for most of the time. Duty cycle is expressed in percent, 100% being fully on.The main advantage of PWM is that power loss in the switching devices is very low. When a switch is off there is practically no current, and when it is on and power is being transferred to the load, there is almost no voltage drop across the switch. Power loss, being the product of voltage and current, is thus in both cases close to zero. PWM also works well with digital controls, which, because of their on/off nature, can easily set the needed duty cycle.PWM has also been used in certain communication systems where its duty cycle has been used to convey information over a communications channel.