* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Project Renovatio
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
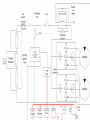
Project Renovatio Joshua Fraser Alastair Fraser Ruofei Fu Chao Jiang Cheng Zhen Dacheng Zheng Tien Truong Project Overview - - Gas to electric motorcycle conversion. Electrical engineering team in charge of electrical components and wiring instructions. Component sourcing finished, all necessary parts ready to be ordered. - DC/DC converter, coolant pump, headlight/taillight, G-force switch, relays, fuses The goal is to have a fully functional electric motorcycle, able to be driven and operated safely. System-Level Wiring Diagram NEXT PAGE System Decomposition System Decomposition System Decomposition Key Technologies ● ● ● ● In order to step down the voltage from the battery packs to a low voltage of 12 V for the low voltage system, a DC to DC converter is required. Only a maximum of 150 W will be pulled by the low voltage system, and the DC to DC converter is able to handle 200 W. In order to ensure that each battery drains equally over time, a battery management system is required to continually balance the battery voltages. There are many key safety mechanisms being employed, since such high voltages and currents can be very unsafe. Fuses will be in use for each wire in the low voltage system to have shutoff capability if something goes wrong. Also for the high voltage system, there will be a couple manual switches, as well as an automatic switch, that will cut power in case of emergency. The Arduino microcontroller is key in controlling the low voltage system. It will handle the braking switch, the lights, the main contactor, and will also monitor the status of several subsystems. Software Processes ● Control Systems Integration Module (CSIM) to collect data, relay it to the rider in an effective way and store in an efficient manner. o Android tablet, Arduino Bluno and CAN shield. ● Collecting data via a Central Area Network (CAN) bus on the Arduino Bluno. o Operates on a serial bus and uses a priority bit system. o Data collected from three systems Two motor controllers and BMS. Software Processes ● Motor Controllers o RPM o Motor Temperature o Motor Side Current o Battery Side Current o Battery Side Voltage ● BMS o Individual Cell Voltage (37 data points) o Sub-Pack Cell Voltage (12 cells) o Entire Pack Voltage (37 cells) o Pack Current o Pack Temperature (4 thermistors) o Minimum Cell Voltage o Maximum Cell Voltage o Calculated Remaining Power o Recharge Power Test Plans Battery & BMS (Sensor, IR temp gun, DC load) -Battery discharge and recharge rate and duration -Max temperature during charging/discharging DC/DC Converter (DC load, Spec Any, IR temp gun) -Voltage stability under highest expected load -Max temperature under highest expected load 1st Week of April 1st Week of April Safety and Accessories (Power supply & Multimeter) 2nd Week of April -Safety switches correctly stop current -Relay turns on high voltage system -Lights operate Test Plans Pre Full Assembly (Sensors, Power, IR temp gun) 3rd Week of April -Water pump and tubing operate without leaking -Motor operates with full control -Max motor temperature Post Assembly (Sensors, IR temp, Dynamometer) 3rd-4th Week of April -All systems operate on lift -Bike top speed and acceleration/torque -Bike distance on full charge -Motor temperature while riding -Water/rain susceptibility Resolving Action Items ● How would the accelerometer gauge an accident instead of someone clutching the brakes? o The minimum trip threshold of the inertial crash is much greater than that can be applied by the brakes without throwing the rider. o Emergency shutdown for the electronics is necessary in the situation of a crash but we don’t believe the accelerometer will be necessary. ● Plans for waterproofing subsystems o Battery boxes will not be waterproof, so a protective polycarbonate shield will be installed around the batteries and electronics. Also will protect against debris picked up under the fairings. Resolving Action Items ● What are the plans for providing overvoltage/overcurrent protection for the Arduino? o Relying on DC-DC converter to maintain its 12V output. o We are collecting data using the CAN bus and requires a low voltage and current. ● How to test G-force necessary for crash? o Accelerating the motorcycle at full current and braking as hard as physically possible without locking the wheels. This is still a stretch goal for us. ● Back-up plans for testing if equipment is not available? o Reserved a date with Rawhide Harley to use their dyno. o Rest of testing can be done using EECS lab equipment such as electronic load and multimeter. Milestones ● Milestone 1: Isolation Testing o Ensure the input and output voltages, currents and power are met for each subsystem. o Deliverables: data measurements, documentation for test equipment and methods. ● Milestone 2: System Integration and Testing o Validate that the LVS and HVS work separately before integrating both. o Deliverables: data measurements, documentation of assembly and test methods. ● Final Demonstration o Showcase bike on a lift and a short video (possibly). Project Schedule Project Items ● On-going ● ● ● Component installation is waiting on parts to be ordered. All needed components have been sourced. Testing and evaluation will proceed when the parts are installed. Some isolation testing will be done. Motorcycle frame and additional infrastructure (battery boxes, extra framing) will be fully built by 4/1. ● Completed ● Created a testing and evaluation plan ● Familiarized with the system and objectives, and have a functional system decomposition Created a risk mitigation plan for all processes we could think of that could potentially be at risk Successfully sourced all of the needed components, and are ready to order and install ● ● Challenges ● Getting everything done before their deadlines. With such a big project, it is difficult to hit every deadline with so many moving parts. But it is critical to hit the deadlines so that Electrical team can pass off the project to Computer team for final construction and wiring. ● Making the motorcycle as safe as possible. With such high voltages and currents it can potentially be dangerous if certain systems fail, or if any potential hazard has gone unnoticed. Questions? ● Project Site: o project-renovatio.bitballoon.com