PNS Extra credit worksheet. Use the text and your power point notes
... Sensory nerves contain information heading __________________ the brain. These are also known as ________________________ nerves. Motor nerves contain information heading __________________ the brain. These are also known as ________________________ nerves. A convenient way to remember this is to us ...
... Sensory nerves contain information heading __________________ the brain. These are also known as ________________________ nerves. Motor nerves contain information heading __________________ the brain. These are also known as ________________________ nerves. A convenient way to remember this is to us ...
The Nervous System
... The Nervous System can be broken into two parts: • The CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: composed of the brain and the spinal cord • The PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: composed of all the nerves that aren’t part of the brain or spinal cord ...
... The Nervous System can be broken into two parts: • The CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: composed of the brain and the spinal cord • The PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: composed of all the nerves that aren’t part of the brain or spinal cord ...
Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Lecture Outline
... Lateral gray horn: throacic and lumbar only, visceral motor nuclei (ANS) Gray commissure: axons for decussation White matter: myelinated axons Posterior white column/funiculus Anterior white coulmn/funiculus Lateral white column/funiculus All 6 columns contain tracts: Ascending tracts: sensory to br ...
... Lateral gray horn: throacic and lumbar only, visceral motor nuclei (ANS) Gray commissure: axons for decussation White matter: myelinated axons Posterior white column/funiculus Anterior white coulmn/funiculus Lateral white column/funiculus All 6 columns contain tracts: Ascending tracts: sensory to br ...
Axon = short Dendrite = long Axon = long or short Dendrite = short
... Dendrite = short -dendrites and cell body are located in spinal cord; axon is outside of spinal cord -PNS ...
... Dendrite = short -dendrites and cell body are located in spinal cord; axon is outside of spinal cord -PNS ...
Worksheet for class 3 • What are the three primary germ layers
... regions visible in this view. Identify the embryonic primary brain vesicle that ultimately gave rise to each of these adult brain regions. (This could be done by colorcoding.) ...
... regions visible in this view. Identify the embryonic primary brain vesicle that ultimately gave rise to each of these adult brain regions. (This could be done by colorcoding.) ...
Central Nervous System
... Spinal Cord - Functions Two main functions: 1. Conduction routes to/from brain 2. Integration or reflex center for all spinal ...
... Spinal Cord - Functions Two main functions: 1. Conduction routes to/from brain 2. Integration or reflex center for all spinal ...
The Nervous System
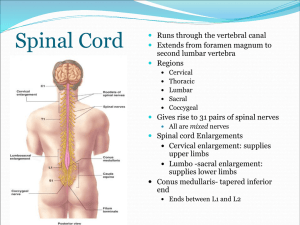
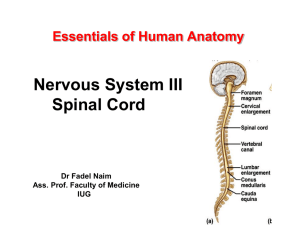
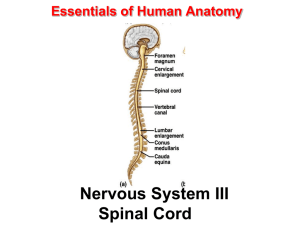
... Lies in vertebral canal Continuous above with medulla oblongata at level of foramen magnum Ends below at the lower border of L1 in the adult; at birth the cord ends at level of L3 ...
... Lies in vertebral canal Continuous above with medulla oblongata at level of foramen magnum Ends below at the lower border of L1 in the adult; at birth the cord ends at level of L3 ...
Spinal Cord
... Physiological response produced by activation of specific types of nerve fibers Experienced because of nociceptors being sensitive to extreme ...
... Physiological response produced by activation of specific types of nerve fibers Experienced because of nociceptors being sensitive to extreme ...
Anatomy of the Spinal Cord
... descending tracts The gray matter is in increased volume in cervical & lumbosacral enlargements for innervation of upper & lower limbs The lateral horn is characteristics of thoracic and upper lumbar segments ...
... descending tracts The gray matter is in increased volume in cervical & lumbosacral enlargements for innervation of upper & lower limbs The lateral horn is characteristics of thoracic and upper lumbar segments ...
Spinal Cord
... column). *synapse at relay nucleus in medulla: dorsal column nucleus. ii. Axons of these neurons from the dorsal column nucleus cross over (decussate) here at the medulla and continue as the medial lemniscus thalamus. iii. These next thalamic neurons send their axons into the internal capsule (whi ...
... column). *synapse at relay nucleus in medulla: dorsal column nucleus. ii. Axons of these neurons from the dorsal column nucleus cross over (decussate) here at the medulla and continue as the medial lemniscus thalamus. iii. These next thalamic neurons send their axons into the internal capsule (whi ...
Nervous System 1 A neurotransmitter, i.e. a chemical compound
... effectors. Cell body located at end of axon, inside CNS, e.g. motor neurons. ...
... effectors. Cell body located at end of axon, inside CNS, e.g. motor neurons. ...
FINAL LECTURE EXAM – HUMAN ANATOMY
... c. decreased blood flow to the placenta, leading to oxygen starvation of the fetus d. decreased venous return in the lower limbs, leading to varicose veins e. increased production of lactic acid by cramping abdominal uterine muscles 3. Which of the following about gray rami is FALSE? a. They carry p ...
... c. decreased blood flow to the placenta, leading to oxygen starvation of the fetus d. decreased venous return in the lower limbs, leading to varicose veins e. increased production of lactic acid by cramping abdominal uterine muscles 3. Which of the following about gray rami is FALSE? a. They carry p ...
Gross Anatomy Lecture 1: Spinal Cord and Nerves I. Basic
... iii. Caudal to T1 all spinal nerves exit column below vertebrae with the same name e. In cervical region, SC segment and vertebral level closely linked f. In lumbar region, they are far apart B. Gray and white matter 1. Gray matter: Central parts of cord contain the cell bodies a. Shape of gray matt ...
... iii. Caudal to T1 all spinal nerves exit column below vertebrae with the same name e. In cervical region, SC segment and vertebral level closely linked f. In lumbar region, they are far apart B. Gray and white matter 1. Gray matter: Central parts of cord contain the cell bodies a. Shape of gray matt ...
Spinal Cord - Welcome to Study Windsor
... with pain and thermal sensations (lateral tract) and also non- discriminative touch and pressure (medial tract) Fibers of the two tracts are intermingled to some extent In brain stem, constitute the spinal lemniscus Fibers are highly somatotopically arranged, with those for the lower limb lying most ...
... with pain and thermal sensations (lateral tract) and also non- discriminative touch and pressure (medial tract) Fibers of the two tracts are intermingled to some extent In brain stem, constitute the spinal lemniscus Fibers are highly somatotopically arranged, with those for the lower limb lying most ...
Chapter 13
... *single synapse- sensory & motor neuron= monosynaptic. *More often the integration center consists of one or more interneurons which may relay the impulse to other interneurons or the motor neuron= polysynaptic ...
... *single synapse- sensory & motor neuron= monosynaptic. *More often the integration center consists of one or more interneurons which may relay the impulse to other interneurons or the motor neuron= polysynaptic ...
ppt file
... the organization of cell types. The outermost layer of the cortex is called the molecular layer, and is nearly cell-free. Instead it is occupied mostly by axons and dendrites. The layer below that is a monolayer of large cells called Purkinje cells, central players in the circuitry of the cerebellum ...
... the organization of cell types. The outermost layer of the cortex is called the molecular layer, and is nearly cell-free. Instead it is occupied mostly by axons and dendrites. The layer below that is a monolayer of large cells called Purkinje cells, central players in the circuitry of the cerebellum ...
02Anatomy of the Spinal Cord
... periphery of the body and whose axons constitute the ascending fasciculi of the white matter, are located in the dorsal horns 2. Lower motor neurons, which transmit impulses to the skeletal muscles, are located in the ventral horns (similar neurons in the lateral horn are the preganglionic neurons o ...
... periphery of the body and whose axons constitute the ascending fasciculi of the white matter, are located in the dorsal horns 2. Lower motor neurons, which transmit impulses to the skeletal muscles, are located in the ventral horns (similar neurons in the lateral horn are the preganglionic neurons o ...
Diapositiva 1
... Bara-Jimenez W, Aksu M, Graham B, Sato S, Hallett M. Periodic limb movements in sleep: state-dependent excitability of the spinal flexor reflex. Neurology 2000;54:1609–1616. Abnormal hyperexcitability along the entire spinal cord, especially its lumbosacral and cervical segments ...
... Bara-Jimenez W, Aksu M, Graham B, Sato S, Hallett M. Periodic limb movements in sleep: state-dependent excitability of the spinal flexor reflex. Neurology 2000;54:1609–1616. Abnormal hyperexcitability along the entire spinal cord, especially its lumbosacral and cervical segments ...
3-As.Tracts 2016-17
... • Contain the axons of primary afferent neurons that have entered cord through dorsal roots of spinal nerves • Fasciculus Gracilis contains fibers that are received at sacral, lumbar and lower thoracic levels, • Fasciculus Cuneatus contains fibers that are received at upper thoracic and cervical lev ...
... • Contain the axons of primary afferent neurons that have entered cord through dorsal roots of spinal nerves • Fasciculus Gracilis contains fibers that are received at sacral, lumbar and lower thoracic levels, • Fasciculus Cuneatus contains fibers that are received at upper thoracic and cervical lev ...
Essentials of Human Anatomy
... • Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. • The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions: – pathway for sensory and motor impulses – responsible for reflexes ...
... • Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. • The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions: – pathway for sensory and motor impulses – responsible for reflexes ...
Essentials of Human Anatomy Nervous System III Spinal Cord The
... • Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. • The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions: – pathway for sensory and motor impulses – responsible for reflexes ...
... • Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. • The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions: – pathway for sensory and motor impulses – responsible for reflexes ...
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). The spinal cord begins at the occipital bone and extends down to the space between the first and second lumbar vertebrae; it does not extend the entire length of the vertebral column. It is around 45 cm (18 in) in men and around 43 cm (17 in) long in women. Also, the spinal cord has a varying width, ranging from 13 mm (1⁄2 in) thick in the cervical and lumbar regions to 6.4 mm (1⁄4 in) thick in the thoracic area. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of neural signals between the brain and the rest of the body but also contains neural circuits that can independently control numerous reflexes and central pattern generators.The spinal cord has three major functions:as a conduit for motor information, which travels down the spinal cord, as a conduit for sensory information in the reverse direction, and finally as a center for coordinating certain reflexes.