Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System
... occurs as a result of upper motor neuron damage (e.g. from brain hemorrhage). Voluntary motor activity is lost, but reflex movements initiated by spinal cord neurons still occur. The muscle does not become limp (flaccid), but instead becomes more tense and shows hyperactive and uncontrolled movement ...
... occurs as a result of upper motor neuron damage (e.g. from brain hemorrhage). Voluntary motor activity is lost, but reflex movements initiated by spinal cord neurons still occur. The muscle does not become limp (flaccid), but instead becomes more tense and shows hyperactive and uncontrolled movement ...
Brain and Spinal Cord
... surrounding CNS • protect CNS • three layers • dura mater – outer, tough • arachnoid mater weblike • pia mater – inner, delicate ...
... surrounding CNS • protect CNS • three layers • dura mater – outer, tough • arachnoid mater weblike • pia mater – inner, delicate ...
Spinal Cord Anatomy - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... – Each of these divided into sensory or motor tracts ...
... – Each of these divided into sensory or motor tracts ...
NeuroSipe Ascending Pathways and Lesions
... Spinomesencephalic Tract • Also indirect pathway to cortex • Sensory neuron cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia • Synapse immediately in dorsal horn & cross over through anterior commissure • Terminates and synapses in superior colliculi, reticular formation, and periaqueductal gray matter • Part ...
... Spinomesencephalic Tract • Also indirect pathway to cortex • Sensory neuron cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia • Synapse immediately in dorsal horn & cross over through anterior commissure • Terminates and synapses in superior colliculi, reticular formation, and periaqueductal gray matter • Part ...
Motor Areas - Motlow State Community College
... 3cm from pons to foramen magnum all sensory and motor tracts connecting brain and spinal cord ...
... 3cm from pons to foramen magnum all sensory and motor tracts connecting brain and spinal cord ...
Laboratory Exercise 10: Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord
... The nervous system is specialized for communication using nerve impulses as its message code. Communication makes possible control. Control permits integration of the body functions and plays a role in homeostasis, i.e. the control allows for maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment ...
... The nervous system is specialized for communication using nerve impulses as its message code. Communication makes possible control. Control permits integration of the body functions and plays a role in homeostasis, i.e. the control allows for maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment ...
The Central Nervous System
... region of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. Motor and sensory neurons travel through the brainstem allowing for the relay of signals between the brain and the spinal cord. ...
... region of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. Motor and sensory neurons travel through the brainstem allowing for the relay of signals between the brain and the spinal cord. ...
The Nervous System - Catherine Huff`s Site
... and emerge from the vertebrae. After leaving the spinal cord the nerves are named after their corresponding vertebrae. A spinal nerve has a dorsal and ventral root. The dorsal root carries afferent (sensory) impulses and the ventral root carries efferent (motor) impulses. ...
... and emerge from the vertebrae. After leaving the spinal cord the nerves are named after their corresponding vertebrae. A spinal nerve has a dorsal and ventral root. The dorsal root carries afferent (sensory) impulses and the ventral root carries efferent (motor) impulses. ...
MCB 163: Mammalian Neuroanatomy
... represent, respectively, flexors in more dorsal parts of the ventral horn, and extensors in the ventral part. Proximal or axial or trunk muscles are represented in more medial parts of the ventral horn (near lamina VIII), and distal muscles are represented more laterally. 5. TRACT OF LISSAUER: This ...
... represent, respectively, flexors in more dorsal parts of the ventral horn, and extensors in the ventral part. Proximal or axial or trunk muscles are represented in more medial parts of the ventral horn (near lamina VIII), and distal muscles are represented more laterally. 5. TRACT OF LISSAUER: This ...
The Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... Objectives • Understand how the nervous system is divided and the types of cells that are found in nervous tissue • Know the anatomy of a neuron and the structural and functional types of neurons • Understand what occurs at the synapse ...
... Objectives • Understand how the nervous system is divided and the types of cells that are found in nervous tissue • Know the anatomy of a neuron and the structural and functional types of neurons • Understand what occurs at the synapse ...
The Peripheral Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System
... The nerve cells of the efferent system, have their dendrites and cell bodies located in the spinal cord and only the axons radiate out from the CNS, to the skeletal muscles. Although the somatic system is voluntary and consciously controlled, there are some involuntary and non-conscious activity suc ...
... The nerve cells of the efferent system, have their dendrites and cell bodies located in the spinal cord and only the axons radiate out from the CNS, to the skeletal muscles. Although the somatic system is voluntary and consciously controlled, there are some involuntary and non-conscious activity suc ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... 1. Describe the basic anatomical organization of the nervous system. (p.7) Anatomical organization divides the nervous system into the central and periphery nervous systems. CNS contains the brain and the spinal cord. PNS contains the 12 pairs of cranial nerves (attaching brain with structures of he ...
... 1. Describe the basic anatomical organization of the nervous system. (p.7) Anatomical organization divides the nervous system into the central and periphery nervous systems. CNS contains the brain and the spinal cord. PNS contains the 12 pairs of cranial nerves (attaching brain with structures of he ...
Anatomical organization divides the nervous system
... 1. Describe the basic anatomical organization of the nervous system. (p.7) Anatomical organization divides the nervous system into the central and periphery nervous systems. CNS contains the brain and the spinal cord. PNS contains the 12 pairs of cranial nerves (attaching brain with structures of he ...
... 1. Describe the basic anatomical organization of the nervous system. (p.7) Anatomical organization divides the nervous system into the central and periphery nervous systems. CNS contains the brain and the spinal cord. PNS contains the 12 pairs of cranial nerves (attaching brain with structures of he ...
The Spinal Cord
... • filum terminale: extension of pia mater extends inferiorly & anchors cord to coccyx • cauda equinae: “horse tail” nerves that arise from lumbar, sacral, & coccygeal portions of spine ...
... • filum terminale: extension of pia mater extends inferiorly & anchors cord to coccyx • cauda equinae: “horse tail” nerves that arise from lumbar, sacral, & coccygeal portions of spine ...
Nervous System
... • Sensory (or afferent) neurons: send information from sensory receptors (e.g., in skin, eyes, nose, tongue, ears) TOWARD the central nervous system. • Motor (or efferent) neurons: send information AWAY from the central nervous system to muscles or glands ...
... • Sensory (or afferent) neurons: send information from sensory receptors (e.g., in skin, eyes, nose, tongue, ears) TOWARD the central nervous system. • Motor (or efferent) neurons: send information AWAY from the central nervous system to muscles or glands ...
Spinal Cord - Mesa Community College
... Shorter than vertebral column because vertebral column grows faster than spinal cord Cauda equina - nerves from lower cord don't leave vertebral column immediately, but instead look like coarse hairs of a horse tail Has grooves on surface – anterior median fissure and posterior median sulcus Central ...
... Shorter than vertebral column because vertebral column grows faster than spinal cord Cauda equina - nerves from lower cord don't leave vertebral column immediately, but instead look like coarse hairs of a horse tail Has grooves on surface – anterior median fissure and posterior median sulcus Central ...
Nervous - Anoka-Hennepin School District
... Spinal Cord FunctionRelays sensory impulses from the sense organs to the brain and motor impulses from the brain to the muscles. It is also involved in the reflex actions. ...
... Spinal Cord FunctionRelays sensory impulses from the sense organs to the brain and motor impulses from the brain to the muscles. It is also involved in the reflex actions. ...
AP-Anatomy
... 1. epidural space 2. dura mater 3. subdural space 4. arachnoid membrane 5. subarachnoid space 6. pia mater -- denticulate ligaments ...
... 1. epidural space 2. dura mater 3. subdural space 4. arachnoid membrane 5. subarachnoid space 6. pia mater -- denticulate ligaments ...
Chapter 7 - Rogue Community College
... Cord- continuation of the brain stem, about 17 inches long. Two ...
... Cord- continuation of the brain stem, about 17 inches long. Two ...
C13 Spinal Cord / Spinal Nerves / Somatic Reflexes / MC3 What are
... What is a “stretch reflex”? What role does the cerebellum play in a “strethch reflex”? Note: outline the “path” between a muscle spindle and the change in muscle tension. What is a muscle spindle? Function? How are muscle spindles “concentrated” in different skeletal muslces? ...
... What is a “stretch reflex”? What role does the cerebellum play in a “strethch reflex”? Note: outline the “path” between a muscle spindle and the change in muscle tension. What is a muscle spindle? Function? How are muscle spindles “concentrated” in different skeletal muslces? ...
The Central Nervous System
... The Spinal Cord About 45 cm long Extends from the foramen magnum to the border of the first lumbar vertebrae Two nerve roots project from each side of the spinal cord – Dorsal carries sensory information – Ventral carries motor information out ...
... The Spinal Cord About 45 cm long Extends from the foramen magnum to the border of the first lumbar vertebrae Two nerve roots project from each side of the spinal cord – Dorsal carries sensory information – Ventral carries motor information out ...
Nervous System Part 6
... Extends from the medulla oblongata to the region of T12 Below T12 is the cauda equina (a collection of spinal nerves) Enlargements occur in the cervical and lumbar regions Where the nerves serving the upper and lower limbs arise and leave the cord ...
... Extends from the medulla oblongata to the region of T12 Below T12 is the cauda equina (a collection of spinal nerves) Enlargements occur in the cervical and lumbar regions Where the nerves serving the upper and lower limbs arise and leave the cord ...
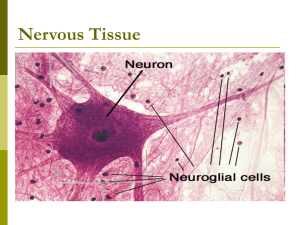
Nervous Tissue
... sensory (afferent) neurons carry info to CNS Interneurons in CNS interpret info and stimulate motor neurons motor (efferent) neurons carry info to effectors ...
... sensory (afferent) neurons carry info to CNS Interneurons in CNS interpret info and stimulate motor neurons motor (efferent) neurons carry info to effectors ...
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). The spinal cord begins at the occipital bone and extends down to the space between the first and second lumbar vertebrae; it does not extend the entire length of the vertebral column. It is around 45 cm (18 in) in men and around 43 cm (17 in) long in women. Also, the spinal cord has a varying width, ranging from 13 mm (1⁄2 in) thick in the cervical and lumbar regions to 6.4 mm (1⁄4 in) thick in the thoracic area. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of neural signals between the brain and the rest of the body but also contains neural circuits that can independently control numerous reflexes and central pattern generators.The spinal cord has three major functions:as a conduit for motor information, which travels down the spinal cord, as a conduit for sensory information in the reverse direction, and finally as a center for coordinating certain reflexes.