Partially coherent image formation with x
... Unlike conventional refractive lenses, the focusing properties of zone plates are based on diffraction. This implies that the focal length of a zone plate lens strongly depends on the wavelength and that multiple diffraction orders exist. In most cases only the first diffraction order is used. The d ...
... Unlike conventional refractive lenses, the focusing properties of zone plates are based on diffraction. This implies that the focal length of a zone plate lens strongly depends on the wavelength and that multiple diffraction orders exist. In most cases only the first diffraction order is used. The d ...
Optical Generation of the Visual Stimulus
... determined simply by measuring the luminance of a surface in cd / m2 and multiplying this value by the area of the pupil in mm2. ...
... determined simply by measuring the luminance of a surface in cd / m2 and multiplying this value by the area of the pupil in mm2. ...
Exam 4-WWP
... 19. A Young's double-slit apparatus is set up so that a screen is positioned 1.6 m from the double slits and the spacing between the two slits is 0.040 mm. What is the distance between the central and 1st bright fringes on the screen if the light source has a wavelength of 630 nm? ...
... 19. A Young's double-slit apparatus is set up so that a screen is positioned 1.6 m from the double slits and the spacing between the two slits is 0.040 mm. What is the distance between the central and 1st bright fringes on the screen if the light source has a wavelength of 630 nm? ...
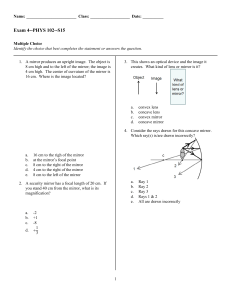
Introduction to Drawing Ray Diagrams Types of
... below PA. Continue this ray // to PA. Place a dot at the intersection. Draw ray #3 to O, and angle ruler so that this ray reaches the point of intersection. All rays will be on left side of mirror with solid lines. For 4: Draw ray #1. Ray #2 cannot be drawn. Draw ray #3 to O, and then continue this ...
... below PA. Continue this ray // to PA. Place a dot at the intersection. Draw ray #3 to O, and angle ruler so that this ray reaches the point of intersection. All rays will be on left side of mirror with solid lines. For 4: Draw ray #1. Ray #2 cannot be drawn. Draw ray #3 to O, and then continue this ...
Light consists of electromagnetic waves that have oscillating electric
... systems, such (infinitely spread) plane waves do not exist because of the finite size of the optical elements. Non-planar optical components cause further deviations of the wave from planarity so the wave acquires a ray direction that varies from point to point on the wave front. In a cylindrically ...
... systems, such (infinitely spread) plane waves do not exist because of the finite size of the optical elements. Non-planar optical components cause further deviations of the wave from planarity so the wave acquires a ray direction that varies from point to point on the wave front. In a cylindrically ...
Interferometric back focal plane microellipsometry
... appropriate here. Figure 1 depicts a linearly polarized, collimated beam of light that is focused by the objective lens to a spot on the sample positioned in the front focal plane. In the object space of the lens, an angular spectrum of plane waves is incident upon the sample. The p and s polarizati ...
... appropriate here. Figure 1 depicts a linearly polarized, collimated beam of light that is focused by the objective lens to a spot on the sample positioned in the front focal plane. In the object space of the lens, an angular spectrum of plane waves is incident upon the sample. The p and s polarizati ...
Partially Coherent Image Formation Theory for X
... Partially coherent image formation theory for a full-field imaging microscope is introduced. Propagation of mutual coherence is presented following Huygens-Fresnel principle. The concept of mutual intensity, together with the quasimonochromatic condition under which it is valid, is also introduced. ...
... Partially coherent image formation theory for a full-field imaging microscope is introduced. Propagation of mutual coherence is presented following Huygens-Fresnel principle. The concept of mutual intensity, together with the quasimonochromatic condition under which it is valid, is also introduced. ...
Capacity of coherent free-space optical links using
... The downconverted heterodyne or homodyne power is maximized when the spatial field of the received signal matches that of the local oscillator. Any mismatch between the amplitudes and phases of the two fields will result in a reduction of the downconverted power, i.e., fading. In the case of cohere ...
... The downconverted heterodyne or homodyne power is maximized when the spatial field of the received signal matches that of the local oscillator. Any mismatch between the amplitudes and phases of the two fields will result in a reduction of the downconverted power, i.e., fading. In the case of cohere ...
Technology for a better society
... The Information limit goes well beyond point resolution limit for FEG microscopes (due to high spatial and temporal coherency). For the microscopes with thermionic electron sources (LaB6 and W), the info limit usually coincides with the point resolution. \ The use of FEG sources minimises the loss o ...
... The Information limit goes well beyond point resolution limit for FEG microscopes (due to high spatial and temporal coherency). For the microscopes with thermionic electron sources (LaB6 and W), the info limit usually coincides with the point resolution. \ The use of FEG sources minimises the loss o ...
On the conservation of fundamental optical quantities in non
... certain conserved quantities and their fluxes. In optics, we identify four fundamental conserved quantities: electric charge, the electromagnetic energy, the electromagnetic linear momentum and the electromagnetic angular momentum. Although extensively studied for paraxial optics (low numerical apert ...
... certain conserved quantities and their fluxes. In optics, we identify four fundamental conserved quantities: electric charge, the electromagnetic energy, the electromagnetic linear momentum and the electromagnetic angular momentum. Although extensively studied for paraxial optics (low numerical apert ...
fourier2012.pdf
... translate the transparency forwards and backwards while examining the output plane and searching for the best correlation peak, which corresponds to the scale compensated correlation. Analyze this system, and show that it indeed performs a scale compensating correlation, at some position along the o ...
... translate the transparency forwards and backwards while examining the output plane and searching for the best correlation peak, which corresponds to the scale compensated correlation. Analyze this system, and show that it indeed performs a scale compensating correlation, at some position along the o ...
F-number
In optics, the f-number (sometimes called focal ratio, f-ratio, f-stop, or relative aperture) of an optical system is the ratio of the lens's focal length to the diameter of the entrance pupil. It is a dimensionless number that is a quantitative measure of lens speed, and an important concept in photography. The number is commonly notated using a hooked f, i.e. f/N, where N is the f-number.