C. Huang, X. Wu, H. Liu, B. Aldalali, J.A. Rogers and H. Jiang
... exposure to the image. In general, the focusing behavior of our artificial RSCEs is equivalent to that by a spherical mirror with the same radius of curvature r (see the bottom half of the sphere in Figure S1a). Since the height of each square tube (i.e. 60 µm) is much smaller than r (i.e. 1.1 cm) o ...
... exposure to the image. In general, the focusing behavior of our artificial RSCEs is equivalent to that by a spherical mirror with the same radius of curvature r (see the bottom half of the sphere in Figure S1a). Since the height of each square tube (i.e. 60 µm) is much smaller than r (i.e. 1.1 cm) o ...
Light-Scattering Study of the Normal Human Eye
... shifts, and n is the refractive index of the lens. Thus, the spatial variation of the bulk modulus K = ρλ2 f 2 /4n2 is directly obtained from the measured Brillouin shift f, and knowledge of n and ρ as the incident laser beam probes at different positions within the lens. The precision and accuracy ...
... shifts, and n is the refractive index of the lens. Thus, the spatial variation of the bulk modulus K = ρλ2 f 2 /4n2 is directly obtained from the measured Brillouin shift f, and knowledge of n and ρ as the incident laser beam probes at different positions within the lens. The precision and accuracy ...
Chapter 33 . Aberration Curves in Lens Design
... optical system, primarily because these curves give a designer important details about the relative contributions of individual aberrations to lens performance. Because a certain design technique may affect only one particular aberration type, these curves are more helpful to the lens designer than ...
... optical system, primarily because these curves give a designer important details about the relative contributions of individual aberrations to lens performance. Because a certain design technique may affect only one particular aberration type, these curves are more helpful to the lens designer than ...
LAB 1 - SIMPLE DIFFRACTION, FOURIER OPTICS AND ACOUSTO
... approximation near the center of the beam. We will use this source to perform Fourier Optics experiments next week. ...
... approximation near the center of the beam. We will use this source to perform Fourier Optics experiments next week. ...
Cost-effective optical coherence tomography spectrometer based on
... demonstrated and depict a reasonable image quality for this preliminary low cost system that is well comparable to competing devices. Further improvement of the optical design and the TFBG fabrication process have potential to optimize the TFBG spectrometer towards smaller size and higher efficiency ...
... demonstrated and depict a reasonable image quality for this preliminary low cost system that is well comparable to competing devices. Further improvement of the optical design and the TFBG fabrication process have potential to optimize the TFBG spectrometer towards smaller size and higher efficiency ...
Coherence properties of light propagated through a
... information content than fully coherent wavefields and that the use of partially coherent illumination in imaging can yield higher spatial resolution.2 Hence, the characterisation of the coherence properties of a wavefield embodied in the MOI is of critical importance for applications including imag ...
... information content than fully coherent wavefields and that the use of partially coherent illumination in imaging can yield higher spatial resolution.2 Hence, the characterisation of the coherence properties of a wavefield embodied in the MOI is of critical importance for applications including imag ...
and the matrix
... (Toronto, McGraw-Hill, 3rd ed., 1957) has been referred to throughout as it uses a sign convention which is consistent with that used in this book. The subject of geometrical optics starts with the laws of refraction and reflection for transparent media. It is then a question of using these laws to ...
... (Toronto, McGraw-Hill, 3rd ed., 1957) has been referred to throughout as it uses a sign convention which is consistent with that used in this book. The subject of geometrical optics starts with the laws of refraction and reflection for transparent media. It is then a question of using these laws to ...
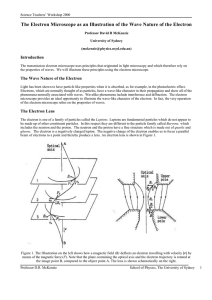
The Electron Microscope as an Illustration of the Wave Nature of the
... A at an angle to the optical axis, and brings it back onto the axis at the image position B. This electron lens is similar to the ones used in the electron microscope. An additional (and sometimes unfortunate), property of this lens is that it rotates the image. A useful property which a light lens ...
... A at an angle to the optical axis, and brings it back onto the axis at the image position B. This electron lens is similar to the ones used in the electron microscope. An additional (and sometimes unfortunate), property of this lens is that it rotates the image. A useful property which a light lens ...
1 Fundamental Optics www.cvimellesgriot.com
... are made to determine critical parameters such as magnification, focal length(s), clear aperture (diameter), and object and image position. These paraxial calculations are covered in the next section of this chapter. Second, actual components are chosen based on these paraxial values, and their actu ...
... are made to determine critical parameters such as magnification, focal length(s), clear aperture (diameter), and object and image position. These paraxial calculations are covered in the next section of this chapter. Second, actual components are chosen based on these paraxial values, and their actu ...
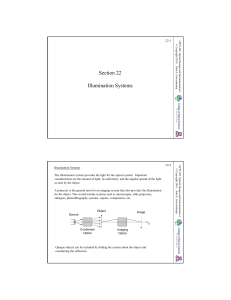
502-22 Illumination Systems
... In many applications the image quality of diffuse illumination is required, but the throughput of specular illumination is needed. A larger light bulb is not always an option (A major rule of optical engineering is that there is never enough light!!). The system should be designed as specular illumi ...
... In many applications the image quality of diffuse illumination is required, but the throughput of specular illumination is needed. A larger light bulb is not always an option (A major rule of optical engineering is that there is never enough light!!). The system should be designed as specular illumi ...
The Optics of the Spherical Fish Lens
... index distribution within a lens of radius R by means of a refractometer on small samples showed an increase towards the centre that followed an approximately parabolic rule of the form: n (r) = X0,, - (NC,,, - Nctx). (r/R)* Typical values he reported are 1.336 for the eye media (Nmed), 1.38 for the ...
... index distribution within a lens of radius R by means of a refractometer on small samples showed an increase towards the centre that followed an approximately parabolic rule of the form: n (r) = X0,, - (NC,,, - Nctx). (r/R)* Typical values he reported are 1.336 for the eye media (Nmed), 1.38 for the ...
Microscopes - Photonics Research Group
... Three-dimensional Diffraction Pattern, Axial Resolution, Depth of Focus, Depth of Field The two-dimensional Airy pattern that is formed in the image plane of a point object is, in fact, a cross section of a three-dimensional pattern that extends along the optical axis of the microscope. As one focus ...
... Three-dimensional Diffraction Pattern, Axial Resolution, Depth of Focus, Depth of Field The two-dimensional Airy pattern that is formed in the image plane of a point object is, in fact, a cross section of a three-dimensional pattern that extends along the optical axis of the microscope. As one focus ...
F-number
In optics, the f-number (sometimes called focal ratio, f-ratio, f-stop, or relative aperture) of an optical system is the ratio of the lens's focal length to the diameter of the entrance pupil. It is a dimensionless number that is a quantitative measure of lens speed, and an important concept in photography. The number is commonly notated using a hooked f, i.e. f/N, where N is the f-number.