7.1 textbook answers - aiss-science-9
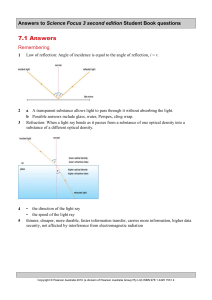
... b Optical fibres work by passing light along the fibre through totally internal reflection. This requires that the surface of the fibre be very smooth. Scratches on the surface of the optical fibre would prevent the light from being reflected. Instead, the light might be scattered or escape from the ...
... b Optical fibres work by passing light along the fibre through totally internal reflection. This requires that the surface of the fibre be very smooth. Scratches on the surface of the optical fibre would prevent the light from being reflected. Instead, the light might be scattered or escape from the ...
System for observing interference phenomenon: In the previous
... thickness of the film, refractive index of material etc. We shall be discussing some of these systems and their applications in the following sections. The major systems for observing interference phenomenon are as follows. ...
... thickness of the film, refractive index of material etc. We shall be discussing some of these systems and their applications in the following sections. The major systems for observing interference phenomenon are as follows. ...
univ. physics
... width, and height are called extended objects. Reflects part of the incident light, or a polished metal surface that reflects almost 100% of the light that strikes it. We will always draw the reflecting surface as a black line with a shaded area behind it, as in Fig.1 Bathroom mirrors have a thin sh ...
... width, and height are called extended objects. Reflects part of the incident light, or a polished metal surface that reflects almost 100% of the light that strikes it. We will always draw the reflecting surface as a black line with a shaded area behind it, as in Fig.1 Bathroom mirrors have a thin sh ...
University of Groningen Unraveling structure and dynamics by
... Fundamentals of Light Microscopy ...
... Fundamentals of Light Microscopy ...
Isotropic Diffraction-Limited Focusing Using a Single Objective Lens
... side lobe amplitudes [9]. A simulation of a pointlike object image obtained with ISO focusing and confocal detection is given in Fig. 6(b). We found a good agreement between the experimental data and the simulation. The observed discrepancy is certainly due to a nonoptimal spot formation, because IS ...
... side lobe amplitudes [9]. A simulation of a pointlike object image obtained with ISO focusing and confocal detection is given in Fig. 6(b). We found a good agreement between the experimental data and the simulation. The observed discrepancy is certainly due to a nonoptimal spot formation, because IS ...
Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit
... these wavelets taking account of their amplitudes and phases." When both the light source and the viewing plane are effectively at infinity with respect to the diffracting aperture,In this case, the incident light is a plane wave so that the phase of the light at ...
... these wavelets taking account of their amplitudes and phases." When both the light source and the viewing plane are effectively at infinity with respect to the diffracting aperture,In this case, the incident light is a plane wave so that the phase of the light at ...
fourier optics - The Institute of Optics
... z-axis and incident on an aperture as in Fig. 2. This is a classic problem in the propagation of waves since the time of Francesco Grimaldi and Christiaan Huygens. We assume there are sources of radiation only in the region z < 0 and that we have knowledge of the “field” in the aperture. The radiati ...
... z-axis and incident on an aperture as in Fig. 2. This is a classic problem in the propagation of waves since the time of Francesco Grimaldi and Christiaan Huygens. We assume there are sources of radiation only in the region z < 0 and that we have knowledge of the “field” in the aperture. The radiati ...
Devil`s lens optical tweezers
... controlling the structure of optical traps has been suggested previously [25] it is not straightforward that a stable trap will be formed in this situation, since radiation pressure from rays originating in different zones of the lens may act to push particles away from the intended trap location. W ...
... controlling the structure of optical traps has been suggested previously [25] it is not straightforward that a stable trap will be formed in this situation, since radiation pressure from rays originating in different zones of the lens may act to push particles away from the intended trap location. W ...
Aperture interference and the volumetric resolution of light field
... Light field photography Inspired by the 4D light field, a geometrical optics parametrization of the light rays emanating from a macroscopic scene [25], light field photography measures both spatial and angular information about the light entering a camera. There exist many schemes for recording a li ...
... Light field photography Inspired by the 4D light field, a geometrical optics parametrization of the light rays emanating from a macroscopic scene [25], light field photography measures both spatial and angular information about the light entering a camera. There exist many schemes for recording a li ...
Transformation-designed optical elements
... image can be generated that is ideal in the sense of the perfect lens (combining both near- and far-field components in a flat, unit transfer function, up to the limits imposed by material imperfection). We also describe elements that perform magnification, free from geometric aberrations, even whil ...
... image can be generated that is ideal in the sense of the perfect lens (combining both near- and far-field components in a flat, unit transfer function, up to the limits imposed by material imperfection). We also describe elements that perform magnification, free from geometric aberrations, even whil ...
Document
... number of times a light wave must oscillate in traveling from one point to another - product of physical path length with refractive index Optical Path Difference (OPD): - comparing the OPL for a ray passing in the plane of exit pupil with the chief ray passing through pupil center - optical aberrat ...
... number of times a light wave must oscillate in traveling from one point to another - product of physical path length with refractive index Optical Path Difference (OPD): - comparing the OPL for a ray passing in the plane of exit pupil with the chief ray passing through pupil center - optical aberrat ...
WHITEPAPER Centration Measurement, Alignment
... the VIS, so specialized image processing algorithms are used to reach the required high resolution. OptiCentric® in the standard reflection mode relies on back-reflection from the lens surface, so the light intensity of the reflected reticule image strongly depends on the type of coating used. Typic ...
... the VIS, so specialized image processing algorithms are used to reach the required high resolution. OptiCentric® in the standard reflection mode relies on back-reflection from the lens surface, so the light intensity of the reflected reticule image strongly depends on the type of coating used. Typic ...
biology 163 laboratory use of the compound light microscope
... Compound light microscopes employ a series of lenses to enlarge (i.e., magnify) the image of the object being studied. Total magnification is the product of the magnifying power of the objective lens times the magnifying power of the ocular lens. Typical microscopes have four objective lenses (4X, 1 ...
... Compound light microscopes employ a series of lenses to enlarge (i.e., magnify) the image of the object being studied. Total magnification is the product of the magnifying power of the objective lens times the magnifying power of the ocular lens. Typical microscopes have four objective lenses (4X, 1 ...
The Research of Near-Infrared Electro-Optics
... f/#:the ratio of the effective focal length to pupil diameter of the lens Once the electro-optics modulation coding signal is created, the detector measures the signal. The most commonly used detector is the photodiode whose property is the incident light is linearly proportional to the output curre ...
... f/#:the ratio of the effective focal length to pupil diameter of the lens Once the electro-optics modulation coding signal is created, the detector measures the signal. The most commonly used detector is the photodiode whose property is the incident light is linearly proportional to the output curre ...
F-number
In optics, the f-number (sometimes called focal ratio, f-ratio, f-stop, or relative aperture) of an optical system is the ratio of the lens's focal length to the diameter of the entrance pupil. It is a dimensionless number that is a quantitative measure of lens speed, and an important concept in photography. The number is commonly notated using a hooked f, i.e. f/N, where N is the f-number.