A new optical configuration in speckle interferometry for contouring
... configuration. Unlike the Leendertz configuration, the proposed configuration uses single beam illumination and dual directions of observation but the sensitivity is large and is equal to that of Leendertz’s method. In this configuration an object point is viewed symmetrically with respect to the su ...
... configuration. Unlike the Leendertz configuration, the proposed configuration uses single beam illumination and dual directions of observation but the sensitivity is large and is equal to that of Leendertz’s method. In this configuration an object point is viewed symmetrically with respect to the su ...
Brightfield Contrasting Techniques
... • Halos result from diffracted light that is intercepted by phase ring • Shade off is caused by greater diffraction at edges of objects than their centers ...
... • Halos result from diffracted light that is intercepted by phase ring • Shade off is caused by greater diffraction at edges of objects than their centers ...
Optics - MIT Fab Lab
... between where a ray starts on the axis on one side of the lens and where it crosses the axis on the other side. Notice that the angles have dropped out of this equation: all rays starting at the same distance from the lens on one side in the object plane are rejoined in a plane on the other side in ...
... between where a ray starts on the axis on one side of the lens and where it crosses the axis on the other side. Notice that the angles have dropped out of this equation: all rays starting at the same distance from the lens on one side in the object plane are rejoined in a plane on the other side in ...
Lens Films and Reflective Polarization Films
... luminance gain with respect to the observation angle. In the diagram, ‘BEF II 90/50(V)/BEF II 90/50(H)’ denotes that two orthogonally arranged films are stacked, resulting in a luminance gain of 2.2. The lens films play a role in converging the light into the normal direction to the plane of the bac ...
... luminance gain with respect to the observation angle. In the diagram, ‘BEF II 90/50(V)/BEF II 90/50(H)’ denotes that two orthogonally arranged films are stacked, resulting in a luminance gain of 2.2. The lens films play a role in converging the light into the normal direction to the plane of the bac ...
Newtons Ring
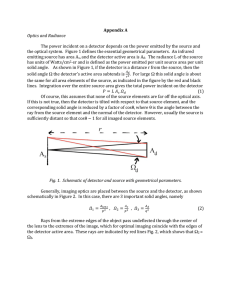
... contact between the lens and the plate as the center. These rings are known as Newton’s ring. For a normal incidence of monochromatic light, the path difference between the reflected rays (see Fig.1) is very nearly equal to 2t where and t are the refractive index and thickness of the air-film res ...
... contact between the lens and the plate as the center. These rings are known as Newton’s ring. For a normal incidence of monochromatic light, the path difference between the reflected rays (see Fig.1) is very nearly equal to 2t where and t are the refractive index and thickness of the air-film res ...
Bright-Field Microscopy
... as microscope lens makers are striving to make “super” apochromatic objective lenses that each have a single wavelength-independent focal length all the way from the ultraviolet to the infrared wavelengths. More lens elements are required to effectively reduce chromatic aberration and this increases ...
... as microscope lens makers are striving to make “super” apochromatic objective lenses that each have a single wavelength-independent focal length all the way from the ultraviolet to the infrared wavelengths. More lens elements are required to effectively reduce chromatic aberration and this increases ...
optics - einstein classes
... Reflection from Curved Surfaces : To calculate the image distance and height of image due to reflection from curved surface, we will use the following formula ...
... Reflection from Curved Surfaces : To calculate the image distance and height of image due to reflection from curved surface, we will use the following formula ...
Telescope Quiz Review
... Review the parts of the telescope. Know what each term describes Tripod ‐ The support for the telescope. The number on one leg is directed South (toward Igor’s tower). Optical Tube ‐ Large tube which holds the pieces of the telescope in place. The main body of the telescope. Finder scope (spotter ...
... Review the parts of the telescope. Know what each term describes Tripod ‐ The support for the telescope. The number on one leg is directed South (toward Igor’s tower). Optical Tube ‐ Large tube which holds the pieces of the telescope in place. The main body of the telescope. Finder scope (spotter ...
F-number
In optics, the f-number (sometimes called focal ratio, f-ratio, f-stop, or relative aperture) of an optical system is the ratio of the lens's focal length to the diameter of the entrance pupil. It is a dimensionless number that is a quantitative measure of lens speed, and an important concept in photography. The number is commonly notated using a hooked f, i.e. f/N, where N is the f-number.