The Optics of the Compound Eye of the Honeybee
... investigated the fine structure of the ommatidia of the worker honeybee (Apis mellifera), and with the help of their data we examined the optics of the honeybee's eye as a representative of the closed-rhabdom type. Morphology The optical apparatus of a bee's ommatidium (Fig. 1) consists of a cuticul ...
... investigated the fine structure of the ommatidia of the worker honeybee (Apis mellifera), and with the help of their data we examined the optics of the honeybee's eye as a representative of the closed-rhabdom type. Morphology The optical apparatus of a bee's ommatidium (Fig. 1) consists of a cuticul ...
Phys Chp 10
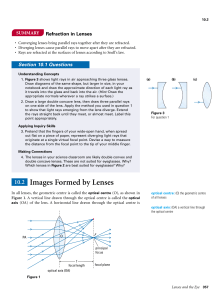
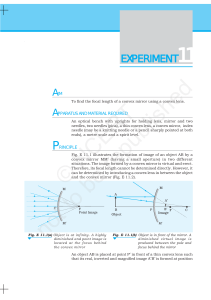
... 1. Create a chart, table, or detailed diagram to summarize the symbols and meanings of these properties or variables of lenses: optical centre, optical axis, principal axis, principal focus, focal length, object distance, object height, image distance, image height, magnification. 2. The word “MALT” ...
... 1. Create a chart, table, or detailed diagram to summarize the symbols and meanings of these properties or variables of lenses: optical centre, optical axis, principal axis, principal focus, focal length, object distance, object height, image distance, image height, magnification. 2. The word “MALT” ...
Non-invasive ophthalmic imaging of adult zebrafish eye using
... based optical coherence tomography set-up and its use for non-invasive optical imaging of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) eyes. The free-space axial and lateral resolutions of the set-up were estimated to be ~ 11 and 17 µm respectively. Images of whole eye, cornea and retina acquired with the set-up h ...
... based optical coherence tomography set-up and its use for non-invasive optical imaging of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) eyes. The free-space axial and lateral resolutions of the set-up were estimated to be ~ 11 and 17 µm respectively. Images of whole eye, cornea and retina acquired with the set-up h ...
In the diagram below, the optical train of a set of binoculars is found
... The Fraunhofer diffraction pattern from two microscopic circular holes separated by a distance d is observed at a wavelength of 500 nm on a screen placed 50 cm from the aperture plane. Inspection of the pattern shows that it is at the Rayleigh limit of resolution (i.e. the principal maximum appears ...
... The Fraunhofer diffraction pattern from two microscopic circular holes separated by a distance d is observed at a wavelength of 500 nm on a screen placed 50 cm from the aperture plane. Inspection of the pattern shows that it is at the Rayleigh limit of resolution (i.e. the principal maximum appears ...
Leaving Cert Physics Notes by Mary Singleton
... Questions 6,7,8, and 9 address various topics. The layout of the questions can be a bit confusing. They don’t label parts of questions (a) (b) (c) etc so it is necessary to read carefully and ensure that you attempt each part. I generally advise my students to put a line through each part when you h ...
... Questions 6,7,8, and 9 address various topics. The layout of the questions can be a bit confusing. They don’t label parts of questions (a) (b) (c) etc so it is necessary to read carefully and ensure that you attempt each part. I generally advise my students to put a line through each part when you h ...
A correlation of thin lens approximation to thick
... negative singlet lenses made of various optical glasses are given in Fig.4. As an example in this application, positive lenses which have the glass designations of 464658, 517642, 785258, and 952204 have the same paraxial focal length, central thickness, and operate at the same relative aperture and ...
... negative singlet lenses made of various optical glasses are given in Fig.4. As an example in this application, positive lenses which have the glass designations of 464658, 517642, 785258, and 952204 have the same paraxial focal length, central thickness, and operate at the same relative aperture and ...
Experimental implementation of the gyrator transform - E
... to the polarization Poincaré sphere. The GT can be considered a universal mode converter, since it allows the generation of all essentially different structurally stable Gaussian modes, which can be obtained from the Hermite–Gaussian (HG) modes by the integral canonical transforms [7]. To use the GT ...
... to the polarization Poincaré sphere. The GT can be considered a universal mode converter, since it allows the generation of all essentially different structurally stable Gaussian modes, which can be obtained from the Hermite–Gaussian (HG) modes by the integral canonical transforms [7]. To use the GT ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... wave from the air side to the focus Fm at the focal length fm in the metamaterial by given εx’ and εz’. The details of the PWC design follows similar principles described in literatures [23– 25]. Due to the hyperbolic dispersion of the metalens, a plane wave comes from the metamaterial side, instead ...
... wave from the air side to the focus Fm at the focal length fm in the metamaterial by given εx’ and εz’. The details of the PWC design follows similar principles described in literatures [23– 25]. Due to the hyperbolic dispersion of the metalens, a plane wave comes from the metamaterial side, instead ...
Lecture_22
... light under water. We said that color depends on wavelength. For example, for an object emitting 650 nm light in air, we see red. But this is true only in air. If we observe this same object when under water, it still looks red. But the wavelength in water λn is 650 nm/1.33 = 489 nm. Light with wave ...
... light under water. We said that color depends on wavelength. For example, for an object emitting 650 nm light in air, we see red. But this is true only in air. If we observe this same object when under water, it still looks red. But the wavelength in water λn is 650 nm/1.33 = 489 nm. Light with wave ...
F-number
In optics, the f-number (sometimes called focal ratio, f-ratio, f-stop, or relative aperture) of an optical system is the ratio of the lens's focal length to the diameter of the entrance pupil. It is a dimensionless number that is a quantitative measure of lens speed, and an important concept in photography. The number is commonly notated using a hooked f, i.e. f/N, where N is the f-number.