Set 5
... 5. You believe that the product of your antenna gene turns on other genes in the antenna. How would you test this idea? What materials would you need? What parts of the regulated genes must you identify? How would you verify a direct interaction in vitro and in vivo, between the protein and candidat ...
... 5. You believe that the product of your antenna gene turns on other genes in the antenna. How would you test this idea? What materials would you need? What parts of the regulated genes must you identify? How would you verify a direct interaction in vitro and in vivo, between the protein and candidat ...
environmental factors and lifestyle choices affect on genetics
... Should exercise frequently and watch their diet. ...
... Should exercise frequently and watch their diet. ...
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disease that causes the body to
... What Causes CF? Approximately 30,000 people in the United States have been diagnosed with CF, which affects both males and females. It's not contagious, so you can't catch CF from another person. Cystic fibrosis is an inherited disease caused by mutations (changes) in a gene on chromosome 7, one of ...
... What Causes CF? Approximately 30,000 people in the United States have been diagnosed with CF, which affects both males and females. It's not contagious, so you can't catch CF from another person. Cystic fibrosis is an inherited disease caused by mutations (changes) in a gene on chromosome 7, one of ...
Modern Genetics
... children with an equal chance for sons and daughters to be affected. Children who do not have the trait will generally not pass the disease on to their children. observed in each generation, usually without skipping a generation. ...
... children with an equal chance for sons and daughters to be affected. Children who do not have the trait will generally not pass the disease on to their children. observed in each generation, usually without skipping a generation. ...
Human Genetic Disorders
... show the carriers of recessive genes. •Males are usually square and females are usually a circle Mrs. Degl ...
... show the carriers of recessive genes. •Males are usually square and females are usually a circle Mrs. Degl ...
Maple syrup urine disease
... an enzyme complex that is responsible for breaking down the amino acids leucine, isoleucine, and valine. The symptoms of MSUD are due to the toxic build-up of these amino acids and their metabolites in the body, especially affecting the nervous system. MSUD is also known as branched-chain ketoacidur ...
... an enzyme complex that is responsible for breaking down the amino acids leucine, isoleucine, and valine. The symptoms of MSUD are due to the toxic build-up of these amino acids and their metabolites in the body, especially affecting the nervous system. MSUD is also known as branched-chain ketoacidur ...
Base composition of genomes
... genes which predispose such family members to these illnesses • Examples are Alzheimer’s disease, cystic fibrosis (CF), breast or colon cancer, or heart diseases. • Some of these diseases can be caused by a problem within a single gene, such as with CF. ...
... genes which predispose such family members to these illnesses • Examples are Alzheimer’s disease, cystic fibrosis (CF), breast or colon cancer, or heart diseases. • Some of these diseases can be caused by a problem within a single gene, such as with CF. ...
DNA Connection (pgs.101-106)
... Along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. ...
... Along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. ...
Genetics: Mendelian Genetics (2) Patterns of Inheritance
... Autosomal Dominant Inheritance One type of dwarfism in humans is caused by a single dominant gene; the condition is called Achondroplastic dwarfism. Dwarf individuals are heterozygous, while persons who are homozygous recessive are of normal stature. The homozygous dominant individuals all die befor ...
... Autosomal Dominant Inheritance One type of dwarfism in humans is caused by a single dominant gene; the condition is called Achondroplastic dwarfism. Dwarf individuals are heterozygous, while persons who are homozygous recessive are of normal stature. The homozygous dominant individuals all die befor ...
The Jacob-Monod Hypothesis of Gene Action in Bacteria
... 1) Give an explanation for this time lag. ...
... 1) Give an explanation for this time lag. ...
The Connectivity Map: using gene-expression signatures
... Microarray technology allows us to analyze expression of thousands of genes in a single experiment quickly and efficiently. Traditionally, comparative microarray analysis has been used in order to pinpoint genetic abnormalities in a disease of interest. By examining genes that are upregulated and do ...
... Microarray technology allows us to analyze expression of thousands of genes in a single experiment quickly and efficiently. Traditionally, comparative microarray analysis has been used in order to pinpoint genetic abnormalities in a disease of interest. By examining genes that are upregulated and do ...
genetics mcq - Pass the FracP
... A low lod score indicates linkage of two genes It is distinct from association Autosomal crossovers are equally frequent in males and females Linked gene loci are sometimes on different chromosomes Linkage disequilibrium is used in DNA diagnosis ...
... A low lod score indicates linkage of two genes It is distinct from association Autosomal crossovers are equally frequent in males and females Linked gene loci are sometimes on different chromosomes Linkage disequilibrium is used in DNA diagnosis ...
A functional polymorphism in miRNA
... identified variants are non-genic that their biological relevance to the disease remain to be elucidated. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) serve as key post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression and are involved in various biological processes. Genetic variation in miRNArelated sequences has been shown to ...
... identified variants are non-genic that their biological relevance to the disease remain to be elucidated. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) serve as key post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression and are involved in various biological processes. Genetic variation in miRNArelated sequences has been shown to ...
QUIZ 4on ch12.doc
... 2. What are alleles? a. specific physical locations of genes on a chromosome b. variations of the same gene (i.e., similar nucleotide sequences on homologous chromosomes) c. homozygotes d. heterozygotes 3. A single gene capable of influencing multiple phenotypes within a single organism is said to b ...
... 2. What are alleles? a. specific physical locations of genes on a chromosome b. variations of the same gene (i.e., similar nucleotide sequences on homologous chromosomes) c. homozygotes d. heterozygotes 3. A single gene capable of influencing multiple phenotypes within a single organism is said to b ...
Chapter 12 Notes
... that is carried on the X chromosome. If a boy is born color-blind, what would have to be true? A. His father had normal vision. B. His grandmother was colorblind. C. His mother carried at least one gene for color blindness. D. His grandfather passed on the color-blind trait to his father ...
... that is carried on the X chromosome. If a boy is born color-blind, what would have to be true? A. His father had normal vision. B. His grandmother was colorblind. C. His mother carried at least one gene for color blindness. D. His grandfather passed on the color-blind trait to his father ...
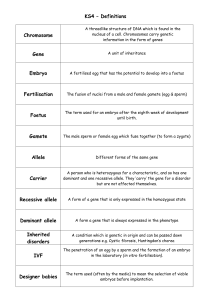
Definitions
... The penetration of an egg by a sperm and the formation of an embryo in the laboratory (in vitro fertilisation). ...
... The penetration of an egg by a sperm and the formation of an embryo in the laboratory (in vitro fertilisation). ...
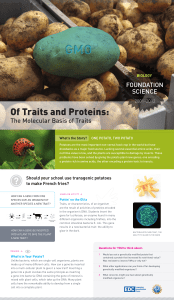
Of Traits and Proteins:
... made up of many different cells. How can a gene be inserted into a multi-cellular plant to give it a new trait? Inserting a gene into a plant involves the same principle as inserting a gene into bacteria: DNA containing the gene of interest is mixed with plant cells, which take up the DNA. Many plan ...
... made up of many different cells. How can a gene be inserted into a multi-cellular plant to give it a new trait? Inserting a gene into a plant involves the same principle as inserting a gene into bacteria: DNA containing the gene of interest is mixed with plant cells, which take up the DNA. Many plan ...
Steubenstraβe 4 Horne Tistrup Dyrlaeger ApS DE
... gene. The dog is genetically clear and will not be affected by Neonatal Encephalopathy. The dog can pass only the normal gene on to all its offspring. The currently known mutation has been analysed. The result is only valid for the submitted sample and for the breed Standard Poodle. The current resu ...
... gene. The dog is genetically clear and will not be affected by Neonatal Encephalopathy. The dog can pass only the normal gene on to all its offspring. The currently known mutation has been analysed. The result is only valid for the submitted sample and for the breed Standard Poodle. The current resu ...
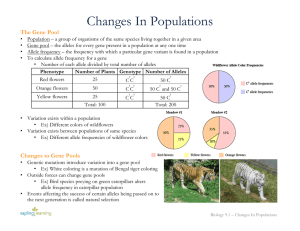
Changes In Populations
... Population – a group of organisms of the same species living together in a given area Gene pool – the alleles for every gene present in a population at any one time Allele frequency – the frequency with which a particular gene variant is found in a population To calculate allele frequency for a gene ...
... Population – a group of organisms of the same species living together in a given area Gene pool – the alleles for every gene present in a population at any one time Allele frequency – the frequency with which a particular gene variant is found in a population To calculate allele frequency for a gene ...
Gene Expression and Regulation
... b) Frameshift mutation = single base is added/deleted A.K.A. nonsense mutation ...
... b) Frameshift mutation = single base is added/deleted A.K.A. nonsense mutation ...
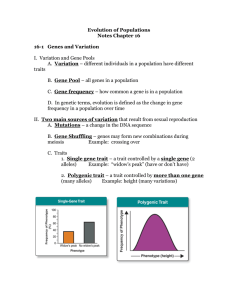
Notes Chapter 16 - Spring Branch ISD
... D. In genetic terms, evolution is defined as the change in gene frequency in a population over time II. Two main sources of variation that result from sexual reproduction A. Mutations – a change in the DNA sequence B. Gene Shuffling – genes may form new combinations during meiosis Example: crossing ...
... D. In genetic terms, evolution is defined as the change in gene frequency in a population over time II. Two main sources of variation that result from sexual reproduction A. Mutations – a change in the DNA sequence B. Gene Shuffling – genes may form new combinations during meiosis Example: crossing ...
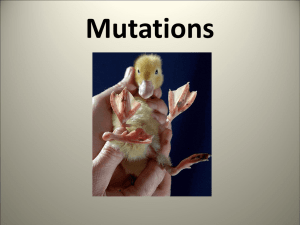
Mutations
... -Are mutagens that cause a mistake in the genetic code that leads to uncontrollable cell division. - This results in CANCER. -Examples include: Mercury, UV rays and cigarettes ...
... -Are mutagens that cause a mistake in the genetic code that leads to uncontrollable cell division. - This results in CANCER. -Examples include: Mercury, UV rays and cigarettes ...
our information sheet
... and allows his family to have some time for themselves. Though not scientifically proven, many boys gain some symptomatic relief from some of the complementary therapies such as cranial osteopathy or massage in the later stages. In boys who are known to have the condition but in whom symptoms have n ...
... and allows his family to have some time for themselves. Though not scientifically proven, many boys gain some symptomatic relief from some of the complementary therapies such as cranial osteopathy or massage in the later stages. In boys who are known to have the condition but in whom symptoms have n ...
Fragile Sites and Cancer Powerpoint
... • The normal protein product of this gene is absent in cells of many ...
... • The normal protein product of this gene is absent in cells of many ...