DNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... 1. RNA is single stranded, DNA is double stranded 2. The 5 carbon sugar is ribose in RNA, deoxyribose in DNA 3. RNA uses the base uracil instead of thymine. Uracil binds with adenine. (A-U ) ...
... 1. RNA is single stranded, DNA is double stranded 2. The 5 carbon sugar is ribose in RNA, deoxyribose in DNA 3. RNA uses the base uracil instead of thymine. Uracil binds with adenine. (A-U ) ...
PDF
... dimensions over time, the authors show that these cells move in two phases, first migrating dorsally and then turning anteriorly. More anteriorly positioned histoblasts turn earlier, whereas more posterior ones migrate faster and turn later. In other tissues, such as the embryonic germband, morphoge ...
... dimensions over time, the authors show that these cells move in two phases, first migrating dorsally and then turning anteriorly. More anteriorly positioned histoblasts turn earlier, whereas more posterior ones migrate faster and turn later. In other tissues, such as the embryonic germband, morphoge ...
Document
... Individual genotypes might operate in ways to restrict development or constrain outcome • Range of reaction principle: • Genotype, or genetic structure, sets the limits on the range of possible phenotypes that a person might display in response to different environments: • Example: Intellectual deve ...
... Individual genotypes might operate in ways to restrict development or constrain outcome • Range of reaction principle: • Genotype, or genetic structure, sets the limits on the range of possible phenotypes that a person might display in response to different environments: • Example: Intellectual deve ...
Chapter 25 Presentation
... The DNA that codes for rRNA evolves very slowly and can be used to analyze organisms that are very old. ...
... The DNA that codes for rRNA evolves very slowly and can be used to analyze organisms that are very old. ...
Gene Section TFE3 (transcription factor E3) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Transcription factor; member of the basic helix-loophelix family (b-HLH) of transcription factors primarily found to bind to the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif, Ig K enhancers and Ig H variable regions promotors; the helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper region is implicated in DNA binding and dimeriz ...
... Transcription factor; member of the basic helix-loophelix family (b-HLH) of transcription factors primarily found to bind to the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif, Ig K enhancers and Ig H variable regions promotors; the helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper region is implicated in DNA binding and dimeriz ...
Activity 3: Mechanisms for Evolution
... When organisms migrate from one population to another, this can alter the frequency of alleles in both populations. This is termed gene flow. Gene flow can also occur when individuals from two populations mate without moving. When this occurs, gene flow can make populations more similar. ...
... When organisms migrate from one population to another, this can alter the frequency of alleles in both populations. This is termed gene flow. Gene flow can also occur when individuals from two populations mate without moving. When this occurs, gene flow can make populations more similar. ...
Tracing the Origins of a MRSA Epidemic (Article for Students)
... USA300, in which the original speG gene is either replaced by a non-functioning mutant copy of the gene, or the gene is deleted from the genome altogether. They expected that the modified version of USA300 would not be able to alter or neutralize spermidine. First they had to prepare the knockout US ...
... USA300, in which the original speG gene is either replaced by a non-functioning mutant copy of the gene, or the gene is deleted from the genome altogether. They expected that the modified version of USA300 would not be able to alter or neutralize spermidine. First they had to prepare the knockout US ...
Lecture 5
... RNA and protein construction • The nucleotide base sequence of mRNA is encoded from DNA and transmits sequences of bases used to determine the amino acid sequence of the protein. • mRNA (“Messenger RNA”) associates with the ribosome (mRNA and protein portion). • RNA (“Transfer RNA”) also required • ...
... RNA and protein construction • The nucleotide base sequence of mRNA is encoded from DNA and transmits sequences of bases used to determine the amino acid sequence of the protein. • mRNA (“Messenger RNA”) associates with the ribosome (mRNA and protein portion). • RNA (“Transfer RNA”) also required • ...
CAPT Embedded Task: Biotechnology: Should There Be a
... human genes that make their immune systems act similarly to those of humans. This allows scientists to study the effects of diseases on the human immune system. Transgenic livestock have been produced with extra copies of growth hormone genes. Such animals grow faster and produce meat that is less f ...
... human genes that make their immune systems act similarly to those of humans. This allows scientists to study the effects of diseases on the human immune system. Transgenic livestock have been produced with extra copies of growth hormone genes. Such animals grow faster and produce meat that is less f ...
MS Word
... How to calculate the frequency or ratio of possible genotypes and phenotypes resulting from a cross Monohybrid, dihybrid, F1, F2, and test cross The conditions under which Mendel’s rules don’t operate accurately Variants of dominance How traits encoded by multiple genes are often expressed as a norm ...
... How to calculate the frequency or ratio of possible genotypes and phenotypes resulting from a cross Monohybrid, dihybrid, F1, F2, and test cross The conditions under which Mendel’s rules don’t operate accurately Variants of dominance How traits encoded by multiple genes are often expressed as a norm ...
Okazaki Fragments
... Replication requires the following steps 1-Unwinding Begins at Origins of Replication Two strands open forming Replication ...
... Replication requires the following steps 1-Unwinding Begins at Origins of Replication Two strands open forming Replication ...
Gene Expression - Bioinformatics and Genomics Department at CIPF
... atgctgatgcatgcatgctgactactgatgtgggg gctattgacttgatgtctatc.... ...
... atgctgatgcatgcatgctgactactgatgtgggg gctattgacttgatgtctatc.... ...
Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis in
... significantly correlated with smoking behavior at a FDR of 5% [2]. Other studies have been performed on buccal mucosa [3], B cells in women [4], small airway epithelium, and alveolar macrophages in healthy individuals [5]. Gene coexpression network analysis, a means for looking at the relationship b ...
... significantly correlated with smoking behavior at a FDR of 5% [2]. Other studies have been performed on buccal mucosa [3], B cells in women [4], small airway epithelium, and alveolar macrophages in healthy individuals [5]. Gene coexpression network analysis, a means for looking at the relationship b ...
Lecture Presentation to accompany Principles of Life
... A group of closely related genes are called gene families . These arose over evolutionary time when different copies of genes underwent separate mutations. For example: Genes encoding the globin proteins in hemoglobin and myoglobin all arose from a single common ancestral gene. ...
... A group of closely related genes are called gene families . These arose over evolutionary time when different copies of genes underwent separate mutations. For example: Genes encoding the globin proteins in hemoglobin and myoglobin all arose from a single common ancestral gene. ...
Mendel Review ppt
... one another during gamete formation What does that mean? The allele a parent gives for one trait does not affect what he/she gives for another trait so you can have many different combinations of traits given to the egg or sperm ...
... one another during gamete formation What does that mean? The allele a parent gives for one trait does not affect what he/she gives for another trait so you can have many different combinations of traits given to the egg or sperm ...
codes for amino acids
... Receptors sense signals and become activated. Activated receptors act to alter gene expression. ...
... Receptors sense signals and become activated. Activated receptors act to alter gene expression. ...
alleles
... Dominant and Recessive Alleles Phenotype is predominantly determined by genotype, but may also be influenced or modified due to interaction with the environment. For example the final height of a human adult depends on a combination of that person’s genotype as well as their nutrition—if they are u ...
... Dominant and Recessive Alleles Phenotype is predominantly determined by genotype, but may also be influenced or modified due to interaction with the environment. For example the final height of a human adult depends on a combination of that person’s genotype as well as their nutrition—if they are u ...
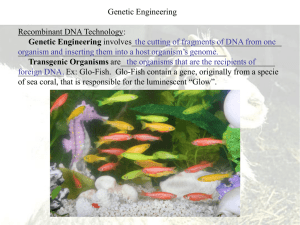
Genetic Engineering
... • Mutagens (such as radiation or chemicals) can occasionally cause favorable traits to enter a population ...
... • Mutagens (such as radiation or chemicals) can occasionally cause favorable traits to enter a population ...
GENE EXPRESSION ANALYSIS
... The genomes of salmonids have undergone two rounds of whole genome duplication (WGD) relative to their last common ancestor with humans. Around 15% and 50% respectively of the duplicated genes (paralogues) from these WGD events have been retained in extant species. The regulatory regions of gene par ...
... The genomes of salmonids have undergone two rounds of whole genome duplication (WGD) relative to their last common ancestor with humans. Around 15% and 50% respectively of the duplicated genes (paralogues) from these WGD events have been retained in extant species. The regulatory regions of gene par ...
11_Lecture_Presen - Bishop Conaty
... An operon is a group of genes under coordinated control in bacteria The lactose (lac) operon includes – Three adjacent genes for lactose-utilization enzymes – Promoter sequence where RNA polymerase binds – Operator sequence is where a repressor can bind and block RNA polymerase action ...
... An operon is a group of genes under coordinated control in bacteria The lactose (lac) operon includes – Three adjacent genes for lactose-utilization enzymes – Promoter sequence where RNA polymerase binds – Operator sequence is where a repressor can bind and block RNA polymerase action ...
Gene Therapy and Genetic Counseling
... Actually change the broken gene’s sequence to regain it’s natural function • Have to know exactly what the mutation is • Then add mutagens that will introduce the “mutation” you want to change the gene back to it’s natural sequence again • Some mutagens introduce transversions, some add or remove sp ...
... Actually change the broken gene’s sequence to regain it’s natural function • Have to know exactly what the mutation is • Then add mutagens that will introduce the “mutation” you want to change the gene back to it’s natural sequence again • Some mutagens introduce transversions, some add or remove sp ...
Pre-exam 2
... Directions: On the iPads or your own computer, look at a few Khan Academy videos. Don’t just be a passive watcher! After each video, use diagrams and your own words to summarize what you saw. • ...
... Directions: On the iPads or your own computer, look at a few Khan Academy videos. Don’t just be a passive watcher! After each video, use diagrams and your own words to summarize what you saw. • ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.