Blueprint of Life
... o Therefore, all F1 plants had the heterozygous genotype Tt In a gene consisting of two possible alleles, one would be dominant and the other recessive. In heterozygous individuals, the dominant allele would be expressed o Hence, the F1 plants with heterozygous genotype presented the dominant phen ...
... o Therefore, all F1 plants had the heterozygous genotype Tt In a gene consisting of two possible alleles, one would be dominant and the other recessive. In heterozygous individuals, the dominant allele would be expressed o Hence, the F1 plants with heterozygous genotype presented the dominant phen ...
Mutations
... Errors when the DNA is copied during replication During protein synthesis- when proteins are constructed When the cell is dividing- Mitosis or meiosis Sometimes external agents, called mutagens, can cause mutations to occur ...
... Errors when the DNA is copied during replication During protein synthesis- when proteins are constructed When the cell is dividing- Mitosis or meiosis Sometimes external agents, called mutagens, can cause mutations to occur ...
The Molecular Pathogenesis of Obesity: An Unfinished Jigsaw Puzzle
... on the obesity genes and chemical mediators were reviewed. Results: Despite exciting discoveries of single gene mutations with haploinsufficiency in human subjects, and single-gene disorders resulting in obesity, most cases of obesity are likely the result of subtle interactions of several related g ...
... on the obesity genes and chemical mediators were reviewed. Results: Despite exciting discoveries of single gene mutations with haploinsufficiency in human subjects, and single-gene disorders resulting in obesity, most cases of obesity are likely the result of subtle interactions of several related g ...
Activation of Transcription
... a mechanism that generates protein diversity Protein diversity also generated via alternate splicing Regulates gene expression at the level of RNA processing A mechanism by which a single gene can encode two or more related proteins ...
... a mechanism that generates protein diversity Protein diversity also generated via alternate splicing Regulates gene expression at the level of RNA processing A mechanism by which a single gene can encode two or more related proteins ...
Document
... THE PROBLEM • At least 30,000 genes • Among 3 BILLION base-pairs of the human genome. • Genes interact with the environment • Genes interact with each other • Environmental influences alone can cause disease • Chance plays a role ...
... THE PROBLEM • At least 30,000 genes • Among 3 BILLION base-pairs of the human genome. • Genes interact with the environment • Genes interact with each other • Environmental influences alone can cause disease • Chance plays a role ...
During DNA replication, which of the following segments
... Before a cell goes through either mitosis or meiosis, which process must be carried out by the DNA in the nucleus? ...
... Before a cell goes through either mitosis or meiosis, which process must be carried out by the DNA in the nucleus? ...
2.2 Genetics, advanced flashcards
... The length of the index finger is sex-influenced. In females, an index finger longer than the fourth finger(ring finger) is dominant. In males, an index finger longer than the fourth finger seems to be recessive. Set of genes in the genome physical features and functional traits of organism The unit ...
... The length of the index finger is sex-influenced. In females, an index finger longer than the fourth finger(ring finger) is dominant. In males, an index finger longer than the fourth finger seems to be recessive. Set of genes in the genome physical features and functional traits of organism The unit ...
pptx format
... Bacteria – one of the most ancient and common live organism on the plant. One bacterium in as single cell and can not be seen with naked eye. ...
... Bacteria – one of the most ancient and common live organism on the plant. One bacterium in as single cell and can not be seen with naked eye. ...
Dow Agrosciences Australia - PDF 170 KB
... EXZACT™ Delete technique is used to delete undesirable DNA sequences to improve specific traits from the plant genome. EXZACT™ Edit allows scientists to re-write gene sequences to improve specific traits, while EXZACT™ Add allows a single gene sequence or a series of gene sequences (stack) to be add ...
... EXZACT™ Delete technique is used to delete undesirable DNA sequences to improve specific traits from the plant genome. EXZACT™ Edit allows scientists to re-write gene sequences to improve specific traits, while EXZACT™ Add allows a single gene sequence or a series of gene sequences (stack) to be add ...
Sex- Linked Traits
... chromosome is much smaller than the X chromosome and only contains fewer genes. Most sex-linked traits are on the X chromosome. ...
... chromosome is much smaller than the X chromosome and only contains fewer genes. Most sex-linked traits are on the X chromosome. ...
Variations from Mendel`s original Crosses
... •Each _________ involved can also have ____________ alleles. •Examples in humans include ________, skin pigmentation, weight, cleft palate, neural tube defects, __________________, the Rhesus factor and, most ______________ characteristics. •As there are ____________ genes involved with polygenic in ...
... •Each _________ involved can also have ____________ alleles. •Examples in humans include ________, skin pigmentation, weight, cleft palate, neural tube defects, __________________, the Rhesus factor and, most ______________ characteristics. •As there are ____________ genes involved with polygenic in ...
Patents and Clinical Genetics
... Scope should be limited to methods, applications Scope should be limited to disclosed uses Sequences are now routine and thus obvious Patent genes only when completely characterized Reject computer-based conjectural gene functions ...
... Scope should be limited to methods, applications Scope should be limited to disclosed uses Sequences are now routine and thus obvious Patent genes only when completely characterized Reject computer-based conjectural gene functions ...
PowerPoint-Präsentation
... Of all CpG sites annotated to these identified genes, only about 10% were concordant with expression. These CpG site were within or immediately upstream of the annotated start of the gene with a maximum distance of ≈1500 nucleotides, indicating that overlap with the promoter site is most likely. A c ...
... Of all CpG sites annotated to these identified genes, only about 10% were concordant with expression. These CpG site were within or immediately upstream of the annotated start of the gene with a maximum distance of ≈1500 nucleotides, indicating that overlap with the promoter site is most likely. A c ...
Chapter 16 summary
... Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection explained how life on Earth changed, or evolved, over many generations. What Darwin did not know was how heritable traits were passed down through each generation. The study of genetics helps scientists understand the relationship between inheritance ...
... Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection explained how life on Earth changed, or evolved, over many generations. What Darwin did not know was how heritable traits were passed down through each generation. The study of genetics helps scientists understand the relationship between inheritance ...
BioSc 231 Exam 4 2008
... The cell has mechanisms to repair these errors. However, the repair enzymes need to know which DNA strand has the correct base. In other words, it needs to know which is the original strand. How is this determined? ...
... The cell has mechanisms to repair these errors. However, the repair enzymes need to know which DNA strand has the correct base. In other words, it needs to know which is the original strand. How is this determined? ...
chapteroutline_ch07
... TAKE-HOME MESSAGE 7.9: Sometimes the effects of both alleles in a heterozygous genotype are evident in the phenotype. With incomplete dominance, the phenotype of a heterozygote appears to be an intermediate blend of the phenotypes of the two homozygotes. With codominance, a heterozygote has a phenot ...
... TAKE-HOME MESSAGE 7.9: Sometimes the effects of both alleles in a heterozygous genotype are evident in the phenotype. With incomplete dominance, the phenotype of a heterozygote appears to be an intermediate blend of the phenotypes of the two homozygotes. With codominance, a heterozygote has a phenot ...
Summary sheet - ThinkChemistry
... ___________________ are needed for photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is where plants react _____________ and _______________ together to make _______________ and ________________. To do this, they need _________________ and _____________ from the sun. This reaction can be shown in a word equation: ____ ...
... ___________________ are needed for photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is where plants react _____________ and _______________ together to make _______________ and ________________. To do this, they need _________________ and _____________ from the sun. This reaction can be shown in a word equation: ____ ...
here
... Study existing genetically-different entities, to see if they differ in behavior Single gene mutants: “Yellow” Drosophila (M. Bastock) Inbred strains: Maze learning in rats (Cooper & Zubeck) (C & Z’s results show that, even where we know there are gene differences that CAN produce behavior differenc ...
... Study existing genetically-different entities, to see if they differ in behavior Single gene mutants: “Yellow” Drosophila (M. Bastock) Inbred strains: Maze learning in rats (Cooper & Zubeck) (C & Z’s results show that, even where we know there are gene differences that CAN produce behavior differenc ...
Transcription
... specific amino acid (building block of protein). • For example, in DNA you might have: ACG ...
... specific amino acid (building block of protein). • For example, in DNA you might have: ACG ...
Chapter 2: Epigenetics of mammalian parenting
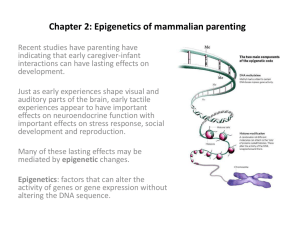
... Epigenetics and the lasting effects of maternal touch • How can gene regulation affect development? • Activity of genes is either suppressed (made less accessible) or enhanced. • DNA methylation: methyl groups are added directly to DNA (cytosine neucleotides) which inhibit accessibility, thus reduc ...
... Epigenetics and the lasting effects of maternal touch • How can gene regulation affect development? • Activity of genes is either suppressed (made less accessible) or enhanced. • DNA methylation: methyl groups are added directly to DNA (cytosine neucleotides) which inhibit accessibility, thus reduc ...
MUTATIONS
... wrong base pairing, e.g. A with G. The repair enzymes go to work, cutting out a chunk from one side of the DNA containing the mistake. Then new enzymes, using the base pairing code, make a new side from the opposite strand of DNA. The new strand is put into place by another enzyme system. ...
... wrong base pairing, e.g. A with G. The repair enzymes go to work, cutting out a chunk from one side of the DNA containing the mistake. Then new enzymes, using the base pairing code, make a new side from the opposite strand of DNA. The new strand is put into place by another enzyme system. ...
Chapter 15~ The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance ______
... – Duchenne muscular dystropy (MD) – hemophilia X-inactivation: 2nd X chromosome in females condenses into a Barr body ...
... – Duchenne muscular dystropy (MD) – hemophilia X-inactivation: 2nd X chromosome in females condenses into a Barr body ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.