Chapter 15~ The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance ______
... – Duchenne muscular dystropy (MD) – hemophilia X-inactivation: 2nd X chromosome in females condenses into a Barr body ...
... – Duchenne muscular dystropy (MD) – hemophilia X-inactivation: 2nd X chromosome in females condenses into a Barr body ...
Higher Biology - Hyndland Secondary School
... 3. The operon (______________) Jacob-Monod hypothesis states that a operator gene is structural gene remains switched off while its ________ repressor from a regulator gene. The combined with a __________ structural gene becomes switched on and codes for its protein inducer prevents the repressor co ...
... 3. The operon (______________) Jacob-Monod hypothesis states that a operator gene is structural gene remains switched off while its ________ repressor from a regulator gene. The combined with a __________ structural gene becomes switched on and codes for its protein inducer prevents the repressor co ...
1 - WordPress.com
... DNA is made up of nitrogen bases, phosphates and sugars. 9. Describe how bases pair up in the DNA molecule. In DNA, A pairs up with T and G pairs up with C. 10. What is chromatin? Chromatin is the substance that makes up chromosomes. It is composed of DNA and protein. 11. How many chromosomes does a ...
... DNA is made up of nitrogen bases, phosphates and sugars. 9. Describe how bases pair up in the DNA molecule. In DNA, A pairs up with T and G pairs up with C. 10. What is chromatin? Chromatin is the substance that makes up chromosomes. It is composed of DNA and protein. 11. How many chromosomes does a ...
Genetics: The Information Broker
... Translation of the information - expressing as proteins (requires new language with new alphabet!) ...
... Translation of the information - expressing as proteins (requires new language with new alphabet!) ...
Health and Technology
... genotypes appear in the F2 generation. Different linked genes are inherited as a group rather than as separate units. The closer 2 genes are on a chromosome, the more likely it is that they will be inherited together. ...
... genotypes appear in the F2 generation. Different linked genes are inherited as a group rather than as separate units. The closer 2 genes are on a chromosome, the more likely it is that they will be inherited together. ...
1. Which of the following enzymes will untangle DNA? A
... 16. In DNA replication, the leading strand is the strand that has which conformation? A) 5 to 3 B) 3 to 5 C) Both strands are leading 17. Which of the following is a purine? A) Thymine B) Cytosine C) Adenine D) Alanine 18. Which of the following does not play a role in DNA replication? A) RNA prime ...
... 16. In DNA replication, the leading strand is the strand that has which conformation? A) 5 to 3 B) 3 to 5 C) Both strands are leading 17. Which of the following is a purine? A) Thymine B) Cytosine C) Adenine D) Alanine 18. Which of the following does not play a role in DNA replication? A) RNA prime ...
Evolution of populations
... by segregation and recombination of alleles 2. so in next generation each allele is equally likely to join with any other allele in offspring 3. mating must be completely random and all allele combinations must survive equally well 4. so we use multiplication rule of probability to predict % o ...
... by segregation and recombination of alleles 2. so in next generation each allele is equally likely to join with any other allele in offspring 3. mating must be completely random and all allele combinations must survive equally well 4. so we use multiplication rule of probability to predict % o ...
Chapter 01 Genetics: The Study of Biological
... Learning Objective: 01.01.02 Differentiate between a chromosome, DNA, a gene, a base pair, and a protein. Section: 01.01 Topic: DNA - The Fundamental Information Molecule of Life ...
... Learning Objective: 01.01.02 Differentiate between a chromosome, DNA, a gene, a base pair, and a protein. Section: 01.01 Topic: DNA - The Fundamental Information Molecule of Life ...
Genomes 3/e
... (start+end) are identified, but the work is just started. How these genes function? ...
... (start+end) are identified, but the work is just started. How these genes function? ...
Text S1.
... contrast. The score identifies the most relevant contrasts as those where the genes 'act as one', showing the same, preferentially large, magnitude of expression change with individual variations ideally only constituting random Gaussian noise. From this notion, the score represents the number of st ...
... contrast. The score identifies the most relevant contrasts as those where the genes 'act as one', showing the same, preferentially large, magnitude of expression change with individual variations ideally only constituting random Gaussian noise. From this notion, the score represents the number of st ...
A1979HV72000001
... showed it to one of my colleagues. However, it took several months to complete a paper on this subject, and the paper was published in 1971.2 "This first theory had some defects; in particular it neglected the genetic polymorphism within populations which was quite common. Around September, 1970, wh ...
... showed it to one of my colleagues. However, it took several months to complete a paper on this subject, and the paper was published in 1971.2 "This first theory had some defects; in particular it neglected the genetic polymorphism within populations which was quite common. Around September, 1970, wh ...
3.A.1 DNA and RNA Without Pictures
... The separation of nucleic acids or proteins, on the basis of their size and electrical charge, by measuring their rate of movement through an electrical field in a ...
... The separation of nucleic acids or proteins, on the basis of their size and electrical charge, by measuring their rate of movement through an electrical field in a ...
Zoo/Bot 3333
... a) in the mother; b) in the father; c) you can not tell just on the basis of this data. 3. Rearrangements in chromosomes may affect gene expression or gene transmission by altering the ________________________ of certain genes in the genome. a) position; b) linkage group; c) ability to pair and segr ...
... a) in the mother; b) in the father; c) you can not tell just on the basis of this data. 3. Rearrangements in chromosomes may affect gene expression or gene transmission by altering the ________________________ of certain genes in the genome. a) position; b) linkage group; c) ability to pair and segr ...
Lecture 14 – 10/5 – Dr. Wormington
... Nuclear Envelope Reforms Chromosomes Decondense Cytokinesis Occurs ...
... Nuclear Envelope Reforms Chromosomes Decondense Cytokinesis Occurs ...
PPT File
... 1. Proteins are made by joining long chains of amino acids together to form polypeptides. a. There are a total of 20 different amino acids. b. Different proteins are made by different combinations and numbers of these amino acids. c. These amino acids are assembled using the Genetic code. Cells stor ...
... 1. Proteins are made by joining long chains of amino acids together to form polypeptides. a. There are a total of 20 different amino acids. b. Different proteins are made by different combinations and numbers of these amino acids. c. These amino acids are assembled using the Genetic code. Cells stor ...
Ch.6: Sexual Identity
... remains active. 2. The inactive chromosome can be from the father, or from the mother. In different cells of the same individual, a female expresses the X chromosome genes inherited from the father in some cells and those from her mother in other cells. 3. Inactivation takes place early in developme ...
... remains active. 2. The inactive chromosome can be from the father, or from the mother. In different cells of the same individual, a female expresses the X chromosome genes inherited from the father in some cells and those from her mother in other cells. 3. Inactivation takes place early in developme ...
Chapter 14 Section 14_2 Human Genetic Disorders
... A new study shows that many can thank a Pny genePc mutaPon – a single leVer change from an A to a G in the enPre human genome. ...
... A new study shows that many can thank a Pny genePc mutaPon – a single leVer change from an A to a G in the enPre human genome. ...
Furry Family Pre
... 8) A scientist crossed a pea plant with yellow wrinkled peas with a pea plant with green smooth peas. The resulting offspring were yellow smooth peas. What does this indicate? a. b. c. d. ...
... 8) A scientist crossed a pea plant with yellow wrinkled peas with a pea plant with green smooth peas. The resulting offspring were yellow smooth peas. What does this indicate? a. b. c. d. ...
Chapter 8 General Science Genetics: The Code of Life trait
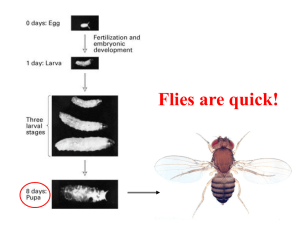
... by DNA. Remember, DNA is a special kind of molecule found in the nuclei of cells. It controls many of the characteristics of living things. Scientists often use fruit flies to study genetics. That is because fruit flies have hundreds of offspring at a time, and they reproduce every ten days. Scienti ...
... by DNA. Remember, DNA is a special kind of molecule found in the nuclei of cells. It controls many of the characteristics of living things. Scientists often use fruit flies to study genetics. That is because fruit flies have hundreds of offspring at a time, and they reproduce every ten days. Scienti ...
Mutation Study Guide
... A chromosomal mutation typically affects more genes because it takes place at a chromosomal level. Chromosomal mutations can have a large effect and may result in a disrupted gene or abnormal regulation of genes. 6. What is translocation? The attachment of a piece of one chromosome to a non-homologo ...
... A chromosomal mutation typically affects more genes because it takes place at a chromosomal level. Chromosomal mutations can have a large effect and may result in a disrupted gene or abnormal regulation of genes. 6. What is translocation? The attachment of a piece of one chromosome to a non-homologo ...
PowerPoint to accompany Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... • People affected produce several symptoms that vary ...
... • People affected produce several symptoms that vary ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.