Test Bank
... 11. The characteristics of an organism are determined by two factors: ____________________. 12. In four o’clock plants, flower color is controlled by two alleles that show _________________________. 13. An organism’s gametes have ____________________ the number of chromosomes found in the organism’s ...
... 11. The characteristics of an organism are determined by two factors: ____________________. 12. In four o’clock plants, flower color is controlled by two alleles that show _________________________. 13. An organism’s gametes have ____________________ the number of chromosomes found in the organism’s ...
Chapter 14 PPT Mendelian Genetics..
... • Mendel called the purple flower color a dominant trait and the white flower color a recessive trait • Mendel observed the same pattern of inheritance in six other pea plant characters, each represented by two traits • What Mendel called a “heritable factor” is what we now call a gene ...
... • Mendel called the purple flower color a dominant trait and the white flower color a recessive trait • Mendel observed the same pattern of inheritance in six other pea plant characters, each represented by two traits • What Mendel called a “heritable factor” is what we now call a gene ...
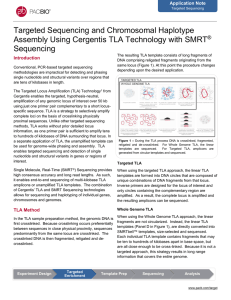
Application Note: Targeted sequencing and chromosomal haplotype
... amplification of any genomic locus of interest over 50 kb using just one primer pair complementary to a short locusspecific sequence. TLA is a strategy to selectively amplify complete loci on the basis of crosslinking physically proximal sequences. Unlike other targeted sequencing methods, TLA works ...
... amplification of any genomic locus of interest over 50 kb using just one primer pair complementary to a short locusspecific sequence. TLA is a strategy to selectively amplify complete loci on the basis of crosslinking physically proximal sequences. Unlike other targeted sequencing methods, TLA works ...
Arsenite as an Electron Donor for Anoxygenic Photosynthesis
... of As(III)-dependent growth via anoxygenic photosynthesis and contained homologs of arxA, but displayed different phenotypes. Comparisons were made with three related species: Ectothiorhodospira shaposhnikovii DSM 2111, Ectothiorhodospira shaposhnikovii DSM 243T , and Halorhodospira halophila DSM 24 ...
... of As(III)-dependent growth via anoxygenic photosynthesis and contained homologs of arxA, but displayed different phenotypes. Comparisons were made with three related species: Ectothiorhodospira shaposhnikovii DSM 2111, Ectothiorhodospira shaposhnikovii DSM 243T , and Halorhodospira halophila DSM 24 ...
Inclusive fitness and the sociobiology of the genome
... frequency q will appear in (1), and b and c may be functions of q as well, so the interpretation of r as relatedness becomes accordingly more complex (Michod and Hamilton 1980). Of course, in general b and c will also depend on the frequency of alleles at other loci of the genome, and since the chan ...
... frequency q will appear in (1), and b and c may be functions of q as well, so the interpretation of r as relatedness becomes accordingly more complex (Michod and Hamilton 1980). Of course, in general b and c will also depend on the frequency of alleles at other loci of the genome, and since the chan ...
Research Associate, Dept
... Cryptosporidium parvum is an obligatory intracellular, parasitic protist that belongs together with other human and animal pathogens like haematozoans Plasmodium sp., Babesia sp. and coccidians Toxoplasma gondii, Isospora sp., Cyclospora sp. and Eimeria sp. to the phylum Apicomplexa. Apicomplexans, ...
... Cryptosporidium parvum is an obligatory intracellular, parasitic protist that belongs together with other human and animal pathogens like haematozoans Plasmodium sp., Babesia sp. and coccidians Toxoplasma gondii, Isospora sp., Cyclospora sp. and Eimeria sp. to the phylum Apicomplexa. Apicomplexans, ...
Processing the RefSeq and CCDS Annotation Datasets Using the SAS System: Creation of Gene Reference
... of STRAND, either Lines 37-171 or Lines 174-331 are executed. The authors avoided using ELSE IF for two reasons: the computational require of two exclusive IF statements is negligible and indenting made the code more difficult to read on a smaller screen. In either set of IF-THEN-DO-END statements, ...
... of STRAND, either Lines 37-171 or Lines 174-331 are executed. The authors avoided using ELSE IF for two reasons: the computational require of two exclusive IF statements is negligible and indenting made the code more difficult to read on a smaller screen. In either set of IF-THEN-DO-END statements, ...
Expression of Allene Oxide Synthase Determines - Bio
... Tyr-30), an Ala residue within ⫺3 to ⫺1 of the proposed cleavage site (Fig. 1a, marked by asterisk), and a -sheet immediately prior to the proposed cleavage site. The mature AOS polypeptide from tomato is presumed to start at Ser-30, whereas that from Arabidopsis and flax starts at Leu-22 and Ser-4 ...
... Tyr-30), an Ala residue within ⫺3 to ⫺1 of the proposed cleavage site (Fig. 1a, marked by asterisk), and a -sheet immediately prior to the proposed cleavage site. The mature AOS polypeptide from tomato is presumed to start at Ser-30, whereas that from Arabidopsis and flax starts at Leu-22 and Ser-4 ...
MOLECULAR RECOGNITION AND RESPONSE IN POLLEN AND
... of two fungal RNases, RNase T2 and RNase Rh. It is this similarity that led to the discovery that S-proteins are RNases (McClure et al 1989). The finding that RNases are employed by the pistil to reject self pollen raised the possibility that the RNase activity is responsible for growth inhibition o ...
... of two fungal RNases, RNase T2 and RNase Rh. It is this similarity that led to the discovery that S-proteins are RNases (McClure et al 1989). The finding that RNases are employed by the pistil to reject self pollen raised the possibility that the RNase activity is responsible for growth inhibition o ...
PDF
... for the genitalia; sources of descriptions of thoracic structures are as previously cited (Ingham, ...
... for the genitalia; sources of descriptions of thoracic structures are as previously cited (Ingham, ...
MSc Seminar: Donald Dunbar
... The gene might not be on the chip Can’t differentiate splice variants well The gene might be below detection limit Can’t differentiate RNA synthesis and degradation Can’t tell us about post translational events Bioinformatics can be difficult Relatively expensive February 26th 2011 ...
... The gene might not be on the chip Can’t differentiate splice variants well The gene might be below detection limit Can’t differentiate RNA synthesis and degradation Can’t tell us about post translational events Bioinformatics can be difficult Relatively expensive February 26th 2011 ...
Text S1.
... [2] or the 1000 Genomes Project [3]). Putatively functional genotypes are only counted if they occur in genes annotated as being associated with the phenotype. Second layer. These nodes represent genes, split into those annotated as high penetrance GH or low penetrance GL. Their values depend on lin ...
... [2] or the 1000 Genomes Project [3]). Putatively functional genotypes are only counted if they occur in genes annotated as being associated with the phenotype. Second layer. These nodes represent genes, split into those annotated as high penetrance GH or low penetrance GL. Their values depend on lin ...
Deep Insight Section The vagaries of non-traditional mendelian Aa = aa !
... What is the mitotic step superseding the meiotic one and resulting in UPD? An early somatic error, namely a mitotic nondisjunction or a chromosome lag restoring diploidy. What is the end-result of the two-step process leading to UPD? - Trisomy rescue by loss of one or the other member of the unipare ...
... What is the mitotic step superseding the meiotic one and resulting in UPD? An early somatic error, namely a mitotic nondisjunction or a chromosome lag restoring diploidy. What is the end-result of the two-step process leading to UPD? - Trisomy rescue by loss of one or the other member of the unipare ...
Cell and Molecular Biology
... • What are the A, P, and E sites of a ribosome? What binds at each of these sites? • Does anything beside the ribosome participate in elongation of the amino acid chain? If so, what is it and what does it do? • What signals where translation starts and stops? • What happens to improperly translated ...
... • What are the A, P, and E sites of a ribosome? What binds at each of these sites? • Does anything beside the ribosome participate in elongation of the amino acid chain? If so, what is it and what does it do? • What signals where translation starts and stops? • What happens to improperly translated ...
Neurospora - DiVA portal
... became known as the “red bread mould” (Davis, 2000). During the first half of the 1900s, Neurospora emerged as a model eukaryotic organism for genetic studies, since it possesses numerous advantageous properties; it is haploid during most of its life cycle, easy to cultivate, susceptible to mutagene ...
... became known as the “red bread mould” (Davis, 2000). During the first half of the 1900s, Neurospora emerged as a model eukaryotic organism for genetic studies, since it possesses numerous advantageous properties; it is haploid during most of its life cycle, easy to cultivate, susceptible to mutagene ...
Landick R, Yanofsky C. 1987. Transcription
... releasing the polymerase and restoring transcription. Polymerase and ribosome then move in unison over the leader region and leader transcript, respectively. At this stage there are two options (176). If there is a deficiency of charged tRNA Trp, the translating ri bosome would stall at one of the T ...
... releasing the polymerase and restoring transcription. Polymerase and ribosome then move in unison over the leader region and leader transcript, respectively. At this stage there are two options (176). If there is a deficiency of charged tRNA Trp, the translating ri bosome would stall at one of the T ...
adapt1
... G. Species Selection - Parthenogenesis arises spontaneously, but extinctions are rapid due to lack of variation and Muller's rachet. Muller's ratchet is the continuous accumulation of mutations in a lineage. In sexual reproduction, since only 1/2 of the genes are passed from each parent, there is a ...
... G. Species Selection - Parthenogenesis arises spontaneously, but extinctions are rapid due to lack of variation and Muller's rachet. Muller's ratchet is the continuous accumulation of mutations in a lineage. In sexual reproduction, since only 1/2 of the genes are passed from each parent, there is a ...
A PCR approach to determine the distribution of toxin genes in
... Of the 40 strains originally named as C. novyi type A or C. novyi type A-like, only 22 (55 %) tested positive for the C. novyi a toxin gene by PCR. All negative strains were tested on at least two further occasions with consistently negative results for the a toxin gene. Whether this result is real ...
... Of the 40 strains originally named as C. novyi type A or C. novyi type A-like, only 22 (55 %) tested positive for the C. novyi a toxin gene by PCR. All negative strains were tested on at least two further occasions with consistently negative results for the a toxin gene. Whether this result is real ...
Role of two-component systems in the virulence of Streptococcus
... membrane-associated sensor histidine kinase (HK) and a cytoplasmic cognate response regulator (RR). Upon receipt of a specific external stimulus the kinase domain of the HK sensor protein is activated to autophosphorylate a conserved histidine residue. HK proteins tend to be found as homodimers that ...
... membrane-associated sensor histidine kinase (HK) and a cytoplasmic cognate response regulator (RR). Upon receipt of a specific external stimulus the kinase domain of the HK sensor protein is activated to autophosphorylate a conserved histidine residue. HK proteins tend to be found as homodimers that ...
Disruption and aberrant expression of HMGA2 as a
... about 100 amino acids, which each possess three copies of a nine amino-acid motif (AT-hook) that interacts with the minor groove of many promoter and enhancer DNA regulatory elements.4 HMG proteins possess no intrinsic transcriptional activity, but instead function to orchestrate the assembly of nuc ...
... about 100 amino acids, which each possess three copies of a nine amino-acid motif (AT-hook) that interacts with the minor groove of many promoter and enhancer DNA regulatory elements.4 HMG proteins possess no intrinsic transcriptional activity, but instead function to orchestrate the assembly of nuc ...
Direct and indirect consequences of meiotic recombination
... has also been discussed [20]. We refer to these processes as the direct effects of recombination (further details are presented in Box 1 and Figure 1). Although one of the advantages of the indirect effects of recombination is the efficient removal of deleterious alleles from a population, its direc ...
... has also been discussed [20]. We refer to these processes as the direct effects of recombination (further details are presented in Box 1 and Figure 1). Although one of the advantages of the indirect effects of recombination is the efficient removal of deleterious alleles from a population, its direc ...
An Introduction to Genetic Analysis Chapter 18 Chromosome
... arise naturally as spontaneous chromosomal mutations and, as such, they must be considered aberrations because they differ from the previous norm. However, many species of plants and animals have clearly arisen through polyploidy, so evidently evolution can take advantage of polyploidy when it arise ...
... arise naturally as spontaneous chromosomal mutations and, as such, they must be considered aberrations because they differ from the previous norm. However, many species of plants and animals have clearly arisen through polyploidy, so evidently evolution can take advantage of polyploidy when it arise ...
A Deterministic Analysis of Stationary Diploid/Dominance
... No recombination will be used here since one desire is to isolate the effects of diploidy. In addition, the complete dominance population is complicated with two kinds of recombination. The first is the usual one, between individual, real string positions. In this case, crossover occurs within the g ...
... No recombination will be used here since one desire is to isolate the effects of diploidy. In addition, the complete dominance population is complicated with two kinds of recombination. The first is the usual one, between individual, real string positions. In this case, crossover occurs within the g ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.