Genomes and their evolution
... •During a process called, transposition, a transposable element moves from one site in a cells DNA to a different target sit by a type of recombination process. •These stretches of DNA move from one location to another in the genome with the aid of an enzyme, transposase. •Transposase can interrupt ...
... •During a process called, transposition, a transposable element moves from one site in a cells DNA to a different target sit by a type of recombination process. •These stretches of DNA move from one location to another in the genome with the aid of an enzyme, transposase. •Transposase can interrupt ...
Tour of the Basics Web Quest
... 17. Does the second baby in the What is Heredity? animation inherit the exact same chromosomes as the first? Do both babies have a complete set? ...
... 17. Does the second baby in the What is Heredity? animation inherit the exact same chromosomes as the first? Do both babies have a complete set? ...
Chapter 3 Practice Tes1
... 3. The human genome is best defined as: a. A complex molecule containing genetic information that makes up the chromosomes. b. A segment of the DNA c. The complete instructions for making an organism d. The four-letter genetic alphabet 4. Most human traits are a. Learned b. Determined by a s ...
... 3. The human genome is best defined as: a. A complex molecule containing genetic information that makes up the chromosomes. b. A segment of the DNA c. The complete instructions for making an organism d. The four-letter genetic alphabet 4. Most human traits are a. Learned b. Determined by a s ...
Test 5 Notecards
... sex-linked disorders: carried on the X chromosome; more common in males because they only have one X; include hemophilia and colorblindness; mother can have the disorder (XhXh), be a carrier (XhX), or be unaffected (XX); father can have the disorder (XhY) or be unaffected XY. Trisomy 21 (Downs syndr ...
... sex-linked disorders: carried on the X chromosome; more common in males because they only have one X; include hemophilia and colorblindness; mother can have the disorder (XhXh), be a carrier (XhX), or be unaffected (XX); father can have the disorder (XhY) or be unaffected XY. Trisomy 21 (Downs syndr ...
Exam301ANS
... Two mutant strains of a microorganism are auxotrophic for compound X. The compounds A, B, and C are related to compound X. One of the mutants can grow when fed compound A or C, but can't grow when fed compound B. The other mutant can grow when fed compound C, but can't grow when fed compound A or B. ...
... Two mutant strains of a microorganism are auxotrophic for compound X. The compounds A, B, and C are related to compound X. One of the mutants can grow when fed compound A or C, but can't grow when fed compound B. The other mutant can grow when fed compound C, but can't grow when fed compound A or B. ...
HEREDITY AND GENETICS vocabulary terms and
... Pairs of genes that occupy a specific position on a chromosome; genes that code for the same trait; alternate forms of the same gene ...
... Pairs of genes that occupy a specific position on a chromosome; genes that code for the same trait; alternate forms of the same gene ...
No Slide Title
... Genetic tools for manipulating cell circuitry a) systematic knockout and mutation of genes: both stable and conditional b) transgenic studies: overexpression of gene products c) redesigning of cellular circuits (e.g., drosophila gal4 ...
... Genetic tools for manipulating cell circuitry a) systematic knockout and mutation of genes: both stable and conditional b) transgenic studies: overexpression of gene products c) redesigning of cellular circuits (e.g., drosophila gal4 ...
Presentation
... Expression of traits is not necessarily related to the nucleotide sequence Some individuals may express traits from their genes where others will not based on histone modifications One twin may express a trait or get a disease that the other does not, despite same genes Schizophrenia Some ...
... Expression of traits is not necessarily related to the nucleotide sequence Some individuals may express traits from their genes where others will not based on histone modifications One twin may express a trait or get a disease that the other does not, despite same genes Schizophrenia Some ...
Chapter 6 Review Terms: Somatic Cell, Game - District 196 e
... A pairs with _____, C pairs with _____, G pairs with _____, and T pairs with _____ ...
... A pairs with _____, C pairs with _____, G pairs with _____, and T pairs with _____ ...
15.3_Applications_of_Genetic_Engineering
... Draw Conclusions Why do you think the levels of adoption fell at certain points of the period Predict What do you think will happen to HT soybeans and HT corn over the nest few yearswhy? Use the graph to support your prediction Infer Why do you think an increasing number of farmers have chosen to gr ...
... Draw Conclusions Why do you think the levels of adoption fell at certain points of the period Predict What do you think will happen to HT soybeans and HT corn over the nest few yearswhy? Use the graph to support your prediction Infer Why do you think an increasing number of farmers have chosen to gr ...
Ch 15 Genetic Engineering
... Draw Conclusions Why do you think the levels of adoption fell at certain points of the period Predict What do you think will happen to HT soybeans and HT corn over the nest few yearswhy? Use the graph to support your prediction Infer Why do you think an increasing number of farmers have chosen to gr ...
... Draw Conclusions Why do you think the levels of adoption fell at certain points of the period Predict What do you think will happen to HT soybeans and HT corn over the nest few yearswhy? Use the graph to support your prediction Infer Why do you think an increasing number of farmers have chosen to gr ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... is the use of transgenic farm animals to produce pharmaceuticals; genes that code for therapeutic and diagnostic proteins are incorporated into an animal’s DNA, and the proteins appear in the animal’s milk. 26.3 Gene Therapy Gene Therapy Gene therapy is the insertion of genetic material into human c ...
... is the use of transgenic farm animals to produce pharmaceuticals; genes that code for therapeutic and diagnostic proteins are incorporated into an animal’s DNA, and the proteins appear in the animal’s milk. 26.3 Gene Therapy Gene Therapy Gene therapy is the insertion of genetic material into human c ...
Genetics Vocabulary
... Also known as behavioral traits. These are traits or characteristics that develop during a lifetime and are not passed to offspring through DNA. A variation that makes an organism better suited to its environment. These traits increase the chance of surviving and reproducing. The basic unit of hered ...
... Also known as behavioral traits. These are traits or characteristics that develop during a lifetime and are not passed to offspring through DNA. A variation that makes an organism better suited to its environment. These traits increase the chance of surviving and reproducing. The basic unit of hered ...
Nair.Amritha.Ashok, Belligere.Kempegowda.Spoorthi, Ashcheulova
... makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. The techniques involve sophisticated manipulations of genetic material and other biologically important chemicals. Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) can be defined as org ...
... makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. The techniques involve sophisticated manipulations of genetic material and other biologically important chemicals. Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) can be defined as org ...
A Nucleotide Consists of what three parts?
... DNA GATAGCCGATTACGGATA Complimentary Strand CTATCGGCTAATGCCTAT RNA CUAUCGGCUAAUGCCUAU A Codon is: Three base pairs: CUA Codon = Amino Acid ...
... DNA GATAGCCGATTACGGATA Complimentary Strand CTATCGGCTAATGCCTAT RNA CUAUCGGCUAAUGCCUAU A Codon is: Three base pairs: CUA Codon = Amino Acid ...
ppt
... http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter15/animations.html# short movie of mRNA editing (introns/exons) ...
... http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter15/animations.html# short movie of mRNA editing (introns/exons) ...
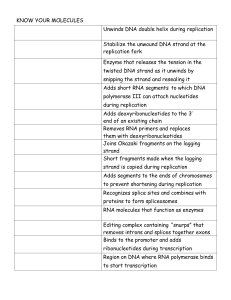
Know your molecules organizer
... Short fragments made when the lagging strand is copied during replication Adds segments to the ends of chromosomes to prevent shortening during replication Recognizes splice sites and combines with proteins to form spliceosomes RNA molecules that function as enzymes Editing complex containing “snurp ...
... Short fragments made when the lagging strand is copied during replication Adds segments to the ends of chromosomes to prevent shortening during replication Recognizes splice sites and combines with proteins to form spliceosomes RNA molecules that function as enzymes Editing complex containing “snurp ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.