May 4, 2004 B4730/5730 Plant Physiological Ecology
... traits • Two copies of alleles determines traits ...
... traits • Two copies of alleles determines traits ...
Virus - World Health Organization
... A virus is an obligate parasite dependent on nutrients inside cells for its metabolic and reproductive needs. It consist of a strand of either DNA or RNA, but not both, separated by a protein covering called a capsid (Symons etal. 2000). Viruses consist of two or three parts : all viruses have genes ...
... A virus is an obligate parasite dependent on nutrients inside cells for its metabolic and reproductive needs. It consist of a strand of either DNA or RNA, but not both, separated by a protein covering called a capsid (Symons etal. 2000). Viruses consist of two or three parts : all viruses have genes ...
Project Title: Characterization of new genes mediating exchange of
... new assay for sensitivity to in vivo expression of the DNA endonuclease HO. This nuclease creates a break in yeast chromosome III at a single site that cannot be repaired if cells are defective in intrachromosomal DNA recombination. She identified 10 previously unrecognized genes that cause cells to ...
... new assay for sensitivity to in vivo expression of the DNA endonuclease HO. This nuclease creates a break in yeast chromosome III at a single site that cannot be repaired if cells are defective in intrachromosomal DNA recombination. She identified 10 previously unrecognized genes that cause cells to ...
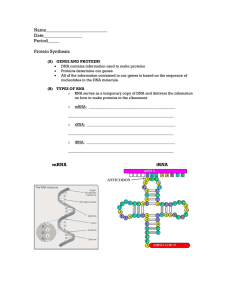
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... RNA Polymerase knows where to bind on the DNA due to spots on the DNA called promoters, which act as start point signals for transcription. ...
... RNA Polymerase knows where to bind on the DNA due to spots on the DNA called promoters, which act as start point signals for transcription. ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS QUESTIONS
... 2. The template strand of a gene contains the sequence 3’ TTCAGTCGT 5’. Draw the nontemplate sequence and the mRNA sequence, indicating 5’ and 3’ ends of each. Compare the two sequences. 3. Imagine that the nontemplate sequence in question 2 was traqnscribed instead of the template sequence. Draw th ...
... 2. The template strand of a gene contains the sequence 3’ TTCAGTCGT 5’. Draw the nontemplate sequence and the mRNA sequence, indicating 5’ and 3’ ends of each. Compare the two sequences. 3. Imagine that the nontemplate sequence in question 2 was traqnscribed instead of the template sequence. Draw th ...
Goal 3
... The “rungs of the DNA ladder” are composed of complementary nitrogenous base pairs (always adenine, A, to thymine, T, and cytosine, C, to guanine, G) joined by weak hydrogen bonds. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA codes for proteins, which is central key to cell function and life. Replication occu ...
... The “rungs of the DNA ladder” are composed of complementary nitrogenous base pairs (always adenine, A, to thymine, T, and cytosine, C, to guanine, G) joined by weak hydrogen bonds. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA codes for proteins, which is central key to cell function and life. Replication occu ...
Chapter 8.4, 8.5, 8.6, 8.7 Study Guide Key terms: Ribonucleic acid
... 1. Why do cells regulate gene expression? 2. What happens to the information on a DNA molecule during transcription? 3. What are repressor proteins and where do they bind? 4. mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm (with or without) a complete set of both introns and exons. (please circle t ...
... 1. Why do cells regulate gene expression? 2. What happens to the information on a DNA molecule during transcription? 3. What are repressor proteins and where do they bind? 4. mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm (with or without) a complete set of both introns and exons. (please circle t ...
Answers to Biological Inquiry Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... ANSWER: Retroelements. A single element can be transcribed into multiple copies of RNA, which can be converted to DNA by reverse transcriptase, and inserted into multiple sites in the genome. Figure 21.8 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: What is the advantage of a gene family? ANSWER: The overall advanta ...
... ANSWER: Retroelements. A single element can be transcribed into multiple copies of RNA, which can be converted to DNA by reverse transcriptase, and inserted into multiple sites in the genome. Figure 21.8 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: What is the advantage of a gene family? ANSWER: The overall advanta ...
Eukaryotic Gene Expression
... cytoplasm Eukaryotic mRNA can last hours or even weeks Length of time before degraded by cellular enzymes is related to quantity of protein synthesis they can direct Translation of mRNA can be delayed until control signal initiates it Initiation factors may be required for translation Polypeptides a ...
... cytoplasm Eukaryotic mRNA can last hours or even weeks Length of time before degraded by cellular enzymes is related to quantity of protein synthesis they can direct Translation of mRNA can be delayed until control signal initiates it Initiation factors may be required for translation Polypeptides a ...
MODULE 7: REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION DURING
... Name the group of genes, identified by Nusslein-Volhard and Caroll that is responsible for the final stages of segmentation in Drosophila embryos ...
... Name the group of genes, identified by Nusslein-Volhard and Caroll that is responsible for the final stages of segmentation in Drosophila embryos ...
One Gene -One polypeptide
... 11.4 One Gene One Polypeptide Each gene codes for a polypeptide (protein). A polypeptide is made up of amino acids (monomer) Proteins can have 1,2,3,or 4 polypeptides, Human traits can have more than 1 gene. ...
... 11.4 One Gene One Polypeptide Each gene codes for a polypeptide (protein). A polypeptide is made up of amino acids (monomer) Proteins can have 1,2,3,or 4 polypeptides, Human traits can have more than 1 gene. ...
Name
... B) serves as a master control gene that functions during embryonic development by controlling the developmental fate of groups of cells. C) represses gene transcription and promotes mRNA translation. D) produces a product that controls the transcription of other genes. E) is found only in adult soma ...
... B) serves as a master control gene that functions during embryonic development by controlling the developmental fate of groups of cells. C) represses gene transcription and promotes mRNA translation. D) produces a product that controls the transcription of other genes. E) is found only in adult soma ...
Vocabulary 7
... 1) DNA – made of subunits known as nucleotides – made of: • sugar • phosphate • base • Shape: Double Helix • Found in the nucleus; chromosomes ...
... 1) DNA – made of subunits known as nucleotides – made of: • sugar • phosphate • base • Shape: Double Helix • Found in the nucleus; chromosomes ...
Protein - UDKeystone
... – The DNA of the gene is transcribed into RNA • Which is translated into protein • The flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to Protein is called the CENTRAL DOGMA DNA ...
... – The DNA of the gene is transcribed into RNA • Which is translated into protein • The flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to Protein is called the CENTRAL DOGMA DNA ...
JHS 2017 Workshop on Return of Genetic Results Glossary ACMG
... The Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) project is part of NHLBI’s TOPMed program and serves as an initial step for the larger initiative. In recent years, genetic research of complex disease using Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) and Exome-sequencing approaches has resulted in an unprecedented explos ...
... The Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) project is part of NHLBI’s TOPMed program and serves as an initial step for the larger initiative. In recent years, genetic research of complex disease using Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) and Exome-sequencing approaches has resulted in an unprecedented explos ...
Biology 101 Section 6
... Two of them; X and Y XX is female, XY is male Sex-linked genes are those found on the sex chromosome but are unrelated to sex determination Most sex-linked genes are found on X chromosome (80%) Passed on maternally ! Most disorders occur in males! Why? There are no such things as male carr ...
... Two of them; X and Y XX is female, XY is male Sex-linked genes are those found on the sex chromosome but are unrelated to sex determination Most sex-linked genes are found on X chromosome (80%) Passed on maternally ! Most disorders occur in males! Why? There are no such things as male carr ...
KEY TERMS Asexual Reproduction: One parent always passes on a
... every trait pass on 1 of each gene to offspring by way of meiosis, gamete formation, and fertilization. Thus the first cell of new individual inherits 2 genes for every trait – one from each parent. ...
... every trait pass on 1 of each gene to offspring by way of meiosis, gamete formation, and fertilization. Thus the first cell of new individual inherits 2 genes for every trait – one from each parent. ...
Insects and genetics
... 2. physical appearance of an organism c. allele 3. location of a gene on a chromosome d. mutation 4. genetic make-up of an organism e. genotype 5. alternative state of a gene or trait f. phenotype 6. segment of DNA on a chromosome coding for a protein or RNA g. chromosome 7. group of coiled DNA stra ...
... 2. physical appearance of an organism c. allele 3. location of a gene on a chromosome d. mutation 4. genetic make-up of an organism e. genotype 5. alternative state of a gene or trait f. phenotype 6. segment of DNA on a chromosome coding for a protein or RNA g. chromosome 7. group of coiled DNA stra ...
Traits: The Puppeteering of Genetics
... Example include height, weight, and skin color, cancer risk, or any trait in which multiple factors come into play (generally quantitative values) ...
... Example include height, weight, and skin color, cancer risk, or any trait in which multiple factors come into play (generally quantitative values) ...
Basic Principles of Genetics: Printable Crossword Puzzle
... 5. Mendel's principle of genetic inheritance stating that different pairs of genes are passed to offspring independently so that new combinations of genes, present in neither parent, are possible. 9. An alternate form of the same gene. 11. The genetic makeup of an individual for a trait or for all o ...
... 5. Mendel's principle of genetic inheritance stating that different pairs of genes are passed to offspring independently so that new combinations of genes, present in neither parent, are possible. 9. An alternate form of the same gene. 11. The genetic makeup of an individual for a trait or for all o ...
Comparative Genomics
... One possibility is horizontal transfer 41 genes may have been transferred in this way For example: MAOs, monoamine oxidases These enzymes deactivate neurotransmitters ...
... One possibility is horizontal transfer 41 genes may have been transferred in this way For example: MAOs, monoamine oxidases These enzymes deactivate neurotransmitters ...
Fill-in-Notes - Pearland ISD
... PAP Molecular Genetics & Biotechnology Notes Applied Genetics: is the _________; of the hereditary characteristics of an organism to improve or create specific traits in ______________. Selective breeding: directed breeding to produce plant and animal with _____________ Ex: breeding plants to produc ...
... PAP Molecular Genetics & Biotechnology Notes Applied Genetics: is the _________; of the hereditary characteristics of an organism to improve or create specific traits in ______________. Selective breeding: directed breeding to produce plant and animal with _____________ Ex: breeding plants to produc ...
Slide ()
... A) The linearized double-stranded DNA genome of KS virus showing important genes of the lytic cycle. The genome contains 87 open reading frames (ORFs) coding for latent proteins, reactivation proteins, and structural proteins. Host genes that help the virus evade immune surveillance and inhibit apop ...
... A) The linearized double-stranded DNA genome of KS virus showing important genes of the lytic cycle. The genome contains 87 open reading frames (ORFs) coding for latent proteins, reactivation proteins, and structural proteins. Host genes that help the virus evade immune surveillance and inhibit apop ...
Study Guide – Unit 6 Test: Genetics and DNA Name: Per: 1 2 3 4 5 6
... How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? ...
... How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? ...
Lec. 26 - Genomics
... genomes (some relatively recently). • Selfish DNAs such as mobile introns and transposons occasionally transfer horizontally. ...
... genomes (some relatively recently). • Selfish DNAs such as mobile introns and transposons occasionally transfer horizontally. ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.