a version - SEA
... After the isolation and sequencing of Mycobacterium phage LittleLaf, various bioinformatic tools were utilized in the annotation of its genome; these tools included the annotation software DNA Master, the gene prediction software GeneMark, the Starterator and Phamerator reports, Shine-Dalgarno value ...
... After the isolation and sequencing of Mycobacterium phage LittleLaf, various bioinformatic tools were utilized in the annotation of its genome; these tools included the annotation software DNA Master, the gene prediction software GeneMark, the Starterator and Phamerator reports, Shine-Dalgarno value ...
Tour of the Basics Web
... /f fr*'o d"*mlnq"m".{.n$gl"es sre rnf'}erifed, fj:c psrssn is hpm"q"ay"gog$ nnd ud// have m irifetuf':ik*rs ftullnib. if twn r$"fiS.$Siti"S eflp"k$,-are fnfterifed, ftoe p*rson rs &gffiffigggtr$ and r,vij/ ftave s sfrafgftf ffrutrnh. lf a person is ftgkfggxggtrs, s$s $,qmit:le*l and one rsfi.e_S$-t" ...
... /f fr*'o d"*mlnq"m".{.n$gl"es sre rnf'}erifed, fj:c psrssn is hpm"q"ay"gog$ nnd ud// have m irifetuf':ik*rs ftullnib. if twn r$"fiS.$Siti"S eflp"k$,-are fnfterifed, ftoe p*rson rs &gffiffigggtr$ and r,vij/ ftave s sfrafgftf ffrutrnh. lf a person is ftgkfggxggtrs, s$s $,qmit:le*l and one rsfi.e_S$-t" ...
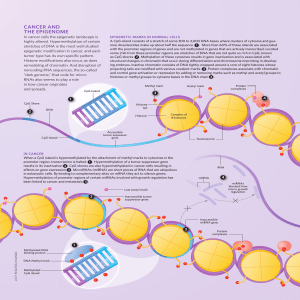
CaNCer aND THe ePIGeNOMe
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
Networks of Genes, Epistasis and a Functionally
... Autism is highly genotypically heterogenous disorder, to which variants in a large number of genes likely to contribute. Identifying the molecular pathways in which these genes act provides not only insight into the pathoetiology but also translational routes to diagnosis, patient stratification and ...
... Autism is highly genotypically heterogenous disorder, to which variants in a large number of genes likely to contribute. Identifying the molecular pathways in which these genes act provides not only insight into the pathoetiology but also translational routes to diagnosis, patient stratification and ...
29 - Karmayog .org
... In every pair, both chromosomes give instructions for the same thing, the same features are coded for by genes in the same place on each chromosome, called the gene locus. So you have two alternative instructions for each feature. Some chromosomes may carry many genes, called polygenes, to code for ...
... In every pair, both chromosomes give instructions for the same thing, the same features are coded for by genes in the same place on each chromosome, called the gene locus. So you have two alternative instructions for each feature. Some chromosomes may carry many genes, called polygenes, to code for ...
Biology Chapter 11 Review
... Punnett Squares use mathematical probability to help predict the genotype and phenotype combinations in genetic crosses. (Know how to do a Punnett Square) ...
... Punnett Squares use mathematical probability to help predict the genotype and phenotype combinations in genetic crosses. (Know how to do a Punnett Square) ...
PART
... m. RNA is similar to DNA except it has a single polynucleotide chain, has ribose instead of deoxyribose, and has uracil instead of thymine. ...
... m. RNA is similar to DNA except it has a single polynucleotide chain, has ribose instead of deoxyribose, and has uracil instead of thymine. ...
Systematic Implications of DNA variation in subfamily Opuntioideae
... Selection of DNA region to compare: ...
... Selection of DNA region to compare: ...
Red line lesson sketch
... First, use DNA subway to show how we can reveal features of a sequence. Create a project using a sample sequence. Once students have mastery, they can come back and create their own projects using real data. ...
... First, use DNA subway to show how we can reveal features of a sequence. Create a project using a sample sequence. Once students have mastery, they can come back and create their own projects using real data. ...
BIOLOGY - San Marcos Unified School District
... make each type of protein the body needs • mRNA takes a “copy” of these coded instructions from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm (usually attached to rough Endoplasmic Reticulum) • Ribosomes use instructions and link together amino acids together to form proteins (polypeptide ...
... make each type of protein the body needs • mRNA takes a “copy” of these coded instructions from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm (usually attached to rough Endoplasmic Reticulum) • Ribosomes use instructions and link together amino acids together to form proteins (polypeptide ...
GENETICS
... acids Are only 20 common amino acids – can be combined in different ways to form thousands of different proteins The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene forms the code that determines what type of protein will be produced –called protein synthesis Before protein synthesis occurs a “messenger” m ...
... acids Are only 20 common amino acids – can be combined in different ways to form thousands of different proteins The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene forms the code that determines what type of protein will be produced –called protein synthesis Before protein synthesis occurs a “messenger” m ...
review 13-15
... A freq of 50% indication that the genes are on diff chromo’s Sex-linked traits are passed on to ...
... A freq of 50% indication that the genes are on diff chromo’s Sex-linked traits are passed on to ...
11-5 Linkage & Gene Maps
... • Some Genes Are Inherited Together Counter To Mendel's Principle Of Independent Assortment • Turns Out, It Is The Chromosomes That Sort Independently, Not Individual Genes. FOOTHILL HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE DEPARTMENT ...
... • Some Genes Are Inherited Together Counter To Mendel's Principle Of Independent Assortment • Turns Out, It Is The Chromosomes That Sort Independently, Not Individual Genes. FOOTHILL HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE DEPARTMENT ...
Sex & Death: Introduction to the Philosophy of Biology
... Area 1:What is a gene? • First Definition: a gene is a “reading sequence” • Second Definition: Dawkins and Williams, ‘evolutionary gene concept’ ...
... Area 1:What is a gene? • First Definition: a gene is a “reading sequence” • Second Definition: Dawkins and Williams, ‘evolutionary gene concept’ ...
Chapter 6 Advanced Genetics
... Changes affecting # of Chromosomes A genome is a complete haploid set of its chromosomes. A diploid cell has two complete genomes. Review haploid and diploid cells if this is confusing. Diploid organisms, like us, have to go through meiosis to produce haploid gametes (either sperm or eggs). ...
... Changes affecting # of Chromosomes A genome is a complete haploid set of its chromosomes. A diploid cell has two complete genomes. Review haploid and diploid cells if this is confusing. Diploid organisms, like us, have to go through meiosis to produce haploid gametes (either sperm or eggs). ...
A4.3.1HowDoChromosomesCarryInformation
... 6. Where are centromeres located on chromosomes? Make a sketch of a chromosome and indicate where its centromere is located. 7. Where are telomeres located on chromosomes? Make a sketch of a chromosome and indicate where its telomeres are located. 8. From the variation window, select one of the chro ...
... 6. Where are centromeres located on chromosomes? Make a sketch of a chromosome and indicate where its centromere is located. 7. Where are telomeres located on chromosomes? Make a sketch of a chromosome and indicate where its telomeres are located. 8. From the variation window, select one of the chro ...
Appendix Genomic
... In DNA and RNA, it is a pyrimidine base that is paired with guanine. It is one of the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA. DIPLOID A cell or organism composed of two sets of chromosomes: usually, one set is from the mother and the other from the father. In the diploid state the haploid numbe ...
... In DNA and RNA, it is a pyrimidine base that is paired with guanine. It is one of the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA. DIPLOID A cell or organism composed of two sets of chromosomes: usually, one set is from the mother and the other from the father. In the diploid state the haploid numbe ...
Honors Biology Final Exam Review Mrs. Speirs Directions: In no
... a substitution (one nucleotide for another nucleotide) Given a sequence of amino acids, determine the codons in DNA, mRNA or even tRNA. Use the decorder box! Causes for genetic diseases/disorders PKU CF Sickle Cell Anemia Polydactylism Biotechnology Inserting genes from one organism into another to ...
... a substitution (one nucleotide for another nucleotide) Given a sequence of amino acids, determine the codons in DNA, mRNA or even tRNA. Use the decorder box! Causes for genetic diseases/disorders PKU CF Sickle Cell Anemia Polydactylism Biotechnology Inserting genes from one organism into another to ...
File
... • Bacterial genomes are larger than viral genomes, but much smaller than a typical eukaryotic genome • Most DNA in a bacterium is found in a single circular chromosome that is composed of double-stranded DNA found in the nucleiod region. ...
... • Bacterial genomes are larger than viral genomes, but much smaller than a typical eukaryotic genome • Most DNA in a bacterium is found in a single circular chromosome that is composed of double-stranded DNA found in the nucleiod region. ...
Chapter 15 / Lecture Outline 36
... 1. Details of RNA polymerase form and function in transcription 2. Translation in prokaryotes starts before transcription ends B. The regulation of gene expression can occur at any one of the many steps that transfer information from DNA via RNA to protein II. The regulation of gene transcription A. ...
... 1. Details of RNA polymerase form and function in transcription 2. Translation in prokaryotes starts before transcription ends B. The regulation of gene expression can occur at any one of the many steps that transfer information from DNA via RNA to protein II. The regulation of gene transcription A. ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.