Annelise Mah - New Genomics Technology: Copy Number Variation Analysis Methods
... are regions of the genome that are copied, deleted, or varied in number in some way. Normally these regions are defined as a kilobase (Kb, 10^3) to several megabases (Mb, 10^6) in size. These CNVRs make up around 12% of the human genome, cause disease, affect gene expression, and alter the organism’ ...
... are regions of the genome that are copied, deleted, or varied in number in some way. Normally these regions are defined as a kilobase (Kb, 10^3) to several megabases (Mb, 10^6) in size. These CNVRs make up around 12% of the human genome, cause disease, affect gene expression, and alter the organism’ ...
Lesson 13: Polygenic Inheritance student notes
... Activity Four: What did Mendel Find when Dealing with Two Genes? Mendel studied 7 traits with contrasting phenotypes, such as wrinkled seed vs. round seed. He was thorough in studying so many. He was also thorough in studying more than one generation and in being highly quantitative. But for this ac ...
... Activity Four: What did Mendel Find when Dealing with Two Genes? Mendel studied 7 traits with contrasting phenotypes, such as wrinkled seed vs. round seed. He was thorough in studying so many. He was also thorough in studying more than one generation and in being highly quantitative. But for this ac ...
Genetic Engineering Activity Directions: Follow the steps below to
... 9. After the donor gene has been inserted into the plasmid vector, the resulting DNA is termed ___________________________ DNA. 10. After the plasmid vector has been taken up by the bacterial cell, the bacteria is termed a _________________________ organism (aka “genetically modified organism” or GM ...
... 9. After the donor gene has been inserted into the plasmid vector, the resulting DNA is termed ___________________________ DNA. 10. After the plasmid vector has been taken up by the bacterial cell, the bacteria is termed a _________________________ organism (aka “genetically modified organism” or GM ...
Document
... 20. Incomplete dominance- 2 alleles are neither dominant nor recessive. They both contribute to the phenotype In 4 O’clock flowers Ex. Red x white flowers = pink ...
... 20. Incomplete dominance- 2 alleles are neither dominant nor recessive. They both contribute to the phenotype In 4 O’clock flowers Ex. Red x white flowers = pink ...
Chapter 11 GENETICS
... Cross two plants that are heterozygous for height and pod color. Tall is dominant to short and green pods are dominant to yellow Step 1 – Make a key and determine the parents ...
... Cross two plants that are heterozygous for height and pod color. Tall is dominant to short and green pods are dominant to yellow Step 1 – Make a key and determine the parents ...
Editorials Hereditary retinopathies: insights into a complex genetic
... sequence itself (so-called restriction fragment length polymorphisms or RFLPs) were developed. More recently, a new generation of DNA markers has been developed through the use of the polymerase chain reaction. Such markers, often referred to as 'microsatellites' are based on polymorphism in the num ...
... sequence itself (so-called restriction fragment length polymorphisms or RFLPs) were developed. More recently, a new generation of DNA markers has been developed through the use of the polymerase chain reaction. Such markers, often referred to as 'microsatellites' are based on polymorphism in the num ...
MICB 201- Learning Objectives
... the genome. For example, genes for siderophore synthesis and genes for siderophore-Fe transport constitute a regulon. • Explain the ways the expression of environmentally-regulated genes is regulated at the level of transcription initiation in prokaryotes and why a particular regulatory response mak ...
... the genome. For example, genes for siderophore synthesis and genes for siderophore-Fe transport constitute a regulon. • Explain the ways the expression of environmentally-regulated genes is regulated at the level of transcription initiation in prokaryotes and why a particular regulatory response mak ...
Evolution of chloroplast genomes in gymnosperms and insights into
... Chloroplasts where photosynthesis takes place have distinct functional genomes from those of mitochondria and nucleus. The chloroplast genomes (cpDNAs) were derived from cyanobacteria via endosymbiosis. Modern cpDNAs contain only about 5-10% as many genes as those of their free-living cousins, becau ...
... Chloroplasts where photosynthesis takes place have distinct functional genomes from those of mitochondria and nucleus. The chloroplast genomes (cpDNAs) were derived from cyanobacteria via endosymbiosis. Modern cpDNAs contain only about 5-10% as many genes as those of their free-living cousins, becau ...
FREE Sample Here
... Mendel focused on the overall appearance of the plant rather than on individual traits. Mendel focused on individual traits of the plant rather than on the overall appearance. Mendel chose to study complex traits that result from interactions between multiple genes. Mendel used an organism that grew ...
... Mendel focused on the overall appearance of the plant rather than on individual traits. Mendel focused on individual traits of the plant rather than on the overall appearance. Mendel chose to study complex traits that result from interactions between multiple genes. Mendel used an organism that grew ...
86K(a)
... C. Messelson & Stahl D. Nierenberg E. Jacob & Monod 35. A certain kind of restriction endonuclease can recognize 6 base pairs, it will cut a DNA strand like this: 5’-AGCTG AATTC-3’(one strand only), what kind of end will be made? A. 5’ sticky end B. 3’ sticky end C. both 5’ and 3’ sticky end D. eith ...
... C. Messelson & Stahl D. Nierenberg E. Jacob & Monod 35. A certain kind of restriction endonuclease can recognize 6 base pairs, it will cut a DNA strand like this: 5’-AGCTG AATTC-3’(one strand only), what kind of end will be made? A. 5’ sticky end B. 3’ sticky end C. both 5’ and 3’ sticky end D. eith ...
Genetics
... Punnett Square: Cross heterozygous tall with homozygous recessive. Give phenotypic and genotypic ratios. ...
... Punnett Square: Cross heterozygous tall with homozygous recessive. Give phenotypic and genotypic ratios. ...
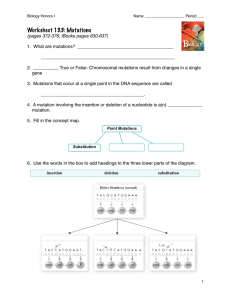
Worksheet 13.3
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
Lecture 27
... convert a primary transcript into a final function RNA product •Eukaryotic pre-mRNAs are capped, polyadenylated, and spliced to yield one or more mature mRNAs before transport to the cytoplasm. These processes are coupled in the nucleus so that only properly processed mRNAs are exported to the cytop ...
... convert a primary transcript into a final function RNA product •Eukaryotic pre-mRNAs are capped, polyadenylated, and spliced to yield one or more mature mRNAs before transport to the cytoplasm. These processes are coupled in the nucleus so that only properly processed mRNAs are exported to the cytop ...
Gene Regulation and Pathological Studies Using Mouse models
... Just upstream from the transcription start point in the lac operon are two regions called the operator (o) and the promoter (p). Operator is the DNA sequence that repressor binds. The promoter is the site where RNA polymerase binds and starts transcription. Operator and promoter are “cis” or associa ...
... Just upstream from the transcription start point in the lac operon are two regions called the operator (o) and the promoter (p). Operator is the DNA sequence that repressor binds. The promoter is the site where RNA polymerase binds and starts transcription. Operator and promoter are “cis” or associa ...
File
... • The process of nuclear division that reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell by half • In humans, the parent cell of the gametes has 46 chromosomes (diploid number). This cell divides by Meiosis to produce four halpoid cells with 23 chromosomes. ...
... • The process of nuclear division that reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell by half • In humans, the parent cell of the gametes has 46 chromosomes (diploid number). This cell divides by Meiosis to produce four halpoid cells with 23 chromosomes. ...
Document
... Genetics Quiz Study Guide Genetics – the study of heredity Heredity – the passing of traits from parent to offspring ...
... Genetics Quiz Study Guide Genetics – the study of heredity Heredity – the passing of traits from parent to offspring ...
Basics of Molecular Biology
... Although each amino acid is different and has unique properties, certain pairs have more similar properties than others. The two nonpolar amino acids leucine and isoleucine, for example, are far more similar to each other in their chemical and physical properties than either is to the charged glutam ...
... Although each amino acid is different and has unique properties, certain pairs have more similar properties than others. The two nonpolar amino acids leucine and isoleucine, for example, are far more similar to each other in their chemical and physical properties than either is to the charged glutam ...
L04_Public_Resources_Luke_Durban_2015
... variation within and across human populations - ~2M single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) genotyped in ~1000 individuals from 11 populations ...
... variation within and across human populations - ~2M single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) genotyped in ~1000 individuals from 11 populations ...
homologous recombination
... this information, it is possible to replace any gene with a DNA construct of your choosing. ...
... this information, it is possible to replace any gene with a DNA construct of your choosing. ...
Unit 5 Review
... 15. Where is RNA found in a cell? 16. What is the sugar found in RNA? 17. Draw a picture of the monomer of RNA, called a In your picture label the following parts: ribose sugar, base, and phosphate group. group ...
... 15. Where is RNA found in a cell? 16. What is the sugar found in RNA? 17. Draw a picture of the monomer of RNA, called a In your picture label the following parts: ribose sugar, base, and phosphate group. group ...
What is Biology? The word biology is 1………………………. from the
... meaning /study/ and is referred to as the science of life or living matter in all its forms and phenomena, 2………………………. with reference to origin, growth, reproduction, structure, and behaviour. An organism is a living entity 3………………………. one cell e.g. bacteria, or several cells e.g. animals, plants an ...
... meaning /study/ and is referred to as the science of life or living matter in all its forms and phenomena, 2………………………. with reference to origin, growth, reproduction, structure, and behaviour. An organism is a living entity 3………………………. one cell e.g. bacteria, or several cells e.g. animals, plants an ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.