Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... physical conspicuity of objects in the receptive field. An LIP neuron responds strongly when a visual stimulus is flashed in its receptive field (left). The same neuron does not respond if the physically identical stimulus is stable in the world and enters the receptive field by virtue of the monkey ...
... physical conspicuity of objects in the receptive field. An LIP neuron responds strongly when a visual stimulus is flashed in its receptive field (left). The same neuron does not respond if the physically identical stimulus is stable in the world and enters the receptive field by virtue of the monkey ...
Are We Paying Attention Yet?
... Attention and eye movements are tightly related During saccade preparation, oculomotor system controls location selection even if attention is directed elsewhere Direction of attention is dissociable from eye position during fixations Findings are do not rule out interdependence or identity hypothes ...
... Attention and eye movements are tightly related During saccade preparation, oculomotor system controls location selection even if attention is directed elsewhere Direction of attention is dissociable from eye position during fixations Findings are do not rule out interdependence or identity hypothes ...
Slide 1
... Responses in excitatory and inhibitory networks of firing-rate neurons. A. Response of a purely excitatory recurrent network to a square step of input (hE). The blue curve is the response without excitatory feedback. Adding recurrent excitation increases the response but makes it rise and fall more ...
... Responses in excitatory and inhibitory networks of firing-rate neurons. A. Response of a purely excitatory recurrent network to a square step of input (hE). The blue curve is the response without excitatory feedback. Adding recurrent excitation increases the response but makes it rise and fall more ...
How is the stimulus represented in the nervous system?
... cortex show different patterns of response depending on sound source direction. ...
... cortex show different patterns of response depending on sound source direction. ...
Background Presentation
... • Enhanced visual response when the stimulus appears in the cell’s receptive field AND the monkey selects it as a target and saccades (overtly attends) to it. Latency of saccade is ...
... • Enhanced visual response when the stimulus appears in the cell’s receptive field AND the monkey selects it as a target and saccades (overtly attends) to it. Latency of saccade is ...
Neural Basis of the Ventriloquist
... Contralateral activation same for illusion trials as for when sound actually came from the illusory location Response found in Planum Temporale What is the Planum Temporale? ...
... Contralateral activation same for illusion trials as for when sound actually came from the illusory location Response found in Planum Temporale What is the Planum Temporale? ...
3.5. Responses to Stimuli – Definitions. Term Definition Tropism
... To give the body the ability to fight infections by the production of antibodies by exposure to infection[by vaccines or by illness] “safe dose” of a pathogen/causing antibody production OR causing an immune response This introduces antigens causing the body to produce corresponding antibodies to ga ...
... To give the body the ability to fight infections by the production of antibodies by exposure to infection[by vaccines or by illness] “safe dose” of a pathogen/causing antibody production OR causing an immune response This introduces antigens causing the body to produce corresponding antibodies to ga ...
PowerPoint - Developmental Disabilities Council
... • Traumatized people respond to their trauma history in the present. They are not able to discern that the context has changed ...
... • Traumatized people respond to their trauma history in the present. They are not able to discern that the context has changed ...
Communication Workbook
... which can secrete chemicals to mark territories. The recipient must have suitable sensory structures to detect the signal. A dog giving a warning by baring its teeth is not useful if the receiver has no eyes. Sensory structures that can detect changes in the environment are called receptors. Effecti ...
... which can secrete chemicals to mark territories. The recipient must have suitable sensory structures to detect the signal. A dog giving a warning by baring its teeth is not useful if the receiver has no eyes. Sensory structures that can detect changes in the environment are called receptors. Effecti ...
SC1l Terminology CLEAN
... A target material used to motivate and assess a canine’s performance during extended operations A conditioning technique in which the subject learns to escape an unpleasant stimulus by performing a desired response. A response identified by the handler that something is true or present when it is no ...
... A target material used to motivate and assess a canine’s performance during extended operations A conditioning technique in which the subject learns to escape an unpleasant stimulus by performing a desired response. A response identified by the handler that something is true or present when it is no ...
Study Questions
... session when the response–reward contingencies reversed. Rats with inactivated action systems learned more slowly to make this adjustment. Rats with inactivated habit systems learned faster. 16. What is the evidence that the DMS and DLS actually store memories needed to support habits and actions? I ...
... session when the response–reward contingencies reversed. Rats with inactivated action systems learned more slowly to make this adjustment. Rats with inactivated habit systems learned faster. 16. What is the evidence that the DMS and DLS actually store memories needed to support habits and actions? I ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 46.1 Lateral viewof a human brain
... elsewhere in the visual field. (B) When the subject directed attention to a peripheral target location and performed an object discrimination task, a distributed frontoparietal network was activated, including the SEF, the FEF, and the SPL. (C) The same network of frontal and parietal areas was acti ...
... elsewhere in the visual field. (B) When the subject directed attention to a peripheral target location and performed an object discrimination task, a distributed frontoparietal network was activated, including the SEF, the FEF, and the SPL. (C) The same network of frontal and parietal areas was acti ...
SC1l Terminology TRACK CHANGES
... A target material used to motivate and assess a canine’s performance during extended operations A conditioning technique in which the subject learns to escape or terminate an unpleasant stimulus by performing a desired response. A response identified by the handler indicating that something is true ...
... A target material used to motivate and assess a canine’s performance during extended operations A conditioning technique in which the subject learns to escape or terminate an unpleasant stimulus by performing a desired response. A response identified by the handler indicating that something is true ...
Now you see it: frontal eye field responses to invisible targets
... reported that the target was not visible. Instead, rather surprisingly, almost all FEF neurons responded strongly to the flashed target regardless of the monkey’s subsequent report. This result raises several interesting issues. First, it constrains the possible neuronal mechanisms underlying backwa ...
... reported that the target was not visible. Instead, rather surprisingly, almost all FEF neurons responded strongly to the flashed target regardless of the monkey’s subsequent report. This result raises several interesting issues. First, it constrains the possible neuronal mechanisms underlying backwa ...
IA_CogCore
... neurons in V1/V2 as well as V4 modulate their responses in concert with Monkey’s percept, as if participating in a massively distributed constraint-satisfaction process. However, some neurons in all areas do not modulate their responses. Thus the conscious percept appears to be correlated with the a ...
... neurons in V1/V2 as well as V4 modulate their responses in concert with Monkey’s percept, as if participating in a massively distributed constraint-satisfaction process. However, some neurons in all areas do not modulate their responses. Thus the conscious percept appears to be correlated with the a ...
PSY105 Neural Networks 2/5
... Hebb Rule governs changes in weights [+ other additional assumptions which are always needed when you try and make a computational recipe] • Mechanism: At least one response neuron, one unconditioned stimulus neuron and one neuron for each conditioned stimulus ...
... Hebb Rule governs changes in weights [+ other additional assumptions which are always needed when you try and make a computational recipe] • Mechanism: At least one response neuron, one unconditioned stimulus neuron and one neuron for each conditioned stimulus ...
HW CH 5 PSY 2513 Submit your answers on canvas
... the areas of the brain are strongly committed to specific functions, and there is a high capacity for learning. b. if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than language skills and are easier to recover afte ...
... the areas of the brain are strongly committed to specific functions, and there is a high capacity for learning. b. if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than language skills and are easier to recover afte ...
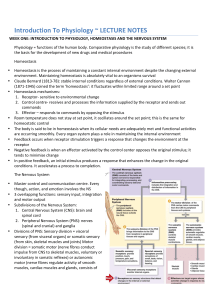
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
... Room temperature does not stay at set point, it oscillates around the set point; this is the same for homeostatic control The body is said to be in homeostasis when its cellular needs are adequate ...
... Room temperature does not stay at set point, it oscillates around the set point; this is the same for homeostatic control The body is said to be in homeostasis when its cellular needs are adequate ...
2) Classical Conditioning
... 2. Neutral Stimulus (NS) ---> does not elicit the response of interest: this stimulus is a neutral stimulus since it does not elicit the Unconditioned (or reflexive) Response. 3. The Neutral Stimulus (NS) is repeatedly paired with the Unconditioned (Natural) Stimulus (US). 4. The NS is transformed i ...
... 2. Neutral Stimulus (NS) ---> does not elicit the response of interest: this stimulus is a neutral stimulus since it does not elicit the Unconditioned (or reflexive) Response. 3. The Neutral Stimulus (NS) is repeatedly paired with the Unconditioned (Natural) Stimulus (US). 4. The NS is transformed i ...
Nervous and Endocrine System
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
Grasping the Ungraspable: How do motor actions and motor metaphors interact?
... Abstract: The discovery of mirror neurons has established that the same neuronal populations are active during action execution, and during action observation (Gallese et al., 1996). The neural areas active while observing an action (e.g., kicking) are also active during the processing of concrete a ...
... Abstract: The discovery of mirror neurons has established that the same neuronal populations are active during action execution, and during action observation (Gallese et al., 1996). The neural areas active while observing an action (e.g., kicking) are also active during the processing of concrete a ...
Nervous and Endocrine System
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
Response priming

In the psychology of perception and motor control, the term response priming denotes a special form of priming. Generally, priming effects take place whenever a response to a target stimulus is influenced by a prime stimulus presented at an earlier time. The distinctive feature of response priming is that prime and target are presented in quick succession (typically, less than 100 milliseconds apart) and are coupled to identical or alternative motor responses. When a speeded motor response is performed to classify the target stimulus, a prime immediately preceding the target can thus induce response conflicts when assigned to a different response as the target. These response conflicts have observable effects on motor behavior, leading to priming effects, e.g., in response times and error rates. A special property of response priming is its independence from visual awareness of the prime.