Derivatives Trading and Its Impact on the Volatility of NSE, India
... some pre-existing risk by taking positions in derivatives markets that offset potential losses in the underlying or spot market. In India, most derivatives users describe themselves as hedgers and Indian laws generally require that derivatives be used for hedging purposes only. Another motive for de ...
... some pre-existing risk by taking positions in derivatives markets that offset potential losses in the underlying or spot market. In India, most derivatives users describe themselves as hedgers and Indian laws generally require that derivatives be used for hedging purposes only. Another motive for de ...
Division 2 - Customer`s Moneys
... authorised to conduct banking business in the country or territory where the account is maintained. Notification and acknowledgment from specified financial institutions 18. Where the holder of a capital markets services licence opens a trust account with a financial institution specified in regula ...
... authorised to conduct banking business in the country or territory where the account is maintained. Notification and acknowledgment from specified financial institutions 18. Where the holder of a capital markets services licence opens a trust account with a financial institution specified in regula ...
PDF
... Insurance and financial markets offer individual and index-based contracts to producers who want to manage their risks. For example, farmers can choose forward contracts and/or futures contracts to deal with commodity price risk. They can also cover crop yield shortfalls using individual yield insur ...
... Insurance and financial markets offer individual and index-based contracts to producers who want to manage their risks. For example, farmers can choose forward contracts and/or futures contracts to deal with commodity price risk. They can also cover crop yield shortfalls using individual yield insur ...
How Do Canadian Banks That Deal in Foreign Exchange Hedge
... identity, as would be necessary in an interdealer trade. Brokers are pure matchmakers; they do not take positions on their own. Participation in the futures market is largely limited to institutions and large corporate customers. The futures market is a close substitute for the forward market, altho ...
... identity, as would be necessary in an interdealer trade. Brokers are pure matchmakers; they do not take positions on their own. Participation in the futures market is largely limited to institutions and large corporate customers. The futures market is a close substitute for the forward market, altho ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES WHAT DOES FUTURES
... We find qualitatively similar, but statistically weaker, evidence for predictability of returns in currency, bond, and stock markets. We find that rising currency market interest, which signals higher US economic activity and rising inflation expectations, predicts appreciation of a portfolio of forei ...
... We find qualitatively similar, but statistically weaker, evidence for predictability of returns in currency, bond, and stock markets. We find that rising currency market interest, which signals higher US economic activity and rising inflation expectations, predicts appreciation of a portfolio of forei ...
2015-51 - National Association of Insurance Commissioners
... 86, unrealized gains and losses, foreign currency premiums, etc.) With regards to futures, although the term “notional” is a reported element in Schedule DB-Part B, it has been communicated to staff that it is not a standard industry term for these types of contracts. In reviewing contract specifica ...
... 86, unrealized gains and losses, foreign currency premiums, etc.) With regards to futures, although the term “notional” is a reported element in Schedule DB-Part B, it has been communicated to staff that it is not a standard industry term for these types of contracts. In reviewing contract specifica ...
put
... Sometimes called futures options, give the holder the right to buy or sell a specified futures contract on or before a given date enter into a long side of a futures contract at a given futures price. Assume that you hold a call option on a bond future @ 98 % of the face value and at the expiration ...
... Sometimes called futures options, give the holder the right to buy or sell a specified futures contract on or before a given date enter into a long side of a futures contract at a given futures price. Assume that you hold a call option on a bond future @ 98 % of the face value and at the expiration ...
Installment options and static hedging
... C 0 = C(t1 , T, S(t1 ), K 0 ), C = C(t1 , T, S(t1 ), K). The maximum loss is p0 − p0 , which is 17.72% of the Black-Scholes premium for the underlying option, and the maximum gain is 20.3% of this premium, realized when the price is on the continuation boundary. Figure 4 shows the distribution of P ...
... C 0 = C(t1 , T, S(t1 ), K 0 ), C = C(t1 , T, S(t1 ), K). The maximum loss is p0 − p0 , which is 17.72% of the Black-Scholes premium for the underlying option, and the maximum gain is 20.3% of this premium, realized when the price is on the continuation boundary. Figure 4 shows the distribution of P ...
Day 1: Foundations of Energy Trading & Risk Management
... Derivatives A derivative is a financial instrument whose value is based upon the underlying physical product/commodity ...
... Derivatives A derivative is a financial instrument whose value is based upon the underlying physical product/commodity ...
note on weighted average strike asian options
... of unexpected situation incurred. In particular, we focus on strike Asian option with weighted average of asset prices. Keywords: Strike options, Weighted average Asian options, ...
... of unexpected situation incurred. In particular, we focus on strike Asian option with weighted average of asset prices. Keywords: Strike options, Weighted average Asian options, ...
The information content of an open limit-order book
... order-book shape for short-term price dynamics, even in the absence of asymmetric information. The shape of the order book (i.e., the number of shares on each price step and how far away price steps are from each other) gives investors a concurrent picture of the market demand and supply. Specifical ...
... order-book shape for short-term price dynamics, even in the absence of asymmetric information. The shape of the order book (i.e., the number of shares on each price step and how far away price steps are from each other) gives investors a concurrent picture of the market demand and supply. Specifical ...
Incomplete-Market Prices for Real Estate
... to exactly replicate a claim on such an asset, so we can expect to be confronted with several price systems for this claim, all of them consistent with the absence of arbitrage. In fact, if we just impose absence of arbitrage, the price will be situated within the arbitrage bounds. For a call option ...
... to exactly replicate a claim on such an asset, so we can expect to be confronted with several price systems for this claim, all of them consistent with the absence of arbitrage. In fact, if we just impose absence of arbitrage, the price will be situated within the arbitrage bounds. For a call option ...
OPTIONS, GREEKS, AND RISK MANAGEMENT Jelena Paunović *
... Options are financial derivatives representing a contract which gives the right to the holder, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a pre-defined strike price during a certain period of time. These derivative contracts can derive their value from almost any underlying asset ...
... Options are financial derivatives representing a contract which gives the right to the holder, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a pre-defined strike price during a certain period of time. These derivative contracts can derive their value from almost any underlying asset ...
La Cassa Controparte Centrale dei Mercati Cash Azionari US
... Method for calculating Initial Margins for shares .........................................................................4 a) Basic Principles ..................................................................................................................... 4 b) Types of Initial Margins ....... ...
... Method for calculating Initial Margins for shares .........................................................................4 a) Basic Principles ..................................................................................................................... 4 b) Types of Initial Margins ....... ...
chapter 2: the structure of options markets
... Full file at http://testbankwizard.eu/Test-Bank-for-Introduction-to-Derivatives-and-Risk-Management-9th-Editionby-Chance a. an option series ...
... Full file at http://testbankwizard.eu/Test-Bank-for-Introduction-to-Derivatives-and-Risk-Management-9th-Editionby-Chance a. an option series ...
Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives in Russia: An Overview
... virtually resurged in 2000, as old and new exchanges opened their floors to derivatives trading, following similarly regenerative developments on other financial markets. The relatively slow re-institution and growth of derivatives markets compared to spot markets has been attributed partly to the i ...
... virtually resurged in 2000, as old and new exchanges opened their floors to derivatives trading, following similarly regenerative developments on other financial markets. The relatively slow re-institution and growth of derivatives markets compared to spot markets has been attributed partly to the i ...
Derivatives Digest
... I was in an early morning flight, well settled in a window seat and looking forward to spending my time in air admiring the rising sun. But as it happened a nice rotund gentleman in a crisp white shirt and carefully creased black trousers came and occupied the seat next to mine. After he had settled ...
... I was in an early morning flight, well settled in a window seat and looking forward to spending my time in air admiring the rising sun. But as it happened a nice rotund gentleman in a crisp white shirt and carefully creased black trousers came and occupied the seat next to mine. After he had settled ...
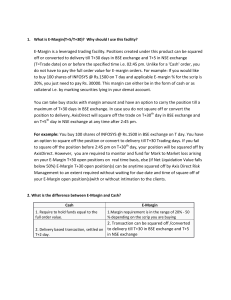
E-Margin is a leveraged trading facility. Positions
... positions together with any other open positions and trades (Equity, F&O etc.). AxisDirect runs this process at various time intervals during the trading day. If the available limit in the trading account is not sufficient any time to bring the available margin to the required margin level, then suc ...
... positions together with any other open positions and trades (Equity, F&O etc.). AxisDirect runs this process at various time intervals during the trading day. If the available limit in the trading account is not sufficient any time to bring the available margin to the required margin level, then suc ...
Day Effects in Korean Stock Market
... , where F, S, r, and d represent the index futures price, index cash price, riskless (risk free) interest rate, and dividend yield of the stock index over the remaining maturity. If this equality does not hold by some reason, arbitrageurs buy and sell the component of index and exploit the price dif ...
... , where F, S, r, and d represent the index futures price, index cash price, riskless (risk free) interest rate, and dividend yield of the stock index over the remaining maturity. If this equality does not hold by some reason, arbitrageurs buy and sell the component of index and exploit the price dif ...
Chapter 20
... – Exchange traded long dated contracts issued by a financial institution to holders who can then trade them (called ‘warrants’ in Australia) – Over-the-counter options on company shares (called ‘company options’ in Australia, but ‘warrants’ on international markets) – Convertible notes issued by com ...
... – Exchange traded long dated contracts issued by a financial institution to holders who can then trade them (called ‘warrants’ in Australia) – Over-the-counter options on company shares (called ‘company options’ in Australia, but ‘warrants’ on international markets) – Convertible notes issued by com ...
Options for Enhancing Risk-Adjusted Returns Covered Call
... types, calls and puts, with expiration dates up to three years in the future. Margin requirement (for options): The amount an uncovered (naked) option writer is required to deposit and maintain to cover a position. The margin requirement is calculated daily. Open interest: The number of outstanding ...
... types, calls and puts, with expiration dates up to three years in the future. Margin requirement (for options): The amount an uncovered (naked) option writer is required to deposit and maintain to cover a position. The margin requirement is calculated daily. Open interest: The number of outstanding ...
The New Risk Management: The Good, the Bad
... value to copper prices varies in response to the interim information, and this changing sensitivity should be reflected in our trades. In the current example, we assume that the firm is using copper futures contracts to hedge changes in copper prices. Futures serve the same economic purpose as forwa ...
... value to copper prices varies in response to the interim information, and this changing sensitivity should be reflected in our trades. In the current example, we assume that the firm is using copper futures contracts to hedge changes in copper prices. Futures serve the same economic purpose as forwa ...
Modeling Asset Prices in Continuous Time
... - N(-d1) = [N (d 1) – 1] • The delta of a European call on a stock paying dividends at rate q is N (d 1)e – q(T-t) • The delta of a European put is e – q(T-t) [N (d 1) – 1] ...
... - N(-d1) = [N (d 1) – 1] • The delta of a European call on a stock paying dividends at rate q is N (d 1)e – q(T-t) • The delta of a European put is e – q(T-t) [N (d 1) – 1] ...
Risk Management Strategies
... shown time and again to be willing to trade less profit for a reduction in the risk they face. The more farmers learn about probability and the arsenal of risk management tools available to them, the better armed they will be in the battle to manage risk. Moreover, learning about how to combine risk ...
... shown time and again to be willing to trade less profit for a reduction in the risk they face. The more farmers learn about probability and the arsenal of risk management tools available to them, the better armed they will be in the battle to manage risk. Moreover, learning about how to combine risk ...
Causes and Consequences of Margin Levels in Futures Markets
... the lack of readily available data on historical margins. Gay et al. (1986) and Fishe et al. (1990), who consider commodity futures, and Goldberg and Hachey (1992), who consider foreign exchange futures, find that margin levels are primarily determined by price volatility. Fenn and Kupiec (1993) find ...
... the lack of readily available data on historical margins. Gay et al. (1986) and Fishe et al. (1990), who consider commodity futures, and Goldberg and Hachey (1992), who consider foreign exchange futures, find that margin levels are primarily determined by price volatility. Fenn and Kupiec (1993) find ...