* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Options for Enhancing Risk-Adjusted Returns Covered Call
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
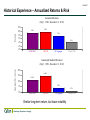
Exhibit 7 March 13, 2013 Options for Enhancing Risk-Adjusted Returns Covered Call Strategy Jim McKee Senior Vice President Hedge Fund Research John Jackson Senior Vice President Fund Sponsor Consulting Exhibit 7 Options for Enhancing Risk-Adjusted Returns Overview – Covered Call Strategy Purpose of Discussion Strategy Defined Pros & Cons Historical Experience Concluding Observations Appendix Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Covered Call Strategy - Purpose Purpose of discussion Target allocation to equity assumes equity-like return over long-term horizon Review alternative equity strategy to deliver equity return with less volatility – Complementary source of superior risk-adjusted return to equity exposure? Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Covered Call Strategy - Defined Covered call, or buywrite, strategy: Buy S&P 500 stock basket and sell, or write, call options* whose notional exposure represents value of stock position Call option premium is kept by seller, but future upside return, if any, above the “strike price” is earned by buyer Option premium cushions downside moves in an equity portfolio, but subject to variability Buywrite strategies outperform stocks in neutral or bear markets, but underperform stocks in bull markets * A call option is the right (but not obligation) to buy a specific amount of an index or security at a specific price within a specific time period. Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Profit and Loss Expectations for CBOE S&P 500 BuyWrite Index Option Premium CBOE S&P 500 BuyWrite Index (BXM) – passive total return benchmark index designed to track performance of a hypothetical covered call strategy: – Purchase and hold an S&P 500 stock index portfolio – Sell (or write) 1-month, at-the-money S&P 500 call options that are systematically replaced in the following month with a new 1-month option Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Option Premium – Sources & Variability of Returns Sources of return embedded in at-the-money call option premium Time until expiration - the longer the time frame until expiration, the greater the chance that the option is profitable, thereby increasing the option value Implied volatility (vs. actual or realized volatility) – the more volatile the stock price, the more likely the option will be profitable over time, thereby increasing the option premium Interest rates - as interest rates rise, the call option’s value increases, since cash spent on owning the underlying index is opportunity (interest) lost, thus increasing the value of the option Dividends - as dividends increase, call or option value decreases, since the option seller (who owns the underlying security) collects the dividend, not the option buyer Variability of return in covered call premium Implied volatility is the primary driver in the short run Average BXM premium* – 1.8% per month * Source: www.cboe.com Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Covered Call Strategy - Implementation The BXM Index was introduced in 2002 Multiple products have been launched, both active and passive, to track the BXM Index Product Vehicle Fund Manager Fee Assets in Product Inception Date S&P 500 BuyWrite Portfolio ETF (PBP) Invesco 0.75% $230 million (est) December 1, 2007 iPath CBOE S&P 500 BuyWrite Index ETN (BWV) Barclays Bank 0.75% $ 11 million (est) May 22, 2007 Some investment management firms have offered separately managed accounts (SMA) designed to replicate the BXM Index – Traction in the institutional marketplace has been limited. Some of the larger players have $100-150 million within this strategy, but may also offer other option oriented strategies. – Fees for the SMAs are typically in the .20%-.40% range, thus more competitive than the ETFs. Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Pros & Cons of Covered Call Strategy Pros – – – – Expected equity-like return with less volatility Very transparent and liquid Exchange-traded instruments – no counterparty risk Income component of the option viewed as an attractive feature for some clients Cons – – – – Significant upside participation may be lost, while involving cash flow management Downside protection is relative, not absolute High tracking error that invites criticism at most difficult time Strategy often abandoned after its most difficult time (e.g., ‘96-’00; ‘03-’07) Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Historical Experience – Cumulative Growth of a Dollar Growth of a Dollar (July 1, 1988 - December 31, 2012) $8.99 - S&P:500 $8.71 - CBOE Buy Write Idx $9 Growth of a Dollar $8 $7 $6 $5.46 - BC Aggregate $5 $4 $3 $2.50 - 3 Month T-Bill $2 $1 8889 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 After almost 25 years, S&P 500 and BXM have similar cumulative returns Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Historical Experience – Annualized Returns & Risk Returns Annualized Returns (July 1, 1988 - December 31, 2012) 12% 10% 8% 6% 4% 2% 0% 9.24% 9.38% 7.18% 3.81% CBOE BXM S&P 500 BC Aggregate 3 Month T-Bill Standard Deviation Annualized Standard Deviation (July 1, 1988 - December 31, 2012) 20% 14.86% 15% 10.56% 10% 3.78% 5% 0.71% 0% CBOE BXM S&P 500 BC Aggregate Similar long-term return, but lower volatility Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. 3 Month T-Bill Exhibit 7 Historical Experience – Annualized Returns & Risk Returns Annualized Returns vs. Standard Deviation for 24 1/2 Years Ended December 31, 2012 12% 10% 8% 6% 4% 2% 0% 0% Callan Large Cap Core Style CBOE Buy Write Idx S&P 500 BC Aggregate 3 Month T-Bill 3% 5% 8% 10% 13% 15% 18% 20% 23% Standard Deviation Performance Statistics vs. S&P 500 for 24 1/2 Years ended December 31, 2012 S&P 500 CBOE Buy Write Idx Callan Large Cap Core Style BC Aggregate 3 Month T-Bill Returns 9.38 9.24 10.46 7.18 3.81 Standard Deviation 16.12 11.71 16.34 4.07 1.23 Sharpe Ratio 0.35 0.46 0.40 0.83 0.00 Tracking Error 0.00 7.48 3.96 17.80 16.53 Downside Risk (vs. T-Bills) 10.57 7.99 10.53 1.85 0.00 Lower volatility, but significant peer group deviation Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Historical Experience – Returns based on Rolling 5-Year Periods Annualized Returns based on Rolling 5 Year Periods From July 1, 1993 - December 31, 2012 30% 25% 20% Returns 15% 10% CBOE Buy Write Idx 5% S&P:500 0% -5% -10% 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 Five-year stretches of notable overperformance - and underperformance Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Historical Experience – Risk based on Rolling 5-Year Periods Standard Deviation based on Rolling 5 Year Periods From July 1, 1993 - December 31, 2012 20% CBOE Buy Write Idx Standard Deviation S&P:500 15% 10% 5% 0% 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 Consistently less volatile, given less upside and downside participation Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Historical Experience – Calendar Year Returns Returns Calendar Year Returns 40% 35% 30% 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% 0% -5% -10% -15% -20% -25% -30% -35% -40% 37.6 33.4 31.7 30.5 26.6 25.0 24.4 21.0 28.7 28.6 26.026.5 23.0 21.221.0 19.4 18.9 14.1 11.5 10.9 8.3 10.1 7.6 4.0 15.8 13.3 15.5 7.4 4.2 4.9 4.5 16.0 15.1 6.6 5.5 5.9 5.7 5.2 2.1 1.3 -3.1 -9.1 -7.6 -10.9 -11.9 CBOE Buy Write Idx S&P:500 -22.1 -28.7 -37.0 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 Worst year: -16.6% underperformance (1995) Best year: +16.5% outperformance (2000) Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Historical Experience – Returns in Rising/Declining Equity Markets Annualized Returns for Domestic Equity Rising/Declining g Periods 49.8 50% 40% 31.1 29.2 30% 30.7 30.7 26.2 23.1 21.2 20% 16.3 19.5 18.6 17.4 18.5 11.2 11.0 11.0 Returns 17.4 16.0 10% 0% (10%) (20%) -2.5 -3.4 -8.8 -9.9 -9.3 S&P:500 -10.3-11.4 -11.7 -13.7 CBOE Buy Write Idx (30%) -8.0 -11.1 -13.9 -20.3 -20.6 -24.8 -33.5 (40%) R: 7/1/88 D: 7/1/90 R: D: 1/1/94 R: 7/1/94 D: 7/1/98 R: D: 4/1/00 R: D: 4/1/02 R: 4/1/03 D: R: 4/1/09 D: 4/1/10 R: 7/1/10 D: 7/1/11 R: 10/1/11 to 6/30/90 to 9/30/90 10/1/90 to to 6/30/94 to 6/30/98 to 9/30/98 10/1/98 to to 9/30/01 10/1/01 to to 3/31/03 to 9/30/07 10/1/07 to to 3/31/10 to 6/30/10 to 6/30/11 to 9/30/11 to 12/31/93 3/31/00 3/31/02 3/31/09 12/31/12 “Decision risk” greatest in the wake of rising markets BXM trails S&P 500 quarterly return almost half (47%) of the time from 1988 to 2012 Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Historical Experience – Returns in Rising/Declining Equity Markets Annualized Returns for Domestic Equity Rising/Declining Periods Group: CAI Large Cap Core Style 50% B (35) 40% 30% A (54) B (69) B (30) A (59) 20% Returns B (57) A (85) B (38) A (98) (988)) A (98) A (30) B (45) A (5) B (56) (10%) (20%) A (9) B (46) A (6) B (51) A (95) A (99) B (68) A (97) B (36) A (36) 10% 0% B (70) A (10) B (34) A (1) A (4) B (23) A (1) B (58) B (39) (30%) B (75) (40%) R: D: R: D: R: D: R: D: R: D: R: D: R: D: R: D: R: 7/1/88 7/1/90 10/1/90 1/1/94 7/1/94 7/1/98 10/1/98 4/1/00 10/1/01 4/1/02 4/1/03 10/1/07 4/1/09 4/1/10 7/1/10 7/1/11 10/1/11 to to to to to to to to to to to to to to to to to 6/30/90 9/30/90 12/31/93 6/30/94 6/30/98 9/30/98 3/31/00 9/30/01 3/31/02 3/31/03 9/30/07 3/31/09 3/31/10 6/30/10 6/30/11 9/30/11 12/31/12 CBOE Buy Write Idx S&P:500 A B 16.31 -8.76 18.57 -2.51 21.21 -8.01 26.17 -9.26 10.98 -11.67 11.17 -20.30 30.71 -10.26 19.52 -11.12 17.38 18.50 -13.74 17.40 -3.39 29.18 -9.95 31.15 -20.61 10.99 -24.76 16.04 -33.53 49.77 -11.43 30.69 -13.87 23.13 Challenge of covered call program is investor’s conviction or willingness to be different from other active managers 46% of BXM’s quarterly returns are below that of median core equity manager Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Covered Call Strategy – Concluding Observations Recap Target allocation to equity assumes equity-like return over long-term horizon Covered call strategy – alternative to deliver equity return with less volatility – Substitute for active or passive management in large cap equity Appeal – Attractive risk-adjusted return properties – Very transparent and liquid, with exchange-traded instruments and no counterparty risk – Income component of the option viewed as an attractive feature for some clients Concerns – Significant upside participation may be lost, while downside protection is relatively limited – High tracking error that invites criticism at most difficult time, leaving strategy vulnerable to abandonment after its most difficult time (e.g., fast-rising bull markets) Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Appendix Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Glossary of Options Terms At-the-money: An option is at-the-money if the strike price of the option is equal to the market price of the underlying security. Call: An option that gives the holder the right to buy an underlying instrument, such as a stock or an index value, at a specified price for a certain, fixed period of time. Covered call option writing: A strategy in which one sells call options while simultaneously owning an equivalent position in the underlying security. Derivative security: A financial security whose value is determined in part from the value and characteristics of another security, the underlying security. Exercise: To invoke the right under which the holder of an option is entitled to buy (in the case of a call) or sell (in the case of a put) the underlying security. Exercise price (See Strike price): Exercise settlement amount. The difference between the exercise price of the option and the exercise settlement value of the index on the day an exercise notice is tendered, multiplied by the index multiplier. Expiration date: Date on which an option and the right to exercise it, cease to exist. In-the-money: A call option is in-the-money if the strike price is less than the market price of the underlying security. A put option is in-the-money if the strike price is greater than the market price of the underlying security. Intrinsic value: The amount by which an option is in-the-money (see above definition). LEAPS®: Long-term Equity Anticipation Securities, or LEAPS®, are longterm stock or index options. LEAPS®, like all options, are available in two types, calls and puts, with expiration dates up to three years in the future. Margin requirement (for options): The amount an uncovered (naked) option writer is required to deposit and maintain to cover a position. The margin requirement is calculated daily. Open interest: The number of outstanding options or futures contracts in the exchange market or in a particular class or series. Refers to unliquidated purchases or sales. Option: The right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying instrument, such as a stock, a futures contract or an index value, at a specified price for a certain, fixed period of time. Out-of-the-money: A call option is out-of-the-money if the strike price is greater than the market price of the underlying security. A put option is outof-the-money if the strike price is less than the market price of the underlying security. Premium: The price of an option contract, determined in the competitive marketplace, which the buyer of the option pays to the option writer for the rights conveyed by the option contract. Put: An option contract that gives the holder the right to sell an underlying instrument, such as a stock or an index value, at a specified price for a certain, fixed period of time. Series: All option contracts of the same class that also have the same unit of trade, expiration date and strike price. Strike price: The stated price per share for which the underlying security may be purchased (in the case of a call) or sold (in the case of a put) by the option holder upon exercise of the option contract. Time value: The portion of the option premium that is attributable to the amount of time remaining until the expiration of the option contract. Time value is whatever value the option has in addition to its intrinsic value. Uncovered call writing: A short call option position in which the writer does not own an equivalent position in the underlying security represented by his option contracts. Uncovered put writing: A short put option position in which the writer does not have a corresponding short position in the underlying security or has not deposited, in a cash account, cash or cash equivalents equal to the exercise value of the put. Underlying security: The security subject to being purchased or sold upon exercise of the option contract. Volatility: A measure of the fluctuation in the market price of the underlying security. Mathematically, volatility is the annualized standard deviation of daily price movements. Writer: The seller of an option contract. * Source: www.cboe.com Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 PutWrite Strategy PutWrite strategy defined: Purchase a portfolio of Treasury bills and sell, or write, put options* whose notional value equals the Treasury bill portfolio’s market value Put option premium is kept by seller, but future downside return, if any, below the “strike price” is paid to the buyer from the Treasury bill portfolio Option premium cushions losses from negative returns in the equity index, but subject to variability PutWrite strategies outperform stocks in neutral or bear markets, but underperform stocks in bull markets Passive strategy represented by CBOE S&P 500 PutWrite Index (PUT) * A put option is the right (but not obligation) to sell a specific amount of an index or security at a specific price within a specific time period. Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7 Profit and Loss Expectations for CBOE S&P 500 PutWrite Index CBOE S&P 500 PutWrite Index (PUT) – passive total return benchmark index designed to track performance of a hypothetical put write strategy: – Purchase and hold a portfolio of Treasury bills – Sell (or write) 1-month, at-the-money S&P 500 put options that are systematically replaced in the following month with a new 1-month option. Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Jim McKee SVP, Director - Hedge Fund Research James C. McKee, Senior Vice President. Jim is Director of Callan's Hedge Fund Research Group. Jim specializes in hedge fund research addressing related issues of asset allocation, manager structure, manager search, and performance evaluation for Callan's institutional clients. Jim is a shareholder of the firm. Jim joined Callan Associates in 1989. Prior to his career at Callan Associates, Jim worked with the Pacific Stock Exchange (PSE) from 1982 to 1989. Until 1985, Jim worked on the PSE's options trading floor. Thereafter, as manager of the PSE's securities research department, he was responsible for developing and monitoring new stock, bond, and option listings. Jim earned a B.A. in Economics/Environmental Studies from Dartmouth College in 1982. He received his M.B.A. in Finance from Golden Gate University in 1987. His graduate studies focused particularly on publicly traded securities and capital markets. Knowledge. Experience. Integrity. Exhibit 7