Solutions
... Day 1: Closing price = $1.3126. You post a gain of ($1.3140 – $1.3126)(125,000) = $175. This is added to your account. Your current balance is $1,700 + $175 = $1,875. Day 2: Closing price = $1.3133. You post a loss of ($1.3126 – $1.3133)(125,000) = $87.50. This is deducted from your account. Your cu ...
... Day 1: Closing price = $1.3126. You post a gain of ($1.3140 – $1.3126)(125,000) = $175. This is added to your account. Your current balance is $1,700 + $175 = $1,875. Day 2: Closing price = $1.3133. You post a loss of ($1.3126 – $1.3133)(125,000) = $87.50. This is deducted from your account. Your cu ...
Derivatives: The Good, The Bad and … the Necessary?
... In response to heightened concern, governments worldwide are acting to rationalize markets, and to rein in risks. In the U.S., proposed legislation will address the credit risks posed by the nature of the bilateral agreement, as well as the risks posed to the financial system from fraud and mark ...
... In response to heightened concern, governments worldwide are acting to rationalize markets, and to rein in risks. In the U.S., proposed legislation will address the credit risks posed by the nature of the bilateral agreement, as well as the risks posed to the financial system from fraud and mark ...
Agricultural Futures for the Beginner
... are legally binding agreements, made through a futures exchange, to buy or sell commodities in the future.” “They are standardized in every way with the exception of price.” “They can protect individuals against dangerous price swings.” ...
... are legally binding agreements, made through a futures exchange, to buy or sell commodities in the future.” “They are standardized in every way with the exception of price.” “They can protect individuals against dangerous price swings.” ...
the structure of forward and futures markets
... the over-the-counter forward market is a highly regulated market forward contracts prevent the writer from assuming the credit risk of the buyer terms and conditions are tailored to the specific needs of the two parties involved transaction information between the two parties involved in the forward ...
... the over-the-counter forward market is a highly regulated market forward contracts prevent the writer from assuming the credit risk of the buyer terms and conditions are tailored to the specific needs of the two parties involved transaction information between the two parties involved in the forward ...
Hedging Interest Rate Risk
... maturity and the payoff is based on the average price of the underlying commodity over the life of the contract. Barrier options: The payoff is contingent on whether or not the underlying commodity has reached a predetermined price Compound Options: The underlying commodity is an option Digital O ...
... maturity and the payoff is based on the average price of the underlying commodity over the life of the contract. Barrier options: The payoff is contingent on whether or not the underlying commodity has reached a predetermined price Compound Options: The underlying commodity is an option Digital O ...
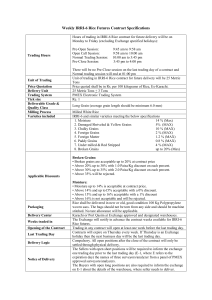
IRRI-6 Weekly
... Rice shall be delivered in new or old, good condition 100 Kg Polypropylene woven sacs. The bags should not be torn from any side and should be machine stitched. No tare allowance will be applicable. Karachi or Port Qasim at Exchange approved and designated warehouses. The Exchange will notify in adv ...
... Rice shall be delivered in new or old, good condition 100 Kg Polypropylene woven sacs. The bags should not be torn from any side and should be machine stitched. No tare allowance will be applicable. Karachi or Port Qasim at Exchange approved and designated warehouses. The Exchange will notify in adv ...
Chapter 259 South African Rand/US Dollar (ZAR/USD)
... Interpretations & Special Notices Section of Chapter 5. A Person seeking an exemption from position limits for bona fide commercial purposes shall apply to the Market Regulation Department on forms provided by the Exchange, and the Market Regulation Department may grant qualified exemptions in its s ...
... Interpretations & Special Notices Section of Chapter 5. A Person seeking an exemption from position limits for bona fide commercial purposes shall apply to the Market Regulation Department on forms provided by the Exchange, and the Market Regulation Department may grant qualified exemptions in its s ...
Mechanics of Futures Markets
... 2. Buy the underlying asset at the current spot price 3. Since the futures price is higher than the current spot price, making the deliver can earn the spread between them (As a result, the spot rate rises and the futures price declines, and the arbitrage opportunity disappears quickly) ...
... 2. Buy the underlying asset at the current spot price 3. Since the futures price is higher than the current spot price, making the deliver can earn the spread between them (As a result, the spot rate rises and the futures price declines, and the arbitrage opportunity disappears quickly) ...
(Platts) Crack Spread (1000mt) BALMO Futures
... SCOPE The provisions of these Rules shall apply to all futures contracts bought or sold on the Exchange for cash settlement based on the Floating Price. ...
... SCOPE The provisions of these Rules shall apply to all futures contracts bought or sold on the Exchange for cash settlement based on the Floating Price. ...
Introduction - the Center for Dairy Profitability
... percent of the value of the futures contract, but sometimes margins are as low as 1 percent of a futures contract’s value. There are really two separate margins involved in futures transactions. The first is called the initial margin. This is the amount of money a trader must have in a futures tradi ...
... percent of the value of the futures contract, but sometimes margins are as low as 1 percent of a futures contract’s value. There are really two separate margins involved in futures transactions. The first is called the initial margin. This is the amount of money a trader must have in a futures tradi ...
International Banking - Module A Part II
... • Futures: A version of exchange traded forward contracts. • Standardized contracts as far as the quantity (amounts) and delivery dates (period) of the contracts. • Conveys an agreement to buy a specific amount of commodity or financial instruments at a particular price on a stipulated future date • ...
... • Futures: A version of exchange traded forward contracts. • Standardized contracts as far as the quantity (amounts) and delivery dates (period) of the contracts. • Conveys an agreement to buy a specific amount of commodity or financial instruments at a particular price on a stipulated future date • ...
(Module A) – Part II
... • Futures: A version of exchange traded forward contracts. • Standardized contracts as far as the quantity (amounts) and delivery dates (period) of the contracts. • Conveys an agreement to buy a specific amount of commodity or financial instruments at a particular price on a stipulated future date • ...
... • Futures: A version of exchange traded forward contracts. • Standardized contracts as far as the quantity (amounts) and delivery dates (period) of the contracts. • Conveys an agreement to buy a specific amount of commodity or financial instruments at a particular price on a stipulated future date • ...
PART 5: RISK MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 15: Hedging Instruments
... Hedge funds represent a pooling of funds from wealthy investors and large institutional investors that use spot and derivative market instruments to reduce investment risk (by combining leverage and short-selling). Page 1 of 8 Copyright © 2004 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited ...
... Hedge funds represent a pooling of funds from wealthy investors and large institutional investors that use spot and derivative market instruments to reduce investment risk (by combining leverage and short-selling). Page 1 of 8 Copyright © 2004 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited ...
on futures contracts
... allows anonymous trading since no credit evaluation is needed. Without this feature you would not have liquid markets. ...
... allows anonymous trading since no credit evaluation is needed. Without this feature you would not have liquid markets. ...
Contd…
... on the trading floor of a futures exchange, to buy or sell a particular commodity or financial instrument at a predetermined price in the future. Futures contracts detail the quality and quantity of the underlying asset; they are standardized to facilitate trading on a futures exchange. Some futures ...
... on the trading floor of a futures exchange, to buy or sell a particular commodity or financial instrument at a predetermined price in the future. Futures contracts detail the quality and quantity of the underlying asset; they are standardized to facilitate trading on a futures exchange. Some futures ...
Chapter 15 PPP
... • Chicago Board of Trade (CBT) began in 1848 • More than a dozen U.S. commodities exchanges – Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) is largest – Chicago Board of Trade and New York Mercantile ...
... • Chicago Board of Trade (CBT) began in 1848 • More than a dozen U.S. commodities exchanges – Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) is largest – Chicago Board of Trade and New York Mercantile ...
on futures contracts
... • Initial Margin: funds that must be deposited in a margin account to provide capital to absorb losses • Marking to Market: each day the profits or losses are realized and reflected in the margin account. • Maintenance or variance margin: an established value below which a trader’s margin may not fa ...
... • Initial Margin: funds that must be deposited in a margin account to provide capital to absorb losses • Marking to Market: each day the profits or losses are realized and reflected in the margin account. • Maintenance or variance margin: an established value below which a trader’s margin may not fa ...
Risk Management
... barrels of July crude oil futures contracts. The crude oil futures price is $59.29/bbl. The options expire on 17 June, 2015. The strike price on the options is $62/bbl. The volatility of oil is 45 percent (annualized). The annualized continuously compounded two-month interest rate is 1.25 percent (a ...
... barrels of July crude oil futures contracts. The crude oil futures price is $59.29/bbl. The options expire on 17 June, 2015. The strike price on the options is $62/bbl. The volatility of oil is 45 percent (annualized). The annualized continuously compounded two-month interest rate is 1.25 percent (a ...
Problem Set 7 Solution
... indicated an expected rise in the next year, but that this was not reflected in the current index price. If you sold the index future short and bought the corresponding basket of stocks at spot you would end up with a certain profit in one year’s time when the prices MUST converge. This argument bre ...
... indicated an expected rise in the next year, but that this was not reflected in the current index price. If you sold the index future short and bought the corresponding basket of stocks at spot you would end up with a certain profit in one year’s time when the prices MUST converge. This argument bre ...
Chapter 371 NY Harbor ULSD vs. Low Sulphur Gasoil (1,000bbl
... are set forth in the Position Limit, Position Accountability and Reportable Level Table in the Interpretations & Special Notices Section of Chapter 5. A Person seeking an exemption from position limits for bona fide commercial purposes shall apply to the Market Regulation Department on forms provide ...
... are set forth in the Position Limit, Position Accountability and Reportable Level Table in the Interpretations & Special Notices Section of Chapter 5. A Person seeking an exemption from position limits for bona fide commercial purposes shall apply to the Market Regulation Department on forms provide ...
an investor`s guide to index futures
... sale of a particular asset at a specific future date. The price at which the asset would change hands in the future is agreed upon at the time of entering into the contract. The actual purchase or sale of the underlying involving payment of cash and delivery of the instrument does not take place unt ...
... sale of a particular asset at a specific future date. The price at which the asset would change hands in the future is agreed upon at the time of entering into the contract. The actual purchase or sale of the underlying involving payment of cash and delivery of the instrument does not take place unt ...
Mechanics of Futures Markets
... A clearing house member is required to maintain a margin with the clearing house (clearing margin). The main purpose of the margining system is to reduce default (credit) risk. Credit risk is a feature of the OTC market. ...
... A clearing house member is required to maintain a margin with the clearing house (clearing margin). The main purpose of the margining system is to reduce default (credit) risk. Credit risk is a feature of the OTC market. ...
Commodity Market - Learning Financial Management
... • Precious Metals: Gold, Silver, Platinum, etc. • Other Metals: Nickel, Aluminum, Copper, Zinc, etc. • Agro-Based Commodities: Wheat, Rice, Corn, Cotton, ...
... • Precious Metals: Gold, Silver, Platinum, etc. • Other Metals: Nickel, Aluminum, Copper, Zinc, etc. • Agro-Based Commodities: Wheat, Rice, Corn, Cotton, ...
Options
... The underlying asset is that which you have the right to buy or sell (with options) or the obligation to buy or deliver (with futures) ...
... The underlying asset is that which you have the right to buy or sell (with options) or the obligation to buy or deliver (with futures) ...
Test Your IQ (Investment Quotient)
... 3. Fixed-Income Securities On what basis do we normally distinguish money market securities from fixed-income securities? a. issuer b. interest rate c. maturity d. tax status 4. Fixed-Income Securities Your friend told you she just received her semi-annual coupon payment on a U.S. Treasury note with ...
... 3. Fixed-Income Securities On what basis do we normally distinguish money market securities from fixed-income securities? a. issuer b. interest rate c. maturity d. tax status 4. Fixed-Income Securities Your friend told you she just received her semi-annual coupon payment on a U.S. Treasury note with ...