Sparta and Athens
... To weave and sew, care for the home 2) What was the basic difference between life in Sparta and life in Athens? Sparta – focused on and organized around the military, so all training and education supported the military Athens – thought that the mind and the body should be trained, so education, cle ...
... To weave and sew, care for the home 2) What was the basic difference between life in Sparta and life in Athens? Sparta – focused on and organized around the military, so all training and education supported the military Athens – thought that the mind and the body should be trained, so education, cle ...
Sparta, known for its militaristic culture and the status
... Sparta was a prominent citystate in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in southeastern Peloponnese. Given its military preeminence, Sparta was recognized as the overall leader of the combined Greek forces during the GrecoPersian Wars, and eventually defeated A ...
... Sparta was a prominent citystate in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in southeastern Peloponnese. Given its military preeminence, Sparta was recognized as the overall leader of the combined Greek forces during the GrecoPersian Wars, and eventually defeated A ...
Alexander the Great
... After becoming King, Philip II envisioned restoring order in Macedon. After doing so, he took control of several Athenian Colonies in the north before attempting to control the heart of Greece. Greek peoples had differing opinions of Philip. ...
... After becoming King, Philip II envisioned restoring order in Macedon. After doing so, he took control of several Athenian Colonies in the north before attempting to control the heart of Greece. Greek peoples had differing opinions of Philip. ...
Glory, war, and decline
... • After several years of fighting, Sparta made a deal with the Persian Empire and agreed to give the Persians some Greek territory in Anatolia. In return, Sparta received enough Persian gold to build its own navy. ...
... • After several years of fighting, Sparta made a deal with the Persian Empire and agreed to give the Persians some Greek territory in Anatolia. In return, Sparta received enough Persian gold to build its own navy. ...
Clash of the Titans: The Persian Wars - WLPCS Middle School
... thus, for you have unjustly punished him even though he's done you no wrong! Xerxes the king will pass over you, whether you wish it or not! It is fitting that no man offer you sacrifices, for you're a muddy and salty river!” – Xerxes (Herodotus, Histories) ...
... thus, for you have unjustly punished him even though he's done you no wrong! Xerxes the king will pass over you, whether you wish it or not! It is fitting that no man offer you sacrifices, for you're a muddy and salty river!” – Xerxes (Herodotus, Histories) ...
Ancient Greece Study Guide Review
... battering ram or earthquake might have been a ___________________. ...
... battering ram or earthquake might have been a ___________________. ...
Event - WordPress.com
... constitution, focusing on the elimination of tribal loyalties Persian Wars, which Greece wins, largely due to Athenian naval power (thus enabling Athens to displace Sparta as the reigning Greek power) Delian League of city states formed to empower the region—lead by Athens First war between Athens a ...
... constitution, focusing on the elimination of tribal loyalties Persian Wars, which Greece wins, largely due to Athenian naval power (thus enabling Athens to displace Sparta as the reigning Greek power) Delian League of city states formed to empower the region—lead by Athens First war between Athens a ...
Persian Wars PPT
... Part 2: Persian War • 10 years later… • Xerxes, son of Darius vowed revenge. • Brought between 100,000-300,000 troops through a narrow mountain pass. ...
... Part 2: Persian War • 10 years later… • Xerxes, son of Darius vowed revenge. • Brought between 100,000-300,000 troops through a narrow mountain pass. ...
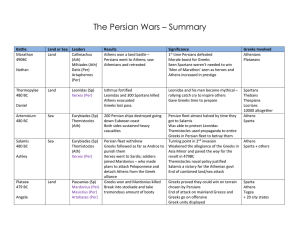
The Persian Wars – Summary Battle Land or Sea Leaders Results
... got to Salamis Was able to protect Leonidas Themistocles used propaganda to entire Greeks in Persian fleet to betray them Turning point in 2nd invasion Weakened the allegiance of the Greeks in Asia Minor and paved the way for the revolt in 479BC Themistocles naval policy justified Salamis a victory ...
... got to Salamis Was able to protect Leonidas Themistocles used propaganda to entire Greeks in Persian fleet to betray them Turning point in 2nd invasion Weakened the allegiance of the Greeks in Asia Minor and paved the way for the revolt in 479BC Themistocles naval policy justified Salamis a victory ...
ANCIENT GREEK PLAYWRIGHTS
... would come down and resolve the issues of the play so that everyone ended up happy usually. • Agon: scene in Old Comedy when both sides discussed the issues of the play. • Most Greek plays began near the climax, with the characters already in the midst of their struggles. • Before Sophocles, there w ...
... would come down and resolve the issues of the play so that everyone ended up happy usually. • Agon: scene in Old Comedy when both sides discussed the issues of the play. • Most Greek plays began near the climax, with the characters already in the midst of their struggles. • Before Sophocles, there w ...
Origins: Thebes an Anti-Athens
... you had understood your mortal natures ! the son of Zeus would have been your ally.! You would now be in blessedness.! ...
... you had understood your mortal natures ! the son of Zeus would have been your ally.! You would now be in blessedness.! ...
The Spartan Hegemony
... The new policy was to fund the weaker side and keep them fighting in a manner that served Persian interests His heir Artaxerxes II successfully continued this policy. His charismatic younger son Cyrus, funded Lysander to defeat Athens , and then revolted against his brother king Artaxerxes with help ...
... The new policy was to fund the weaker side and keep them fighting in a manner that served Persian interests His heir Artaxerxes II successfully continued this policy. His charismatic younger son Cyrus, funded Lysander to defeat Athens , and then revolted against his brother king Artaxerxes with help ...
Sparta and Athens
... rigorous training in warfare for the majority of their lives. The fact that Sparta constantly feared the uprising of the helots, who greatly outnumbered them, also helped to drive their intense training. Athens, on the other hand, went to great lengths to reorganize its political structure to ensure ...
... rigorous training in warfare for the majority of their lives. The fact that Sparta constantly feared the uprising of the helots, who greatly outnumbered them, also helped to drive their intense training. Athens, on the other hand, went to great lengths to reorganize its political structure to ensure ...
Delian League, Athens in the Age of Pericles, and The
... This was considered a golden age for Athens. The city was under the leadership of Pericles at this time. Pericles- statesman (former general ...
... This was considered a golden age for Athens. The city was under the leadership of Pericles at this time. Pericles- statesman (former general ...
Lecture 22
... [4] The cities that took part were, of the Peloponnesians, Argos, Epidaurus, Sicyon, Troezen, the Eleans, the Phliasians, Messene; on the other side of the Corinthian isthmus the Locrians, the Phocians, the Thessalians, Carystus, the Acarnanians belonging to the Aetolian League. The Boeotians, who o ...
... [4] The cities that took part were, of the Peloponnesians, Argos, Epidaurus, Sicyon, Troezen, the Eleans, the Phliasians, Messene; on the other side of the Corinthian isthmus the Locrians, the Phocians, the Thessalians, Carystus, the Acarnanians belonging to the Aetolian League. The Boeotians, who o ...
Chap 5 Sec 5
... Persian Leader 480 Invades Greece Battle of Thermopylae: 300 Spartans stop Persians –Spartans refuse to surrender –All 300 die: allowed for other Greek city states to prepare ...
... Persian Leader 480 Invades Greece Battle of Thermopylae: 300 Spartans stop Persians –Spartans refuse to surrender –All 300 die: allowed for other Greek city states to prepare ...
Athens
... who were not Athenians 560 B.C. Pesistratus stated that a person no longer had to own land to be a citizen. Athenian males became citizens at 18 years old. ...
... who were not Athenians 560 B.C. Pesistratus stated that a person no longer had to own land to be a citizen. Athenian males became citizens at 18 years old. ...
Name: Date: SECTION 1- THE POLIS = city
... What was the message Spartan women gave their men when they went into battle? “Come home with your shield, or on it!” = Win or die trying! Spartans tried to prevent change in their city. Provide two examples of this from the reading. 1. Spartans could not travel outside Sparta except for war 2. No c ...
... What was the message Spartan women gave their men when they went into battle? “Come home with your shield, or on it!” = Win or die trying! Spartans tried to prevent change in their city. Provide two examples of this from the reading. 1. Spartans could not travel outside Sparta except for war 2. No c ...
Chapter 7 The Ancient Greeks Ancient Greece Greek Geography
... Creator of all things and leader of the forces of good A person should choose good and bad in the world, but at the end good would prevail. The Persians began to view their monarchy as a sacred institution or role Today, Zoroastrianism has over 200,000 followers in South Asia. The Persian ...
... Creator of all things and leader of the forces of good A person should choose good and bad in the world, but at the end good would prevail. The Persians began to view their monarchy as a sacred institution or role Today, Zoroastrianism has over 200,000 followers in South Asia. The Persian ...
day4
... How did the goals of the Delian League change? What was the significance of the Delian League for Athens? • What was the significance of the revolt of Thasos? ...
... How did the goals of the Delian League change? What was the significance of the Delian League for Athens? • What was the significance of the revolt of Thasos? ...
In 499BC, the Athenians helped cities under
... The exciting conclusion… • The Athenians, led by Pericles, decide to stay within the walls of their city and rely on their navy. – The Spartans surround ...
... The exciting conclusion… • The Athenians, led by Pericles, decide to stay within the walls of their city and rely on their navy. – The Spartans surround ...
Greek City-States Study Guide
... Oligarchies: Only a few people have ruling power. This means that decisions could be made quicker and without much debate. However, most people do not have an opportunity to make contributions/voice opinions. It may be difficult to get into power. Democracies: All citizens have an opportunity to con ...
... Oligarchies: Only a few people have ruling power. This means that decisions could be made quicker and without much debate. However, most people do not have an opportunity to make contributions/voice opinions. It may be difficult to get into power. Democracies: All citizens have an opportunity to con ...
Warring City
... Athens emerges as the dominant power in Greece after the formation of the Delian League. The Delian League was an alliance between Athens and other Greek city-states (not Sparta) that made Athens wealthy and powerful. ...
... Athens emerges as the dominant power in Greece after the formation of the Delian League. The Delian League was an alliance between Athens and other Greek city-states (not Sparta) that made Athens wealthy and powerful. ...
Unit 5 Greek Test Review
... It became an important center of the Greek army and weapons production. it became the most important center of Hellenistic culture. ...
... It became an important center of the Greek army and weapons production. it became the most important center of Hellenistic culture. ...
Thebes, Greece

Thebes (/ˈθiːbz/; Ancient Greek: Θῆβαι, Thēbai, Greek pronunciation: [tʰɛ̂ːbai̯]; Modern Greek: Θήβα, Thíva [ˈθiva]) is a city in Boeotia, central Greece. It played an important role in Greek myth, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus and others. Archaeological excavations in and around Thebes have revealed a Mycenaean settlement and clay tablets written in the Linear B script, indicating the importance of the site in the Bronze Age.Thebes was the largest city of the ancient region of Boeotia and was the leader of the Boeotian confederacy. It was a major rival of ancient Athens, and sided with the Persians during the 480 BC invasion under Xerxes. Theban forces ended the power of Sparta at the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC under the command of Epaminondas. The Sacred Band of Thebes (an elite military unit) famously fell at the battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC against Philip II and Alexander the Great. Prior to its destruction by Alexander in 335 BC, Thebes was a major force in Greek history, and was the most dominant city-state at the time of the Macedonian conquest of Greece. During the Byzantine period, the city was famous for its silks.The modern city contains an Archaeological Museum, the remains of the Cadmea (Bronze Age and forward citadel), and scattered ancient remains. Modern Thebes is the largest town of the regional unit of Boeotia.