1 III CLASSICAL GREECE The Classical period of ancient Greek
... kingdom of Persia to the east. The conquest of the whole of Greece by Philip II of Macedonia in 338 marked the end of this period. As a result of the Greco-Persian Wars Athens became more powerful than the other Greek city states. It was at the height of its cultural achievements and imperial power ...
... kingdom of Persia to the east. The conquest of the whole of Greece by Philip II of Macedonia in 338 marked the end of this period. As a result of the Greco-Persian Wars Athens became more powerful than the other Greek city states. It was at the height of its cultural achievements and imperial power ...
Athens vs. Sparta Great Cities at Life and War!
... The Spartan government was founded on the principle that the life of every individual, from the moment of birth, belonged absolutely to the state. The elders of the city-state inspected the newborn infants and ordered the weak and unhealthy ones to be carried to a nearby chasm and left to die; only ...
... The Spartan government was founded on the principle that the life of every individual, from the moment of birth, belonged absolutely to the state. The elders of the city-state inspected the newborn infants and ordered the weak and unhealthy ones to be carried to a nearby chasm and left to die; only ...
Sparta Vs Athens: A case for Sparta that you don`t have to agree with
... taken away from their normal work by serving on the Assembly lowered their earning potential , causing their already poor situation to worsen. Life may have been sophisticated and graceful in Athens but the Athenians were often mocked by opposing countries and other city-states for having no bravery ...
... taken away from their normal work by serving on the Assembly lowered their earning potential , causing their already poor situation to worsen. Life may have been sophisticated and graceful in Athens but the Athenians were often mocked by opposing countries and other city-states for having no bravery ...
Ch4_2 Notes
... Oligarchy-- rule by a few powerful people (i.e. Sparta) Sparta Sparta was built a military state. Two groups governed Sparta. o Assembly o Council of Elders Spartan Education o Boys daily life centered around military training. At birth they were determined fit or weak. If weak, they were ab ...
... Oligarchy-- rule by a few powerful people (i.e. Sparta) Sparta Sparta was built a military state. Two groups governed Sparta. o Assembly o Council of Elders Spartan Education o Boys daily life centered around military training. At birth they were determined fit or weak. If weak, they were ab ...
alexander`s
... While fighting in the North Alexander heard that the Greeks were rebelling yet again. So he was forced to travel South at great speed to fight them. When and why did the Greeks rebel for a second time? In the spring of 335BC. The new king of Persia Darius III (came to the throne at 336BC) sent agent ...
... While fighting in the North Alexander heard that the Greeks were rebelling yet again. So he was forced to travel South at great speed to fight them. When and why did the Greeks rebel for a second time? In the spring of 335BC. The new king of Persia Darius III (came to the throne at 336BC) sent agent ...
Demosthenes and Isocrates Address Philip of Macedonia
... right to, heavens! how much more monstrous and exasperating all would have called it! Yet they have no such qualms about Philip and his present conduct, though he is not only no Greek, nor related to the Greeks, but not even a barbarian from any place that can be named with honor, but a pestilent kn ...
... right to, heavens! how much more monstrous and exasperating all would have called it! Yet they have no such qualms about Philip and his present conduct, though he is not only no Greek, nor related to the Greeks, but not even a barbarian from any place that can be named with honor, but a pestilent kn ...
CLAS 0810A
... nephew Amyntas, after Macedonian king Perdikkas killed in battle against Illyrians in 360 BC. Philip seized full power shortly afterwards, and then moved to (a) liquidate political rivals, (b) placate Greek states such as Athens, and (c) forge marriage alliances with tribal kingdoms to north and wes ...
... nephew Amyntas, after Macedonian king Perdikkas killed in battle against Illyrians in 360 BC. Philip seized full power shortly afterwards, and then moved to (a) liquidate political rivals, (b) placate Greek states such as Athens, and (c) forge marriage alliances with tribal kingdoms to north and wes ...
The City-States of Greece
... fox to gnaw him rather than let the theft be revealed. He died of the wounds. If he had been discovered, the disgrace would not have been in the stealing, but in allowing it to be detected. The boy's action illustrates the main purpose of the Spartan educational system, which was to produce men capa ...
... fox to gnaw him rather than let the theft be revealed. He died of the wounds. If he had been discovered, the disgrace would not have been in the stealing, but in allowing it to be detected. The boy's action illustrates the main purpose of the Spartan educational system, which was to produce men capa ...
Greece Notes Continued*
... Review: GEOGRAPHY Ancient Greece developed individual city-states due to the islands and mountainous regions. Greece was divided into many City-States. The two that we will focus on: 1. Athens 2. Sparta Years: 700 BC to 400 BC. ...
... Review: GEOGRAPHY Ancient Greece developed individual city-states due to the islands and mountainous regions. Greece was divided into many City-States. The two that we will focus on: 1. Athens 2. Sparta Years: 700 BC to 400 BC. ...
Chapter 5 Section 2 Notes
... 4. Pisistratus in 546 provided funds for farmers to buy back their farms from nobles 5. Cleisthenes in 508 B.C. reorganizes the assembly to break up the power of the nobles. a. Creates the Council of Five Hundred F. These political reforms kept Athenian farmers from revolution and led to Athens beco ...
... 4. Pisistratus in 546 provided funds for farmers to buy back their farms from nobles 5. Cleisthenes in 508 B.C. reorganizes the assembly to break up the power of the nobles. a. Creates the Council of Five Hundred F. These political reforms kept Athenian farmers from revolution and led to Athens beco ...
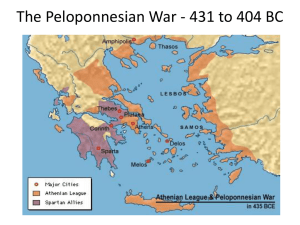
The Peloponnesian War 431 to 404 BC
... 3) The Decelean War, or the Ionian War. Sparta, receives support from Persia, supported rebellions in Athens' subject states in the Aegean Sea and Ionia, undermining Athens' empire, and, eventually, depriving the city of naval supremacy. The destruction of Athens' fleet at Aegospotami effectively en ...
... 3) The Decelean War, or the Ionian War. Sparta, receives support from Persia, supported rebellions in Athens' subject states in the Aegean Sea and Ionia, undermining Athens' empire, and, eventually, depriving the city of naval supremacy. The destruction of Athens' fleet at Aegospotami effectively en ...
Study Guide for Greece Test
... seas for trade and settlement in other lands (due to the fact that they did not have enough farmable land). PEOPLE TO MEET Who are these people and what are the known for…? ...
... seas for trade and settlement in other lands (due to the fact that they did not have enough farmable land). PEOPLE TO MEET Who are these people and what are the known for…? ...
Empire - World History
... • Individualism was not encouraged. Everyone was to dedicate themselves to their country. Every boy lived in a boot camp from age 7-30. Spartan women had a lot of freedom and also received military training. ...
... • Individualism was not encouraged. Everyone was to dedicate themselves to their country. Every boy lived in a boot camp from age 7-30. Spartan women had a lot of freedom and also received military training. ...
Greek Wars Review
... on the island of Sicily. Athens is defeated in 413 B.C. Athens and its allies surrender to Sparta in 404 B.C. ...
... on the island of Sicily. Athens is defeated in 413 B.C. Athens and its allies surrender to Sparta in 404 B.C. ...
Sparta vs. Athens - Franklin County Public Schools
... come to them and they would fight from behind their city walls This may have worked but a terrible plague infected the city and killed Pericles and many others Peace was made in 421 BC ...
... come to them and they would fight from behind their city walls This may have worked but a terrible plague infected the city and killed Pericles and many others Peace was made in 421 BC ...
The Rise of Greek City-States Chapter 5 Sec.2 Sparta
... At age 20 they could marry but could not move out of the military barracks until the age of 30 ...
... At age 20 they could marry but could not move out of the military barracks until the age of 30 ...
The Rise of Greek City-States Chapter 5 Sec.2
... At age 20 they could marry but could not move out of the military barracks until the age of 30 ...
... At age 20 they could marry but could not move out of the military barracks until the age of 30 ...
Delian League and Spartan Confederacy
... For much of the war Sparta was in charge of the Greek alliance against the Persians After the Delian league was established, Sparta gave up its leadership of the war against Persia As a result, relations between Athens and Sparta eventually became strained-especially, once Athens began to appear to ...
... For much of the war Sparta was in charge of the Greek alliance against the Persians After the Delian league was established, Sparta gave up its leadership of the war against Persia As a result, relations between Athens and Sparta eventually became strained-especially, once Athens began to appear to ...
The Myceneans
... pottery, bronze objects, gold, copper, tin, spices, elephant tusks, and dye. Lots of gold and bronze work, writing, ...
... pottery, bronze objects, gold, copper, tin, spices, elephant tusks, and dye. Lots of gold and bronze work, writing, ...
document
... – Spartans held off Persians at mountain pass – Greek traitor showed Persians how to get around them – Spartans were slaughtered – Athens was abandoned ...
... – Spartans held off Persians at mountain pass – Greek traitor showed Persians how to get around them – Spartans were slaughtered – Athens was abandoned ...
CHAPTER 3 - CLASSICAL AND HELLENISTIC GREECE
... The chapter continues with a more detailed narration of the Great Peloponnesian War which was fought, with a short period of unstable peace, for the next 27 years (431-404 B.C.E.). This long and disastrous war eventually led to the defeat of Athens and shook the foundations of Greek civilization. Th ...
... The chapter continues with a more detailed narration of the Great Peloponnesian War which was fought, with a short period of unstable peace, for the next 27 years (431-404 B.C.E.). This long and disastrous war eventually led to the defeat of Athens and shook the foundations of Greek civilization. Th ...
Athens
... Every social class in Athens grew more and more discontent and wanted change—their needs were not being met by the gov’t Example: ...
... Every social class in Athens grew more and more discontent and wanted change—their needs were not being met by the gov’t Example: ...
What Really Happened….
... For much of the war Sparta was in charge of the Greek alliance against the Persians After the Delian league was established, Sparta gave up its leadership of the war against Persia As a result, relations between Athens and Sparta eventually became strained-especially, once Athens began to appear to ...
... For much of the war Sparta was in charge of the Greek alliance against the Persians After the Delian league was established, Sparta gave up its leadership of the war against Persia As a result, relations between Athens and Sparta eventually became strained-especially, once Athens began to appear to ...
File - Mr. C at Hamilton
... powers, able to summon large land armies which were very nearly unbeatable (thanks to the legendary Spartan forces). The Athenian Empire, although based in the peninsula of Attica, spread out across the islands of the Aegean Sea; Athens drew its immense wealth from tribute paid from these islands. A ...
... powers, able to summon large land armies which were very nearly unbeatable (thanks to the legendary Spartan forces). The Athenian Empire, although based in the peninsula of Attica, spread out across the islands of the Aegean Sea; Athens drew its immense wealth from tribute paid from these islands. A ...
Thebes, Greece

Thebes (/ˈθiːbz/; Ancient Greek: Θῆβαι, Thēbai, Greek pronunciation: [tʰɛ̂ːbai̯]; Modern Greek: Θήβα, Thíva [ˈθiva]) is a city in Boeotia, central Greece. It played an important role in Greek myth, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus and others. Archaeological excavations in and around Thebes have revealed a Mycenaean settlement and clay tablets written in the Linear B script, indicating the importance of the site in the Bronze Age.Thebes was the largest city of the ancient region of Boeotia and was the leader of the Boeotian confederacy. It was a major rival of ancient Athens, and sided with the Persians during the 480 BC invasion under Xerxes. Theban forces ended the power of Sparta at the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC under the command of Epaminondas. The Sacred Band of Thebes (an elite military unit) famously fell at the battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC against Philip II and Alexander the Great. Prior to its destruction by Alexander in 335 BC, Thebes was a major force in Greek history, and was the most dominant city-state at the time of the Macedonian conquest of Greece. During the Byzantine period, the city was famous for its silks.The modern city contains an Archaeological Museum, the remains of the Cadmea (Bronze Age and forward citadel), and scattered ancient remains. Modern Thebes is the largest town of the regional unit of Boeotia.