5073 Chemistry IGCSE ordinary level for 2016
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
File
... the study of quantitative relationships between amounts of ______________________________________________________________ reactants used and products formed by a chemical reaction ______________________________________________________________ ...
... the study of quantitative relationships between amounts of ______________________________________________________________ reactants used and products formed by a chemical reaction ______________________________________________________________ ...
St. Xavier`s College – Autonomous Mumbai Syllabus for 3 Semester
... 4. To motivate students to solve numerical problems with different systems of units which illustrate the applicability of these concepts in chemistry. 5. To provide an introduction to analytical chemistry and information about latest developments in analytical techniques widely used in quality contr ...
... 4. To motivate students to solve numerical problems with different systems of units which illustrate the applicability of these concepts in chemistry. 5. To provide an introduction to analytical chemistry and information about latest developments in analytical techniques widely used in quality contr ...
HONORS LAB MANUAL - Tenafly High School
... CONCLUSION ALWAYS REFERS BACK TO THE PURPOSE. If there is an unknown, the number of the unknown must be included in the identification. 2. A discussion of errors; how they could have been avoided; what could be improved in the lab procedure to reduce the errors. 3. For some labs, the scientific theo ...
... CONCLUSION ALWAYS REFERS BACK TO THE PURPOSE. If there is an unknown, the number of the unknown must be included in the identification. 2. A discussion of errors; how they could have been avoided; what could be improved in the lab procedure to reduce the errors. 3. For some labs, the scientific theo ...
Integrated Physics and Chemistry
... Name simple ionic and covalent compounds; Predict the charge of a transition metal cation in an ionic compound; Write chemical formulas for simple ionic compounds; Distinguish a covalent compound’s empirical formula from its molecular formula Describe how carbon atoms bond covalently to form organic ...
... Name simple ionic and covalent compounds; Predict the charge of a transition metal cation in an ionic compound; Write chemical formulas for simple ionic compounds; Distinguish a covalent compound’s empirical formula from its molecular formula Describe how carbon atoms bond covalently to form organic ...
Redox Reactions - Hillsborough County Public Schools
... Replacement Reactions are always redox reactions! Combustion reactions are always redox reactions! Any time an oxidation number changes (which means electrons are gained or lost) during the reaction, a redox reaction is occurring. ...
... Replacement Reactions are always redox reactions! Combustion reactions are always redox reactions! Any time an oxidation number changes (which means electrons are gained or lost) during the reaction, a redox reaction is occurring. ...
Now we turn to the study of chemical kinetics. Kinetics is the study of
... What controls the speed of a reaction? One factor is the identity of reactants and products. If one of the reactants is particularly stable, then the speed of the reaction is likely to be slow. If on the other hand a substance is intrinsically unstable, then it will react quickly. A second factor is ...
... What controls the speed of a reaction? One factor is the identity of reactants and products. If one of the reactants is particularly stable, then the speed of the reaction is likely to be slow. If on the other hand a substance is intrinsically unstable, then it will react quickly. A second factor is ...
Synthesis of Imidazolium Room-Temperature Ionic
... pure by 1H NMR. Several purification protocols can be utilized to remove colored impurities either at the stage of the bromide or later (10), if spectroscopic grade ionic liquids are desired. Carrying out the reaction in a solvent ensures that the resulting ionic liquid does not develop a brown colo ...
... pure by 1H NMR. Several purification protocols can be utilized to remove colored impurities either at the stage of the bromide or later (10), if spectroscopic grade ionic liquids are desired. Carrying out the reaction in a solvent ensures that the resulting ionic liquid does not develop a brown colo ...
Ch. 18 Class PowerPoint
... • But theoretically, every reaction can proceed in two directions, forward and reverse. • Essentially all chemical reactions are considered to be reversible under suitable conditions. • A chemical reaction in which the products can react to re-form the reactants is called a reversible reaction. ...
... • But theoretically, every reaction can proceed in two directions, forward and reverse. • Essentially all chemical reactions are considered to be reversible under suitable conditions. • A chemical reaction in which the products can react to re-form the reactants is called a reversible reaction. ...
Influence of physical and chemical factors on biological leaching
... The article presents the results of the research regarding the biological leaching of this metal from electronic wastes components in the form of printed circuit boards. The purpose of the study was t o evaluate the influence of some physical and chemical factors (e.g. pH, oxidation-reduction potent ...
... The article presents the results of the research regarding the biological leaching of this metal from electronic wastes components in the form of printed circuit boards. The purpose of the study was t o evaluate the influence of some physical and chemical factors (e.g. pH, oxidation-reduction potent ...
Chemical Equilibria - Beck-Shop
... (Rb ). When this happens, the concentration of every reactant and product remains constant, and the system is in a state of balance, known as equilibrium. More specifically, the system is said to be in dynamic equilibrium. As the rates of these reactions are equal, it may seem that the reactions have ...
... (Rb ). When this happens, the concentration of every reactant and product remains constant, and the system is in a state of balance, known as equilibrium. More specifically, the system is said to be in dynamic equilibrium. As the rates of these reactions are equal, it may seem that the reactions have ...
Example 7.1: The following decomposition was studied at a given
... Determination of the Rate Law In the previous section we noted that the order of each reactant could be determined experimentally by measuring the initial rate of reaction over a range of initial concentrations. If we do this for each reactant then it is possible to determine the overall order of th ...
... Determination of the Rate Law In the previous section we noted that the order of each reactant could be determined experimentally by measuring the initial rate of reaction over a range of initial concentrations. If we do this for each reactant then it is possible to determine the overall order of th ...
Chemistry English
... Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding 4.1 Introduction Chemical bonds are the attractive forces which join atoms. The distance between the centers of two atoms joined by a chemical bond is between 70 pm and 300pm. The energy needed to break a chemical bond between two atoms is called the bond energy. Chemical ...
... Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding 4.1 Introduction Chemical bonds are the attractive forces which join atoms. The distance between the centers of two atoms joined by a chemical bond is between 70 pm and 300pm. The energy needed to break a chemical bond between two atoms is called the bond energy. Chemical ...
Physical Chemistry 3: — Chemical Kinetics - Christian
... and Seakins2 gives a good introduction especially to gas phase kinetics. The book by Houston3 includes more information on the dynamics of chemical reactions. The book by Barrante4 is highly recommended for everyone who wants to brush-up some math skills. A highly recommended web site for looking up ...
... and Seakins2 gives a good introduction especially to gas phase kinetics. The book by Houston3 includes more information on the dynamics of chemical reactions. The book by Barrante4 is highly recommended for everyone who wants to brush-up some math skills. A highly recommended web site for looking up ...
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY Course Book for M.Sc. in Chemistry
... Objective: Quantum Mechanics is a branch of science that deals with discrete, indivisible units of energy called quanta as described by the Quantum. It is an interfacial subject between Physics, chemistry and mathematics. Hence the objective of this course in chemistry is to understand clearly the m ...
... Objective: Quantum Mechanics is a branch of science that deals with discrete, indivisible units of energy called quanta as described by the Quantum. It is an interfacial subject between Physics, chemistry and mathematics. Hence the objective of this course in chemistry is to understand clearly the m ...
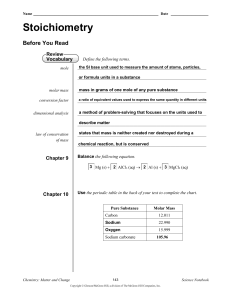
Stoichiometry
... • A 2.00 g sample of ammonia is mixed with 4.00 g of oxygen. Which is the limiting reactant and how much excess reactant remains after the reaction has stopped? • First, we need to create a balanced equation for the reaction: 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g)4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g) • Next we can use stoichiometry to ca ...
... • A 2.00 g sample of ammonia is mixed with 4.00 g of oxygen. Which is the limiting reactant and how much excess reactant remains after the reaction has stopped? • First, we need to create a balanced equation for the reaction: 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g)4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g) • Next we can use stoichiometry to ca ...
as PDF - Heriot
... with chromium oxalates at the temperatures at which phosphoresce is quenched, a feature whose explanation caused much debate in the past. Possible explanations included nonradiative depopulation of the 4 T2 state, or relaxation pathways through 2 E states.8, 9 Luminescence in Cr (III) oxalate system ...
... with chromium oxalates at the temperatures at which phosphoresce is quenched, a feature whose explanation caused much debate in the past. Possible explanations included nonradiative depopulation of the 4 T2 state, or relaxation pathways through 2 E states.8, 9 Luminescence in Cr (III) oxalate system ...
Catalysis for a Sustainable World
... Naonobu Katada received the MS degree in Nagoya University under the supervision of Professor Yuichi Murakami in 1990. After a period of researching for Nippon Shokubai Co. Ltd. in 1990 - 1992, he was appointed a research associate in Tottori University in 1992. He received the PhD degree from Nagoy ...
... Naonobu Katada received the MS degree in Nagoya University under the supervision of Professor Yuichi Murakami in 1990. After a period of researching for Nippon Shokubai Co. Ltd. in 1990 - 1992, he was appointed a research associate in Tottori University in 1992. He received the PhD degree from Nagoy ...
Chemical Equations and Stoichiometry
... Instead of saying all that, we can write the following equation: ...
... Instead of saying all that, we can write the following equation: ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.