Chapter5.pdf
... designated as standards of hardness from 1 to 10. Talc, a very soft mineral, is a 1 and diamond, which is the hardest natural substance on earth, is a 10. The Mohs scale tests the property of “scratchability”. Most geologists don’t carry around these 10 samples but use other handy items such as thei ...
... designated as standards of hardness from 1 to 10. Talc, a very soft mineral, is a 1 and diamond, which is the hardest natural substance on earth, is a 10. The Mohs scale tests the property of “scratchability”. Most geologists don’t carry around these 10 samples but use other handy items such as thei ...
Chapter 13…States of Matter
... 4. Miscible: liquids that are capable of dissolving each other 5. Dilute: when a solution has a low concentration of solute 6. Concentrated: when a solution has a high concentration of solute 7. Saturated solution: cannot hold any more of a given solute at a given temperature 8. Unsaturated solution ...
... 4. Miscible: liquids that are capable of dissolving each other 5. Dilute: when a solution has a low concentration of solute 6. Concentrated: when a solution has a high concentration of solute 7. Saturated solution: cannot hold any more of a given solute at a given temperature 8. Unsaturated solution ...
Lecture 25 – The Solid State: types of crystals, lattice energies and
... Molecules of Argon g gas g ...
... Molecules of Argon g gas g ...
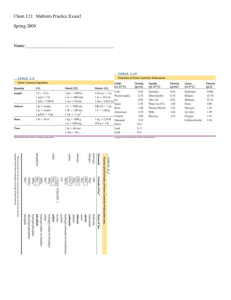
semester two review sheet
... 2. Draw four water molecules. Label the types of bonds (covalent vs. hydrogen), oxygen atoms, hydrogen atoms, and respective charges on the atoms. 3. Is water polar or nonpolar? Explain. 4. Why is water considered the universal solvent? 5. What are the special properties of water and why do they occ ...
... 2. Draw four water molecules. Label the types of bonds (covalent vs. hydrogen), oxygen atoms, hydrogen atoms, and respective charges on the atoms. 3. Is water polar or nonpolar? Explain. 4. Why is water considered the universal solvent? 5. What are the special properties of water and why do they occ ...
PPS - School of Physics
... The dust particles suspended in the plasma are illuminated using a Helium-Neon laser. The laser beam enters the discharge chamber through a 40-mm diameter window. A window mounted on a side port in a perpendicular direction allows a view of the light scattered at 90° by the suspended dust particles ...
... The dust particles suspended in the plasma are illuminated using a Helium-Neon laser. The laser beam enters the discharge chamber through a 40-mm diameter window. A window mounted on a side port in a perpendicular direction allows a view of the light scattered at 90° by the suspended dust particles ...
UNIT 1-C INVESTIGATING THE CAUSE OF THE FISH KILL
... happens to chemical reactions of the fish? Explain the purpose of refrigeration. When water temperatures increase what happens to the temperature of the fish? If the temperature of the water is raised, the fish's chemical reactions are what? The fish now require what, since the temperature of the wa ...
... happens to chemical reactions of the fish? Explain the purpose of refrigeration. When water temperatures increase what happens to the temperature of the fish? If the temperature of the water is raised, the fish's chemical reactions are what? The fish now require what, since the temperature of the wa ...
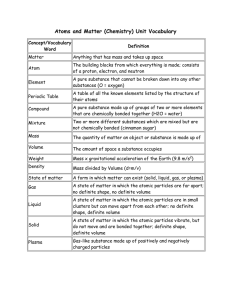
Matter
... particles of substances separate and spread evenly amongst each other. • Solute – substance that is dissolved. A solute is soluble, or able to dissolve. • A substance that is insoluble is unable to dissolve, forms a mixture that is not homogeneous, and therefore NOT a solution. ...
... particles of substances separate and spread evenly amongst each other. • Solute – substance that is dissolved. A solute is soluble, or able to dissolve. • A substance that is insoluble is unable to dissolve, forms a mixture that is not homogeneous, and therefore NOT a solution. ...
Structural, growth and characterizations of NLO crystal
... transmittance in the ultraviolet and visible region. The efficiency of second harmonic generation was analyzed by Kurtz-Perry powder technique and compared with standard KDP crystal. Thermogravimetric and differential thermal analysis have been performed to determine the thermal stability of the cry ...
... transmittance in the ultraviolet and visible region. The efficiency of second harmonic generation was analyzed by Kurtz-Perry powder technique and compared with standard KDP crystal. Thermogravimetric and differential thermal analysis have been performed to determine the thermal stability of the cry ...
Photonic Crystals
... are ones of the most promising materials in modern photonics. They all have direct energy bandgap, which causes the high efficiency of photon’s emission, and absorption. In case of gallium nitride there is a possibility of forming solid solutions with InN and AlN, which allow tailoring of optical an ...
... are ones of the most promising materials in modern photonics. They all have direct energy bandgap, which causes the high efficiency of photon’s emission, and absorption. In case of gallium nitride there is a possibility of forming solid solutions with InN and AlN, which allow tailoring of optical an ...
Structure of Bacillus halmapalus α-amylase crystallized with and
... the loop domain. Also observed by Davies et al. (2005) were two calcium ions and a sodium ion between the ( / )8-barrel domain and the loop domain and a third calcium ion positioned at the interface between the ( / )8-barrel domain and the -sheet domain. In addition to the nonasaccharide, we found ...
... the loop domain. Also observed by Davies et al. (2005) were two calcium ions and a sodium ion between the ( / )8-barrel domain and the loop domain and a third calcium ion positioned at the interface between the ( / )8-barrel domain and the -sheet domain. In addition to the nonasaccharide, we found ...
WeekofOct4 - MabryOnline.org
... minerals related? TSWBAT: - define crystal systems; - classify crystal shapes into six different groups. EQ: What is the difference between a rock and a mineral? SWBAT: - compare minerals and rocks; - distinguish minerals from rocks; - classify samples of rocks and minerals. EQ: How can I tell one m ...
... minerals related? TSWBAT: - define crystal systems; - classify crystal shapes into six different groups. EQ: What is the difference between a rock and a mineral? SWBAT: - compare minerals and rocks; - distinguish minerals from rocks; - classify samples of rocks and minerals. EQ: How can I tell one m ...
Matter
... • Combo of 2 or more pure substances • Physically combined not chemically combined • Each substance retains its own identity and properties ...
... • Combo of 2 or more pure substances • Physically combined not chemically combined • Each substance retains its own identity and properties ...
Preparation of spherical DDNP study Liu off on a journey
... Experience factor levels are shown in Table 1, the orthogonal experiment results shown in Table 2. According to Table 2 Orthogonal test results that: poor value for the size relationship between the various factors: ...
... Experience factor levels are shown in Table 1, the orthogonal experiment results shown in Table 2. According to Table 2 Orthogonal test results that: poor value for the size relationship between the various factors: ...
PREM NMHU Highlights - FY 14-15
... Marina Fonari, Stephen Barlow, Seth R. Marder, Tatiana V. Timofeeva NMHU, DMR 0934212 The promise of low-cost processing and flexible circuitry has driven intense research in carbon-based electronics. The performance of carbon-based materials can be effectively tuned by the application of redox reag ...
... Marina Fonari, Stephen Barlow, Seth R. Marder, Tatiana V. Timofeeva NMHU, DMR 0934212 The promise of low-cost processing and flexible circuitry has driven intense research in carbon-based electronics. The performance of carbon-based materials can be effectively tuned by the application of redox reag ...
practice test2(Answers)
... A) The temperature of steam cannot exceed 100°C. B) The temperature of ice remains at 0°C as it melts. C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 100°C as it boils E) Both liquid water and ice are present at 0°C. ...
... A) The temperature of steam cannot exceed 100°C. B) The temperature of ice remains at 0°C as it melts. C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 100°C as it boils E) Both liquid water and ice are present at 0°C. ...
File
... A state of matter in which the atomic particles are in small clusters but can move apart from each other; no definite ...
... A state of matter in which the atomic particles are in small clusters but can move apart from each other; no definite ...
“SunOyster Crystal” helps solar technology reach 30% electric
... The receiver is the heart of the SunOyster. After the parabolic mirrors have concentrated the direct sun light 30 to 40 times onto the receiver, the receiver concentrates it a second time and transforms it into electricity and heat. In order to reach this target, a glass lens in the receiver is conc ...
... The receiver is the heart of the SunOyster. After the parabolic mirrors have concentrated the direct sun light 30 to 40 times onto the receiver, the receiver concentrates it a second time and transforms it into electricity and heat. In order to reach this target, a glass lens in the receiver is conc ...
LADI Quasi Laue diffractometer LADI
... horizontal and the opening for the sample holder has only a diameter of 10 cm, so this detector would generally be unsuitable for physics/chemistry type work, where bulky environment-control units - often with vertical geometry - are used. (Such experiments may be carried out on the VIVADI instrumen ...
... horizontal and the opening for the sample holder has only a diameter of 10 cm, so this detector would generally be unsuitable for physics/chemistry type work, where bulky environment-control units - often with vertical geometry - are used. (Such experiments may be carried out on the VIVADI instrumen ...
What has been presented?
... unit cells of different lattices. •The corner of each lattice are shared by eight unit cells. Subsequently, ONLY one eighth of each corner atom belongs to any one unit cell. ...
... unit cells of different lattices. •The corner of each lattice are shared by eight unit cells. Subsequently, ONLY one eighth of each corner atom belongs to any one unit cell. ...
hot water cools - Effingham County Schools
... • Mineral crystals that are valued for their beauty rather than for usefulness, are attractive and rare, and are hard enough to be cut and polished are called gems. ...
... • Mineral crystals that are valued for their beauty rather than for usefulness, are attractive and rare, and are hard enough to be cut and polished are called gems. ...
Ch. 4 Study Guide Answers
... What is a crystal? A solid in which the atoms are arranged in repeating patterns What is magma? Molten rock material beneath Earth's surface When magma cools quickly, small crystals form, and when magma cools slowly, large crystals forms. Saturated vs. supersaturated solutions. Saturated- completely ...
... What is a crystal? A solid in which the atoms are arranged in repeating patterns What is magma? Molten rock material beneath Earth's surface When magma cools quickly, small crystals form, and when magma cools slowly, large crystals forms. Saturated vs. supersaturated solutions. Saturated- completely ...
Characterization of the pH-Mediated Solubility of Bacillus
... at acidic and alkaline p H indicated that the toxin peptide remained intact regardless of the p H used in the solubilization (Figure 2). The solubility below p H 4, has not been reported for any other B.t. 6-endotoxin. It still fails, however, to explain dissolution of the crystals at midgut pH valu ...
... at acidic and alkaline p H indicated that the toxin peptide remained intact regardless of the p H used in the solubilization (Figure 2). The solubility below p H 4, has not been reported for any other B.t. 6-endotoxin. It still fails, however, to explain dissolution of the crystals at midgut pH valu ...
Crystallization

Crystallization is the (natural or artificial) process of formation of solid crystals precipitating from a solution, melt or more rarely deposited directly from a gas. Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs. In chemical engineering crystallization occurs in a crystallizer. Crystallization is therefore an aspect of precipitation, obtained through a variation of the solubility conditions of the solute in the solvent, as compared to precipitation due to chemical reaction.