Resumen Science I Trimestre II Parcial Definitions: Element: pure
... Molecule: particle of a compound; formed when atoms of 2 or more elements join together. Compound: pure substances composed of 2 or more elements that are chemically combined; elements combine reaction with one another. Chemical Formula: is the fundamental unit of an element. The symbols for the ele ...
... Molecule: particle of a compound; formed when atoms of 2 or more elements join together. Compound: pure substances composed of 2 or more elements that are chemically combined; elements combine reaction with one another. Chemical Formula: is the fundamental unit of an element. The symbols for the ele ...
GC-Final-Review-2014
... a. A substances resistance to flow b. The substance being dissolved c. Solutions that have solutes that settle out, more than one phase d. Substances that can interfere with H bonds, i.e. soap e. Temp at which a liquid turns to a vapor/gas f. A substance that contain reflective particles that displa ...
... a. A substances resistance to flow b. The substance being dissolved c. Solutions that have solutes that settle out, more than one phase d. Substances that can interfere with H bonds, i.e. soap e. Temp at which a liquid turns to a vapor/gas f. A substance that contain reflective particles that displa ...
Mineral Composition of Igneous Rock
... Texture is the size, shape and distribution of the crystals or grains in the rock. It is either coarse grained or fine grained. coarse fine ...
... Texture is the size, shape and distribution of the crystals or grains in the rock. It is either coarse grained or fine grained. coarse fine ...
Compulsory textbook Recommended textbooks Topics of the first
... • Nucleation • Particle growth • At large relative supersaturation the rate of nucleation is large – large naumber of small particles are formed • At small relative supersaturation the particle growth dominates, large particles are formed ☺ • In practice: elevate temperature to increase solubility, ...
... • Nucleation • Particle growth • At large relative supersaturation the rate of nucleation is large – large naumber of small particles are formed • At small relative supersaturation the particle growth dominates, large particles are formed ☺ • In practice: elevate temperature to increase solubility, ...
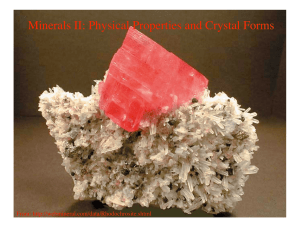
Minerals II: Physical Properties and Crystal Forms
... Physical properties of minerals • Based on the principles discussed during the last lecture and above, we now know that minerals are composed of atoms, arranged in a specific order, with a well defined chemical composition. We might expect then that the microscopic variations in bond environment d ...
... Physical properties of minerals • Based on the principles discussed during the last lecture and above, we now know that minerals are composed of atoms, arranged in a specific order, with a well defined chemical composition. We might expect then that the microscopic variations in bond environment d ...
Physical properties of minerals
... Physical properties of minerals • Based on the principles discussed during the last lecture and above, we now know that minerals are composed of atoms, arranged in a specific order, with a well defined chemical composition. We might expect then that the microscopic variations in bond environment di ...
... Physical properties of minerals • Based on the principles discussed during the last lecture and above, we now know that minerals are composed of atoms, arranged in a specific order, with a well defined chemical composition. We might expect then that the microscopic variations in bond environment di ...
solution is a solution that contains the maximum amount of solute
... of __metals_ combined with __non-metals_ while molecular compounds are usually composed of __nonmetals__ combined with ___non-metals___ . ...
... of __metals_ combined with __non-metals_ while molecular compounds are usually composed of __nonmetals__ combined with ___non-metals___ . ...
Igneous Rock Video
... A Closer Look at an Igneous Rock Obsidian is a dark-colored volcanic glass that forms from the very rapid cooling of molten rock material. It cools so rapidly that crystals do not form. ...
... A Closer Look at an Igneous Rock Obsidian is a dark-colored volcanic glass that forms from the very rapid cooling of molten rock material. It cools so rapidly that crystals do not form. ...
What is a mineral?
... Definite chemical composition – made of one or more elements (see periodic table of elements in back of book). There are actually eight elements that make up most minerals. They are oxygen, silicon, aluminum, iron, calcium, sodium, potassium, and magnesium. These elements make up about 98% of Eart ...
... Definite chemical composition – made of one or more elements (see periodic table of elements in back of book). There are actually eight elements that make up most minerals. They are oxygen, silicon, aluminum, iron, calcium, sodium, potassium, and magnesium. These elements make up about 98% of Eart ...
Solution-Solubility-Equilibrium
... POLAR SOLVENT such as WATER or acid will dissolve an IONIC SOLUTE such as salt. Gasoline, benzene or carbon tetrachloride (dry cleaning solvent) are NON-POLAR SOLVENTS and they will best dissolve non-polar solutes such as fats, oils, paints. Water does not dissolve fats and oils very well. (Use of a ...
... POLAR SOLVENT such as WATER or acid will dissolve an IONIC SOLUTE such as salt. Gasoline, benzene or carbon tetrachloride (dry cleaning solvent) are NON-POLAR SOLVENTS and they will best dissolve non-polar solutes such as fats, oils, paints. Water does not dissolve fats and oils very well. (Use of a ...
Mechanism for linear and nonlinear optical effects in SrBe3O4 crystal
... 共SHG兲 effect of the SrBe3 O4 crystal.2 The crystal structure of SrBe3 O4 has been reported by Harris and Yakel.3 They confirmed that the crystal belongs to the P6̄2c space group. Its hexagonal unit cell with a⫽b⫽4.5961 Å and c⫽8.9300 Å contains two formula weights. In Fig. 1 the unit cell structure ...
... 共SHG兲 effect of the SrBe3 O4 crystal.2 The crystal structure of SrBe3 O4 has been reported by Harris and Yakel.3 They confirmed that the crystal belongs to the P6̄2c space group. Its hexagonal unit cell with a⫽b⫽4.5961 Å and c⫽8.9300 Å contains two formula weights. In Fig. 1 the unit cell structure ...
Crystals and photons*
... lattice excited by the incident light and occurs in every case with a change of frequency. Unfortunately, however, actual crystals are far from being perfect. Internal flaws and surface imperfections result in a strong scattering of light with unaltered frequency. Theoretically this should not troub ...
... lattice excited by the incident light and occurs in every case with a change of frequency. Unfortunately, however, actual crystals are far from being perfect. Internal flaws and surface imperfections result in a strong scattering of light with unaltered frequency. Theoretically this should not troub ...
tic tac toe science homework
... chlorine and sodium are most salt or sugar in needed to grow this used today. one liter of water. crystal? What steps What can you do to would you have to take to create this crystal? increase the amount of salt or sugar in the water? Take 2 ice cubes out of the freezer. Put one in the refrigerator ...
... chlorine and sodium are most salt or sugar in needed to grow this used today. one liter of water. crystal? What steps What can you do to would you have to take to create this crystal? increase the amount of salt or sugar in the water? Take 2 ice cubes out of the freezer. Put one in the refrigerator ...
CH225h - Oregon State chemistry
... temperature is too low, the forward rate constant may be too small. The optimal temperature is about 500 °C. 3. Extract NH3 while it’s formed , to keep the concentration low. 4. Use an appropriate catalyst (Fe metal based). ...
... temperature is too low, the forward rate constant may be too small. The optimal temperature is about 500 °C. 3. Extract NH3 while it’s formed , to keep the concentration low. 4. Use an appropriate catalyst (Fe metal based). ...
Role of Solvents in Improvement of Dissolution Rate of Drugs
... crystal habit. This might be due to the solute-solvent interaction at various crystal–solution interfaces, which leads to altered roundness of the interfaces, changes in crystal growth kinetics, and enhancement27 or inhibition28 of growth at certain crystal faces. Thus it is assumable that polarity ...
... crystal habit. This might be due to the solute-solvent interaction at various crystal–solution interfaces, which leads to altered roundness of the interfaces, changes in crystal growth kinetics, and enhancement27 or inhibition28 of growth at certain crystal faces. Thus it is assumable that polarity ...
Lecture 25 – The Solid State: types of crystals
... It should be realized that the value of any ionic radius only serves as a useful but approximate size of the ion.. The fact that the ionic radius of Na+ is 0.98Å does not mean that the electron cloud of the ion never extends beyond this value. It is significant because when it is added together with ...
... It should be realized that the value of any ionic radius only serves as a useful but approximate size of the ion.. The fact that the ionic radius of Na+ is 0.98Å does not mean that the electron cloud of the ion never extends beyond this value. It is significant because when it is added together with ...
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. Examples
... Density is the mass per unit of volume. It is affected by a change in temperature. Formula: Density = mass D=m Volume V ...
... Density is the mass per unit of volume. It is affected by a change in temperature. Formula: Density = mass D=m Volume V ...
2nd Semester Exam Review
... – Particle size – larger molecules = higher viscosity – Temperature – lower temperature = higher viscosity ...
... – Particle size – larger molecules = higher viscosity – Temperature – lower temperature = higher viscosity ...
Chapter 5 2004.ppt
... adjacent faces of quartz is always exactly the same. Other minerals were also found to have this regularity. This observation became known as the law of constancy of interfacial angles. • Atoms of different minerals are clustered into geometric forms such as cubes, bricks, hexagons, etc. and so the ...
... adjacent faces of quartz is always exactly the same. Other minerals were also found to have this regularity. This observation became known as the law of constancy of interfacial angles. • Atoms of different minerals are clustered into geometric forms such as cubes, bricks, hexagons, etc. and so the ...
幻灯片 1 - Read
... the atoms in the system are in a highly disordered state, and the total energy of the system is also high. Lowering the temperature of the system results in the atoms of the system acquiring a more orderly state, thus reducing the energy of the system. This process of cooling is known as annealing . ...
... the atoms in the system are in a highly disordered state, and the total energy of the system is also high. Lowering the temperature of the system results in the atoms of the system acquiring a more orderly state, thus reducing the energy of the system. This process of cooling is known as annealing . ...
Chapter505.ppt
... adjacent faces of quartz is always exactly the same. Other minerals were also found to have this regularity. This observation became known as the law of constancy of interfacial angles. • Atoms of different minerals are clustered into geometric forms such as cubes, bricks, hexagons, etc. and so the ...
... adjacent faces of quartz is always exactly the same. Other minerals were also found to have this regularity. This observation became known as the law of constancy of interfacial angles. • Atoms of different minerals are clustered into geometric forms such as cubes, bricks, hexagons, etc. and so the ...
Crystallization

Crystallization is the (natural or artificial) process of formation of solid crystals precipitating from a solution, melt or more rarely deposited directly from a gas. Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs. In chemical engineering crystallization occurs in a crystallizer. Crystallization is therefore an aspect of precipitation, obtained through a variation of the solubility conditions of the solute in the solvent, as compared to precipitation due to chemical reaction.