Jens Prescher, Establishment and Optimization of Super
... rainwater which he originally called 'animalcules' [3]. This was the beginning of a completely new understanding of natural processes. For example, it was van Leeuwenhoek who could falsify the ruling opinion that small animals like fleas and mussels spontaneously develop from dirt and earth, but cou ...
... rainwater which he originally called 'animalcules' [3]. This was the beginning of a completely new understanding of natural processes. For example, it was van Leeuwenhoek who could falsify the ruling opinion that small animals like fleas and mussels spontaneously develop from dirt and earth, but cou ...
... liquid crystal placed between two polarizers (see, for example [8]). As has been shown in Ref. 9, depending on the mutual orientation of the main axes of polarizers, this modulator may produce to a good approximation either intensity-only or phase-only modulation of optical field. To demonstrate the ...
Localized measurement of longitudinal and transverse
... at which the power spectrum peaks corresponds well to the Doppler frequency shift. However, the Gaussian and exponential terms describing the transverse directional and longitudinal diffusive dynamics are not sufficient to describe the broadening of the Doppler peak. For the second case (gray solid ...
... at which the power spectrum peaks corresponds well to the Doppler frequency shift. However, the Gaussian and exponential terms describing the transverse directional and longitudinal diffusive dynamics are not sufficient to describe the broadening of the Doppler peak. For the second case (gray solid ...
Fluorescence Fidelity Depends on Filters
... emission path. Stray light from room lighting does not present a significant problem for confocal fluorescence microscopy, due to the fact that small diameter pinholes are used. However, this source of optical noise should be minimized in microscopy applications where pinholes are not used, such as ...
... emission path. Stray light from room lighting does not present a significant problem for confocal fluorescence microscopy, due to the fact that small diameter pinholes are used. However, this source of optical noise should be minimized in microscopy applications where pinholes are not used, such as ...
Analysis of a single-atom dipole trap
... single atom in our dipole trap we use the MOT cooling laser 共CL兲, red detuned to the unperturbed hyperfine transition 5 2S1/2, F = 2 → 5 2 P3/2, F⬘ = 3 共inset of Fig. 4兲 by ⌬CL = −5⌫ 共⌫ = 2 ⫻ 6 MHz is the natural linewidth兲. To avoid optical pumping to the 5 2S1/2, F = 1 hyperfine ground level we a ...
... single atom in our dipole trap we use the MOT cooling laser 共CL兲, red detuned to the unperturbed hyperfine transition 5 2S1/2, F = 2 → 5 2 P3/2, F⬘ = 3 共inset of Fig. 4兲 by ⌬CL = −5⌫ 共⌫ = 2 ⫻ 6 MHz is the natural linewidth兲. To avoid optical pumping to the 5 2S1/2, F = 1 hyperfine ground level we a ...
AOTF-based system for image cytometry
... for biological multispectral imaging are Lyot filter-based liquid-crystal tunable filters (LCTF)4-6, Fourier-transformed interferometry (FTI), pushbroom imagers (2-dimensional imaging spectrometers)7,8, and whiskbroom (raster-scanning) multispectral devices – usually part of confocal instruments9. A ...
... for biological multispectral imaging are Lyot filter-based liquid-crystal tunable filters (LCTF)4-6, Fourier-transformed interferometry (FTI), pushbroom imagers (2-dimensional imaging spectrometers)7,8, and whiskbroom (raster-scanning) multispectral devices – usually part of confocal instruments9. A ...
Joint Symposium of Waseda University and Peking University
... thin films, nanoplates, hollow spheres, and rhombdodecahedral cages, has been realized in aqueous solution in the presence of organic additives or specific templates. It has been revealed that polyanionic additives can exhibit significant influence on the morphology of the silver crystals. For examp ...
... thin films, nanoplates, hollow spheres, and rhombdodecahedral cages, has been realized in aqueous solution in the presence of organic additives or specific templates. It has been revealed that polyanionic additives can exhibit significant influence on the morphology of the silver crystals. For examp ...
Photofragmentation-laser induced fluorescence: a
... pumping wavelengths, X and X2, depends both on the type of molecular species being detected as well as the type of high energy driver laser used to excite the dye lasers. For example, for some chemical systems either the fundamental wavelength from the driver laser or some harmonic of the fundamenta ...
... pumping wavelengths, X and X2, depends both on the type of molecular species being detected as well as the type of high energy driver laser used to excite the dye lasers. For example, for some chemical systems either the fundamental wavelength from the driver laser or some harmonic of the fundamenta ...
Single Photon Sources - University of Rochester
... The field of quantum cryptography promises the creation of indecipherably secure communication utilizing the principles of quantum mechanics. Even with the advent of extremely powerful quantum computers, the security of information transferred by quantum communication systems remains unthreatened. W ...
... The field of quantum cryptography promises the creation of indecipherably secure communication utilizing the principles of quantum mechanics. Even with the advent of extremely powerful quantum computers, the security of information transferred by quantum communication systems remains unthreatened. W ...
Modulation of spatial coherence of optical field by means of liquid
... liquid crystal placed between two polarizers (see, for example [8]). As has been shown in Ref. 9, depending on the mutual orientation of the main axes of polarizers, this modulator may produce to a good approximation either intensity-only or phase-only modulation of optical field. To demonstrate the ...
... liquid crystal placed between two polarizers (see, for example [8]). As has been shown in Ref. 9, depending on the mutual orientation of the main axes of polarizers, this modulator may produce to a good approximation either intensity-only or phase-only modulation of optical field. To demonstrate the ...
Lecture 18
... microscope can be characterized by the modulation transfer function (MTF) • MTF is measurement of microscope's ability to transfer contrast from the specimen to the image plane at specific resolution. • Incorporates resolution and contrast into one specification ...
... microscope can be characterized by the modulation transfer function (MTF) • MTF is measurement of microscope's ability to transfer contrast from the specimen to the image plane at specific resolution. • Incorporates resolution and contrast into one specification ...
Raman Spectroscopy: Introductory Tutorial
... Organic: The Handbook of Infrared and Raman Characteristic Frequencies of Organic Molecules by Daimay Lin-Vien, et al ...
... Organic: The Handbook of Infrared and Raman Characteristic Frequencies of Organic Molecules by Daimay Lin-Vien, et al ...
Sec. 10.3 - Midland Park School District
... volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of particles. Further, one mole (or 6.02 x 1023 particles) of a gas (no matter what it is) will always have the same volume. ...
... volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of particles. Further, one mole (or 6.02 x 1023 particles) of a gas (no matter what it is) will always have the same volume. ...
Rotational Dynamics of Naphthalene-Labeled Cross
... samples at 320 nm was 0.2. B. Characterization. Time-dependent decay of fluorescence anisotropy was measured by using the time-correlated single photon counting technique. The frequency doubled output of a Spectra Physics mode-locked, Nd:YAG laser was used to synchronously pump a dye laser. The dye ...
... samples at 320 nm was 0.2. B. Characterization. Time-dependent decay of fluorescence anisotropy was measured by using the time-correlated single photon counting technique. The frequency doubled output of a Spectra Physics mode-locked, Nd:YAG laser was used to synchronously pump a dye laser. The dye ...
Determination of bandwidth and beamwidth of a
... The acronym LASER stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. In contrast to conventional light sources a laser is monochromatic and coherent over a long distance. These characteristics are usefull for many applications in science where e.g. constant beamwidths are demanded. ...
... The acronym LASER stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. In contrast to conventional light sources a laser is monochromatic and coherent over a long distance. These characteristics are usefull for many applications in science where e.g. constant beamwidths are demanded. ...
A short introduction to light and electron microscopy
... For point objects that are self-luminous the resolving power of the microscope is defined as: d = 0.61 λ/NA d is the minimum resolved distance in µm, λ is the wavelength, and NA is the numerical aperture of the objective lens. The equation describes the Rayleigh criterion for the resolution of two c ...
... For point objects that are self-luminous the resolving power of the microscope is defined as: d = 0.61 λ/NA d is the minimum resolved distance in µm, λ is the wavelength, and NA is the numerical aperture of the objective lens. The equation describes the Rayleigh criterion for the resolution of two c ...
Sidelobe decline in single-photon 4Pi microscopy by Toraldo rings
... Confocal scanning microscopy is an imaging technique whose main feature is its optical sectioning capacity (Wilson, 1990). The confocal technique was specifically designed to improve the axial resolution. However, it is notable that, due to the laws of diffraction, the resolution in the direction of ...
... Confocal scanning microscopy is an imaging technique whose main feature is its optical sectioning capacity (Wilson, 1990). The confocal technique was specifically designed to improve the axial resolution. However, it is notable that, due to the laws of diffraction, the resolution in the direction of ...
Isotropic Diffraction-Limited Focusing Using a Single Objective Lens
... side lobe amplitudes [9]. A simulation of a pointlike object image obtained with ISO focusing and confocal detection is given in Fig. 6(b). We found a good agreement between the experimental data and the simulation. The observed discrepancy is certainly due to a nonoptimal spot formation, because IS ...
... side lobe amplitudes [9]. A simulation of a pointlike object image obtained with ISO focusing and confocal detection is given in Fig. 6(b). We found a good agreement between the experimental data and the simulation. The observed discrepancy is certainly due to a nonoptimal spot formation, because IS ...
Basic Fluorescence Principles I
... Robert Boyle (1664) was inspired by Monardes’ report and investigated this system more fully. He discovered that after many infusions the wood lost its power to give color to the water and concluded that there was some “essential salt” in the wood responsible for the effect. He also discovered tha ...
... Robert Boyle (1664) was inspired by Monardes’ report and investigated this system more fully. He discovered that after many infusions the wood lost its power to give color to the water and concluded that there was some “essential salt” in the wood responsible for the effect. He also discovered tha ...
Optical Microscopy Beyond the Diffraction Limit
... phenomena that were not previously accessible. The NAIL subsurface microscopy technique we describe significantly increases the NA without introducing an additional spherical aberration. Using the NAIL technique in the near infrared inspection of a Si IC, the theoretical lateral spatial resolution l ...
... phenomena that were not previously accessible. The NAIL subsurface microscopy technique we describe significantly increases the NA without introducing an additional spherical aberration. Using the NAIL technique in the near infrared inspection of a Si IC, the theoretical lateral spatial resolution l ...
Absorption Measurements on PC1
... meant to reduce the light intensity reaching the sample and eventually the light detector. The level of PMT counts should be around 100K. It is important to keep the PMT gain knob position at its maximum (10). The absorption measurement is performed in two steps: ...
... meant to reduce the light intensity reaching the sample and eventually the light detector. The level of PMT counts should be around 100K. It is important to keep the PMT gain knob position at its maximum (10). The absorption measurement is performed in two steps: ...
Tomographic Interference Microscopy of Living Cells
... cells gives important information about morphology, spatial distribution of proteins and concentration of chemical drugs inside the cell. In microscopy three types of samples are usually investigated: fluorescent or emissive samples; stained or amplitude samples; and transparent or phase samples. Fo ...
... cells gives important information about morphology, spatial distribution of proteins and concentration of chemical drugs inside the cell. In microscopy three types of samples are usually investigated: fluorescent or emissive samples; stained or amplitude samples; and transparent or phase samples. Fo ...
Two-Color Two-Photon Excitation Using Femtosecond Laser Pulses
... extend the wavelength range where the Ti:Sa laser can be used under retention of all advantages of two-photon excitation. According to theoretical considerations, spatial resolution13 and penetration ability,14 depending on the microscopical setup, are expected to improve for 2c2p excitation compare ...
... extend the wavelength range where the Ti:Sa laser can be used under retention of all advantages of two-photon excitation. According to theoretical considerations, spatial resolution13 and penetration ability,14 depending on the microscopical setup, are expected to improve for 2c2p excitation compare ...
Diffusing-wave spectroscopy in a shear flow
... propagation of light in a strongly scattering medium in terms of a random walk. Thus the transport of light is assumed to be diffusive. 6 The photon-diffusion approximation has recently been exploited to develop an expression for the temporal fluctuations of the intensity of the scattered light and ...
... propagation of light in a strongly scattering medium in terms of a random walk. Thus the transport of light is assumed to be diffusive. 6 The photon-diffusion approximation has recently been exploited to develop an expression for the temporal fluctuations of the intensity of the scattered light and ...
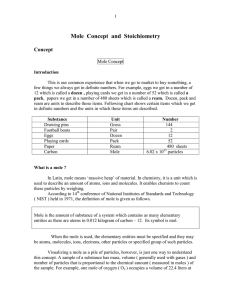
Mole Concept and Stoichiometry
... and contains about 6.022 x 1023 molecules of oxygen. Measuring one of these quantities allows the calculation of the others and this is frequently done in stoichiometry. One interpretation : A specific number of particles When a quantity of particles is to be described, mole is a grouping unit analo ...
... and contains about 6.022 x 1023 molecules of oxygen. Measuring one of these quantities allows the calculation of the others and this is frequently done in stoichiometry. One interpretation : A specific number of particles When a quantity of particles is to be described, mole is a grouping unit analo ...
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy

Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) is a correlation analysis of fluctuation of the fluorescence intensity. The analysis provides parameters of the physics under the fluctuations. One of the interesting applications of this is an analysis of the concentration fluctuations of fluorescent particles (molecules) in solution. In this application, the fluorescence emitted from a very tiny space in solution containing a small number of fluorescent particles (molecules) is observed. The fluorescence intensity is fluctuating due to Brownian motion of the particles. In other words, the number of the particles in the sub-space defined by the optical system is randomly changing around the average number. The analysis gives the average number of fluorescent particles and average diffusion time, when the particle is passing through the space. Eventually, both the concentration and size of the particle (molecule) are determined. Both parameters are important in biochemical research, biophysics, and chemistry.FCS is such a sensitive analytical tool because it observes a small number of molecules (nanomolar to picomolar concentrations) in a small volume (~1μm3). In contrast to other methods (such as HPLC analysis) FCS has no physical separation process; instead, it achieves its spatial resolution through its optics. Furthermore, FCS enables observation of fluorescence-tagged molecules in the biochemical pathway in intact living cells. This opens a new area, ""in situ or in vivo biochemistry"": tracing the biochemical pathway in intact cells and organs.Commonly, FCS is employed in the context of optical microscopy, in particular Confocal microscopy or two-photon excitation microscopy. In these techniques light is focused on a sample and the measured fluorescence intensity fluctuations (due to diffusion, physical or chemical reactions, aggregation, etc.) are analyzed using the temporal autocorrelation. Because the measured property is essentially related to the magnitude and/or the amount of fluctuations, there is an optimum measurement regime at the level when individual species enter or exit the observation volume (or turn on and off in the volume). When too many entities are measured at the same time the overall fluctuations are small in comparison to the total signal and may not be resolvable – in the other direction, if the individual fluctuation-events are too sparse in time, one measurement may take prohibitively too long. FCS is in a way the fluorescent counterpart to dynamic light scattering, which uses coherent light scattering, instead of (incoherent) fluorescence.When an appropriate model is known, FCS can be used to obtain quantitative information such as diffusion coefficients hydrodynamic radii average concentrations kinetic chemical reaction rates singlet-triplet dynamicsBecause fluorescent markers come in a variety of colors and can be specifically bound to a particular molecule (e.g. proteins, polymers, metal-complexes, etc.), it is possible to study the behavior of individual molecules (in rapid succession in composite solutions). With the development of sensitive detectors such as avalanche photodiodes the detection of the fluorescence signal coming from individual molecules in highly dilute samples has become practical. With this emerged the possibility to conduct FCS experiments in a wide variety of specimens, ranging from materials science to biology. The advent of engineered cells with genetically tagged proteins (like green fluorescent protein) has made FCS a common tool for studying molecular dynamics in living cells.