1 3. Molecular mass transport 3.1 Introduction to mass transfer 3.2
... Certain molecules diffuse as molecules, while others which are designated as electrolytes ionize in solutions and diffuse as ions. For example, sodium chloride (NaCl), diffuses in water as ions Na + and Cl-. Though each ions has a different mobility, the electrical neutrality of the solution indicat ...
... Certain molecules diffuse as molecules, while others which are designated as electrolytes ionize in solutions and diffuse as ions. For example, sodium chloride (NaCl), diffuses in water as ions Na + and Cl-. Though each ions has a different mobility, the electrical neutrality of the solution indicat ...
Confocal microscopy with a volume holographic filter
... in-focus point-source objects are imaged exactly inside the pinhole and give maximal intensity. An out-offocus object, even when it is on axis, is equivalent to an extended source on the input focal plane. The off-axis portion of this extended source is filtered out by the limited aperture of the pi ...
... in-focus point-source objects are imaged exactly inside the pinhole and give maximal intensity. An out-offocus object, even when it is on axis, is equivalent to an extended source on the input focal plane. The off-axis portion of this extended source is filtered out by the limited aperture of the pi ...
Light sheet-based fluorescence microscopy: more dimensions, more
... antiparallel manner commonly known as epifluorescence. Since the lateral extent of the point spread function (PSF) is smaller than its axial extent, the use of a single lens always results in an anisotropic PSF, which is elongated along the z axis. In LSFM, the specimen is illuminated from the side ...
... antiparallel manner commonly known as epifluorescence. Since the lateral extent of the point spread function (PSF) is smaller than its axial extent, the use of a single lens always results in an anisotropic PSF, which is elongated along the z axis. In LSFM, the specimen is illuminated from the side ...
Medical Laboratory Instrumentation 2010-2011 Third Year
... almost any type of sample. • AAS are that no information is obtained on the chemical form of the analyte (no “speciation”) and that often only one element can be etermined at a time. • This last disadvantage makes AAS of very limited use for qualitative analysis. • AAS is used almost exclusively for ...
... almost any type of sample. • AAS are that no information is obtained on the chemical form of the analyte (no “speciation”) and that often only one element can be etermined at a time. • This last disadvantage makes AAS of very limited use for qualitative analysis. • AAS is used almost exclusively for ...
A Theoretical Model of the Water Vapor Diffusion through the
... temperature T, if known the saturation water vapor pressure value , at the temperature T0, for example: ...
... temperature T, if known the saturation water vapor pressure value , at the temperature T0, for example: ...
Lowering of the L10 ordering temperature of FePt
... Before and after the complete annealing procedure, the particles are characterized by scanning electron microscopy 共SEM兲 and atomic force microscopy 共AFM兲 to determine particle diameters and to check for possible particle agglomerations. Figure 1 shows SEM images before the sample is exposed to 1016 ...
... Before and after the complete annealing procedure, the particles are characterized by scanning electron microscopy 共SEM兲 and atomic force microscopy 共AFM兲 to determine particle diameters and to check for possible particle agglomerations. Figure 1 shows SEM images before the sample is exposed to 1016 ...
Quantitative chemistry 1
... Base SI units of some physical quantities used in chemistry; volume is a derived unit as it depends on length. ...
... Base SI units of some physical quantities used in chemistry; volume is a derived unit as it depends on length. ...
File
... The volume of 1 mole of a solid and liquid are very different depending on the substance However, the volume of one mole of a gas is equal for every gas at the same ...
... The volume of 1 mole of a solid and liquid are very different depending on the substance However, the volume of one mole of a gas is equal for every gas at the same ...
Optics in Confocal Microscopy
... When white light is brought to a focus by a simple single-element lens, such as a magnifying glass, the blue component is refracted more by the glass and comes to a focus closer to the lens than the red. This separation of colours along the axis is called longitudinal chromatic aberration. An image ...
... When white light is brought to a focus by a simple single-element lens, such as a magnifying glass, the blue component is refracted more by the glass and comes to a focus closer to the lens than the red. This separation of colours along the axis is called longitudinal chromatic aberration. An image ...
Monte Carlo Studies of Particle Diffusion on a
... one decreases the particle energy and the jump rate. For the kMC simulations we use the BKL algorithm [4]. The algorithm operates in a space of possible events. In contrast to the standard technique, where we consider fixed time intervals at which a jump may occur with a certain probability, the BKL ...
... one decreases the particle energy and the jump rate. For the kMC simulations we use the BKL algorithm [4]. The algorithm operates in a space of possible events. In contrast to the standard technique, where we consider fixed time intervals at which a jump may occur with a certain probability, the BKL ...
File - Evergreen Tutor Zone
... Using the masses and densities of other gases, we find that 1 mole of any/every gas occupies 22,4 dm3 ...
... Using the masses and densities of other gases, we find that 1 mole of any/every gas occupies 22,4 dm3 ...
Fluorescence: Fluorescence studies prone to self
... oriented either parallel or perpendicular to the plane of polarization of the incident beam. ...
... oriented either parallel or perpendicular to the plane of polarization of the incident beam. ...
Lecture 3
... Flow diagram for revolutionary science:Extraordinary claims that become accepted and are integrated into “normal science.” ...
... Flow diagram for revolutionary science:Extraordinary claims that become accepted and are integrated into “normal science.” ...
Conroy2005-SurfaceMetrology.pdf
... however the wavelength of the light would need to be at least 750 nm in order to get reliable data. One common problem with optical systems is that mixtures of materials that have very different optical properties can give errors in measurement. In the past it has been overcome by adding a constant ...
... however the wavelength of the light would need to be at least 750 nm in order to get reliable data. One common problem with optical systems is that mixtures of materials that have very different optical properties can give errors in measurement. In the past it has been overcome by adding a constant ...
Effect of cytochrome c on the phase behavior of charged
... To evaluate the amount of bound protein from the confocal images, we first measured the background intensities of samples containing the buffer or a solution of the labeled protein in buffer only. These intensities were compared with the intensity in a sample containing the vesicles and the protein ...
... To evaluate the amount of bound protein from the confocal images, we first measured the background intensities of samples containing the buffer or a solution of the labeled protein in buffer only. These intensities were compared with the intensity in a sample containing the vesicles and the protein ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... for further experiments. In a conical flask 0.5ml of 0.01M HAucl 4 is is dissolved in 20ml of deionised water, then drop wise green tea extract is added with stirring on a magnetic stirrer until the colour changes to wine red which indicates the formation of gold nanoparticles. 2.4. Instrumentation: ...
... for further experiments. In a conical flask 0.5ml of 0.01M HAucl 4 is is dissolved in 20ml of deionised water, then drop wise green tea extract is added with stirring on a magnetic stirrer until the colour changes to wine red which indicates the formation of gold nanoparticles. 2.4. Instrumentation: ...
Exponential and Power-Law Kinetics in Single-Molecule
... transient intensity, but with different time resolution. Panel b represents the complete time trace with an integration time of 5 ms, whereas panel c is a blow-up of a very short period of the whole transient with 100 µs integration time. Both traces show features characteristic for single-molecule ...
... transient intensity, but with different time resolution. Panel b represents the complete time trace with an integration time of 5 ms, whereas panel c is a blow-up of a very short period of the whole transient with 100 µs integration time. Both traces show features characteristic for single-molecule ...
L09 Instru Spectrofluorometery
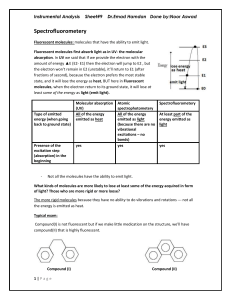
... Then to measure the intensity of the monochromatic emitted light, we’ll use a photocell *detector*(the photocell in UV designed to measure I° and It and take the ratio but here in spectrofluorometer it will measure the intensity of the monochromatic emitted light). Note the design of the spectrofluo ...
... Then to measure the intensity of the monochromatic emitted light, we’ll use a photocell *detector*(the photocell in UV designed to measure I° and It and take the ratio but here in spectrofluorometer it will measure the intensity of the monochromatic emitted light). Note the design of the spectrofluo ...
Transport Across The Cell Membrane
... • Facilitated Diffusion does NOT use ATP so is PASSIVE TRANSPORT. ...
... • Facilitated Diffusion does NOT use ATP so is PASSIVE TRANSPORT. ...
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
... improving, four centuries after scientists started using it. Perhaps the most important improvement in the past three decades has been confocal microscopy, in which a pair of pinhole apertures is used to collect only in-focus light in the focal plane – thereby allowing both a higher-resolution image ...
... improving, four centuries after scientists started using it. Perhaps the most important improvement in the past three decades has been confocal microscopy, in which a pair of pinhole apertures is used to collect only in-focus light in the focal plane – thereby allowing both a higher-resolution image ...
AP Chemistry Unit 1 Essential Questions Screencast 1
... Screencast 1-6 Dimensional Analysis 1. When converting a unit, how is the conversion factor set up? (what’s on top and bottom) 2. Correct answers in chemistry always include what 3 things? 3. When converting units with a power what is important to remember? Screencast 1-7 Basic Atomic Structure, Is ...
... Screencast 1-6 Dimensional Analysis 1. When converting a unit, how is the conversion factor set up? (what’s on top and bottom) 2. Correct answers in chemistry always include what 3 things? 3. When converting units with a power what is important to remember? Screencast 1-7 Basic Atomic Structure, Is ...
Vol 1 No 2.10
... by the same equation as that for the colloidal particles. For this reason, may be, irrespective of the sizes of the diffusing species, the Eqs. (1 & 2) have been always thought to be identical with the transport coefficients related by the Eq. (4). ...
... by the same equation as that for the colloidal particles. For this reason, may be, irrespective of the sizes of the diffusing species, the Eqs. (1 & 2) have been always thought to be identical with the transport coefficients related by the Eq. (4). ...
A Brief History of the Microscope and its Significance
... back aperture of the microscope objective. When the laser operates in the TEM00 mode, it forms a Gaussian beam; in that case an illumination pinhole aperture is not needed, because the light appears to originate from a point source at infinity. The laser beam may be expanded. With a high-NA microsco ...
... back aperture of the microscope objective. When the laser operates in the TEM00 mode, it forms a Gaussian beam; in that case an illumination pinhole aperture is not needed, because the light appears to originate from a point source at infinity. The laser beam may be expanded. With a high-NA microsco ...
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy

Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) is a correlation analysis of fluctuation of the fluorescence intensity. The analysis provides parameters of the physics under the fluctuations. One of the interesting applications of this is an analysis of the concentration fluctuations of fluorescent particles (molecules) in solution. In this application, the fluorescence emitted from a very tiny space in solution containing a small number of fluorescent particles (molecules) is observed. The fluorescence intensity is fluctuating due to Brownian motion of the particles. In other words, the number of the particles in the sub-space defined by the optical system is randomly changing around the average number. The analysis gives the average number of fluorescent particles and average diffusion time, when the particle is passing through the space. Eventually, both the concentration and size of the particle (molecule) are determined. Both parameters are important in biochemical research, biophysics, and chemistry.FCS is such a sensitive analytical tool because it observes a small number of molecules (nanomolar to picomolar concentrations) in a small volume (~1μm3). In contrast to other methods (such as HPLC analysis) FCS has no physical separation process; instead, it achieves its spatial resolution through its optics. Furthermore, FCS enables observation of fluorescence-tagged molecules in the biochemical pathway in intact living cells. This opens a new area, ""in situ or in vivo biochemistry"": tracing the biochemical pathway in intact cells and organs.Commonly, FCS is employed in the context of optical microscopy, in particular Confocal microscopy or two-photon excitation microscopy. In these techniques light is focused on a sample and the measured fluorescence intensity fluctuations (due to diffusion, physical or chemical reactions, aggregation, etc.) are analyzed using the temporal autocorrelation. Because the measured property is essentially related to the magnitude and/or the amount of fluctuations, there is an optimum measurement regime at the level when individual species enter or exit the observation volume (or turn on and off in the volume). When too many entities are measured at the same time the overall fluctuations are small in comparison to the total signal and may not be resolvable – in the other direction, if the individual fluctuation-events are too sparse in time, one measurement may take prohibitively too long. FCS is in a way the fluorescent counterpart to dynamic light scattering, which uses coherent light scattering, instead of (incoherent) fluorescence.When an appropriate model is known, FCS can be used to obtain quantitative information such as diffusion coefficients hydrodynamic radii average concentrations kinetic chemical reaction rates singlet-triplet dynamicsBecause fluorescent markers come in a variety of colors and can be specifically bound to a particular molecule (e.g. proteins, polymers, metal-complexes, etc.), it is possible to study the behavior of individual molecules (in rapid succession in composite solutions). With the development of sensitive detectors such as avalanche photodiodes the detection of the fluorescence signal coming from individual molecules in highly dilute samples has become practical. With this emerged the possibility to conduct FCS experiments in a wide variety of specimens, ranging from materials science to biology. The advent of engineered cells with genetically tagged proteins (like green fluorescent protein) has made FCS a common tool for studying molecular dynamics in living cells.