Fundamental of Organic chemistry
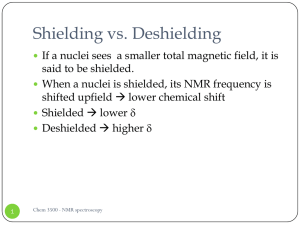
... <1> One sp—sp ________ is formed between two carbon atoms. <2> Two pairs of unhybridized. 2p orbitals overlap each other laterally to form two it bonds which are mutually at right angles to each other. <3> The difference in bonding and electronic structure of the C— C, C=C and CC bonds is reflected ...
... <1> One sp—sp ________ is formed between two carbon atoms. <2> Two pairs of unhybridized. 2p orbitals overlap each other laterally to form two it bonds which are mutually at right angles to each other. <3> The difference in bonding and electronic structure of the C— C, C=C and CC bonds is reflected ...
Grade 10 NSC Chemistry Curriculum
... and oxygen; and - the synthesis reaction that occurs when hydrogen burns in oxygen to form water. (Why do we consider these reactions to be chemical changes?) • Describe - the energy involved in these chemical changes as much larger than those of the physical change i.e. hydrogen is used as a rocket ...
... and oxygen; and - the synthesis reaction that occurs when hydrogen burns in oxygen to form water. (Why do we consider these reactions to be chemical changes?) • Describe - the energy involved in these chemical changes as much larger than those of the physical change i.e. hydrogen is used as a rocket ...
Problems - El Camino College
... periodic wble, ii helps you remember their namci.. Another reason for doing this is that the 1 a Jue of the periodic table cannot be overstated. You are usmg 11 nO\\ 1n Chapter 6 to learn the system of naming chemical compounds; after that, it \VIII help you in many other ways. For example. you will ...
... periodic wble, ii helps you remember their namci.. Another reason for doing this is that the 1 a Jue of the periodic table cannot be overstated. You are usmg 11 nO\\ 1n Chapter 6 to learn the system of naming chemical compounds; after that, it \VIII help you in many other ways. For example. you will ...
4.1 Introduction to Atoms
... move in certain orbits (similar to how the planets orbit the sun). ...
... move in certain orbits (similar to how the planets orbit the sun). ...
FREE Sample Here
... The results of an experiment are referred to as the data. Data should be observable and objective, rather than subjective or based on opinion. ...
... The results of an experiment are referred to as the data. Data should be observable and objective, rather than subjective or based on opinion. ...
KEY - chem.uwec.edu
... transport system (and “reverse” electron transport by NADH oxidation by NADH-Q oxidoreductase? QH2FAD). This may produce another ATP in the proton gradient formed. The end product would be succinate. 5. Some organisms can grow using ethanol as their sole carbon source (and I believe I have spotted ...
... transport system (and “reverse” electron transport by NADH oxidation by NADH-Q oxidoreductase? QH2FAD). This may produce another ATP in the proton gradient formed. The end product would be succinate. 5. Some organisms can grow using ethanol as their sole carbon source (and I believe I have spotted ...
Page 1 MISE - Physical Basis of Chemistry First Set of Problems
... If this cartoon were to scale…. and represented a typical hydrogen atom… The diameter of the hydrogen atom’s nucleus would about 1 x 10-13 cm and have a mass of about 1.00 amu. The diameter of the entire hydrogen is about 1 x 10-8 cm and its mass is about the same (1.00 amu). Please answer the follo ...
... If this cartoon were to scale…. and represented a typical hydrogen atom… The diameter of the hydrogen atom’s nucleus would about 1 x 10-13 cm and have a mass of about 1.00 amu. The diameter of the entire hydrogen is about 1 x 10-8 cm and its mass is about the same (1.00 amu). Please answer the follo ...
CHEMISTRY 123-07 Midterm #1 – Answer key October 14, 2010
... PART II: SHORT ANSWER (Each short answer question has a 1-point value!!) 31. Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per volume of solution in liters. 32. Ions that contain atoms of more than one element are called polyatomic ions. 33. Proton donors are known as Brønsted acids. 34. A co ...
... PART II: SHORT ANSWER (Each short answer question has a 1-point value!!) 31. Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per volume of solution in liters. 32. Ions that contain atoms of more than one element are called polyatomic ions. 33. Proton donors are known as Brønsted acids. 34. A co ...
Periodic Table Extra Practice ANSWER KEY 2014
... 1.8 I can describe the relationship between isotopes of the same element. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different masses (or weights) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. All atoms of the same element must have the same number of protons (and thus the same number of el ...
... 1.8 I can describe the relationship between isotopes of the same element. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different masses (or weights) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. All atoms of the same element must have the same number of protons (and thus the same number of el ...
Chapter 6 Chemical Composition
... 1. To understand the concept of average mass 2. To learn how counting can be done by weighing 3. To understand atomic mass and learn how it is determined 4. To understand the mole concept and Avogadro’s number 5. To learn to convert among moles, mass, and number of atoms ...
... 1. To understand the concept of average mass 2. To learn how counting can be done by weighing 3. To understand atomic mass and learn how it is determined 4. To understand the mole concept and Avogadro’s number 5. To learn to convert among moles, mass, and number of atoms ...
A – Z - washburnsciencelies
... This occurs when two smaller nuclei combine together to form a single larger nuclei. This produces far more energy than a fission reaction, and also does not have a dangerous by-product. However we currently don’t have the means to use it as a reliable energy source, as we barely get more energy out ...
... This occurs when two smaller nuclei combine together to form a single larger nuclei. This produces far more energy than a fission reaction, and also does not have a dangerous by-product. However we currently don’t have the means to use it as a reliable energy source, as we barely get more energy out ...
N - WordPress.com
... tryptamine, and serotonin) and xenobiotics based on the structures of these endogenous neurotransmitters are metabolized, however, via oxidative deamination by a specialized family of enzymes called monoamine oxidases (MAOs). • Differences between MAO & CYP enzymes?? ...
... tryptamine, and serotonin) and xenobiotics based on the structures of these endogenous neurotransmitters are metabolized, however, via oxidative deamination by a specialized family of enzymes called monoamine oxidases (MAOs). • Differences between MAO & CYP enzymes?? ...
1) Basic familiarity with Atomic Labels. You will need a Periodic
... 3) Basic familiarity with isotopes and average atomic masses 3.1) Carbon has two naturally occurring isotopes, 12C and 13C. How are they different? What are the two naturally occurring isotopes of boron? The isotope of hydrogen, 2H, is called deuterium and has its own atomic symbol, D. How many prot ...
... 3) Basic familiarity with isotopes and average atomic masses 3.1) Carbon has two naturally occurring isotopes, 12C and 13C. How are they different? What are the two naturally occurring isotopes of boron? The isotope of hydrogen, 2H, is called deuterium and has its own atomic symbol, D. How many prot ...
1 Atoms and Molecules
... electrons from four hydrogen atoms, is oxidized as it loses them to two oxygen atoms. The oxygen atoms of O2 , which had shared their electrons with each other, are reduced as they gain electrons from the carbon atom and from the hydrogen atoms. Electronegative implications: Because the electronegat ...
... electrons from four hydrogen atoms, is oxidized as it loses them to two oxygen atoms. The oxygen atoms of O2 , which had shared their electrons with each other, are reduced as they gain electrons from the carbon atom and from the hydrogen atoms. Electronegative implications: Because the electronegat ...
IsotopeGeochemistry Chapter1 - Earth and Atmospheric Sciences
... rise. Comparing this with stable isotope geothermometry shows that melting lagged warming (not too surprisingly). Other isotopic studies revealed changes in the ocean circulation system as the last ice age ended. Changes in ocean circulation may also be an important feedback mechanism affecting clim ...
... rise. Comparing this with stable isotope geothermometry shows that melting lagged warming (not too surprisingly). Other isotopic studies revealed changes in the ocean circulation system as the last ice age ended. Changes in ocean circulation may also be an important feedback mechanism affecting clim ...
CHEM 1405 Practice Exam #2
... 4) How many valence electrons do atoms with the following electron configurations have? A) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p4 B) 1s22s22p63s2 C) 1s22s22p63s23p64s1 D) 1s22s22p6 5) Fill in the chart below for each of the following isotopes. ...
... 4) How many valence electrons do atoms with the following electron configurations have? A) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p4 B) 1s22s22p63s2 C) 1s22s22p63s23p64s1 D) 1s22s22p6 5) Fill in the chart below for each of the following isotopes. ...
50 Frequently Forgotten Facts Answer Key
... b) Write the decay for K-37:________ 3719K 0+1e + 3718Ar ____________ c) Write the decay for P-32:_______ 3215P 0-1e + 3216S __________ 5) Artificial Transmutation is when a relatively stable nucleus is impacted by a particle bullet at high speeds and becomes an unstable nucleus of a different e ...
... b) Write the decay for K-37:________ 3719K 0+1e + 3718Ar ____________ c) Write the decay for P-32:_______ 3215P 0-1e + 3216S __________ 5) Artificial Transmutation is when a relatively stable nucleus is impacted by a particle bullet at high speeds and becomes an unstable nucleus of a different e ...
Final review packet
... There will be a total of 80 multiple-choice questions, given in a 1 hour and 45 minutes block of exam time. The exam time includes the time it takes to pass out exam materials at the start of the exam. You may use a non-programmable calculator. (No cell phones. No graphing calculators.) It is highly ...
... There will be a total of 80 multiple-choice questions, given in a 1 hour and 45 minutes block of exam time. The exam time includes the time it takes to pass out exam materials at the start of the exam. You may use a non-programmable calculator. (No cell phones. No graphing calculators.) It is highly ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.