Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds
... 11. Nicotine has the formula CxHyNz. To determine its composition, a sample is burned in excess oxygen, producing the following results: 1.0 mol of CO2 0.70 mol of H2O 0.20 mol of NO2 Assume that all the atoms in nicotine are present as products. a. Determine the number of moles of carbon present in ...
... 11. Nicotine has the formula CxHyNz. To determine its composition, a sample is burned in excess oxygen, producing the following results: 1.0 mol of CO2 0.70 mol of H2O 0.20 mol of NO2 Assume that all the atoms in nicotine are present as products. a. Determine the number of moles of carbon present in ...
AQA Additional Sci C2 Revision Guide
... Alloys are usually made from two or more different metals. Alloying metals changes their properties and results in new materials which are more suited to their different uses. Most metals in everyday use are alloys e.g. pure gold is too soft to make jewellery but it can be hardened by adding metals ...
... Alloys are usually made from two or more different metals. Alloying metals changes their properties and results in new materials which are more suited to their different uses. Most metals in everyday use are alloys e.g. pure gold is too soft to make jewellery but it can be hardened by adding metals ...
Slide 1
... fraction of remaining soil organic matter (SOC) – approximated by the calculated value of fSOC 13Cf isotopic composition of SOC when sampled 13Ci isotopic composition of input from biomass α fractionation factor between SOC and respired CO2 e efficiency of microbial assimilation t fraction of assi ...
... fraction of remaining soil organic matter (SOC) – approximated by the calculated value of fSOC 13Cf isotopic composition of SOC when sampled 13Ci isotopic composition of input from biomass α fractionation factor between SOC and respired CO2 e efficiency of microbial assimilation t fraction of assi ...
Atomic Structure Powerpoints - Warren County Public Schools
... • Properties of elements repeat in a predictable way when atomic numbers are used to arrange elements into groups;; • The pattern of repeating properties is the periodic law;; ...
... • Properties of elements repeat in a predictable way when atomic numbers are used to arrange elements into groups;; • The pattern of repeating properties is the periodic law;; ...
Counting Atoms
... • Copper consists of 69.15% copper-63, which has an atomic mass of 62.929 601 amu, and 30.85% copper-65, which has an atomic mass of 64.927 794 amu. • The average atomic mass of copper can be calculated by multiplying the atomic mass of each isotope by its relative abundance (expressed in decimal fo ...
... • Copper consists of 69.15% copper-63, which has an atomic mass of 62.929 601 amu, and 30.85% copper-65, which has an atomic mass of 64.927 794 amu. • The average atomic mass of copper can be calculated by multiplying the atomic mass of each isotope by its relative abundance (expressed in decimal fo ...
Scott et al. 2006
... world. In fact, microorganisms examined in this study could be placed within one of three metabolic groups: (1) heterotrophs that grow by oxidizing compounds containing three or more carbon-to-carbon bonds (fermenters and organotrophs), (2) autotrophs that grow by taking up carbon dioxide (chemolito ...
... world. In fact, microorganisms examined in this study could be placed within one of three metabolic groups: (1) heterotrophs that grow by oxidizing compounds containing three or more carbon-to-carbon bonds (fermenters and organotrophs), (2) autotrophs that grow by taking up carbon dioxide (chemolito ...
Cumulative Review, entire quarter
... There are 2 nitrogens, 8 hydrogens, 2 carbons and 4 oxygens in one molecule. The nitrogen and hydrogen occur in two groups of 4 hydrogens and one nitrogen The carbons and oxygens occur as one group of 2 carbons and 4 oxygens. Chemical compounds are electrically neutral; if composed of charged ions, ...
... There are 2 nitrogens, 8 hydrogens, 2 carbons and 4 oxygens in one molecule. The nitrogen and hydrogen occur in two groups of 4 hydrogens and one nitrogen The carbons and oxygens occur as one group of 2 carbons and 4 oxygens. Chemical compounds are electrically neutral; if composed of charged ions, ...
U-6 Stoichiometry Notes
... 2. Solve one stoichiometry problem for each reactant (A & B). Solve each for quantity of the same product (ideally the one you are asked about). 3. Compare answers to step 2. Whichever reactant (A or B) produces the LEAST amount of product is the limiting reactant. 4. The smaller amount of product i ...
... 2. Solve one stoichiometry problem for each reactant (A & B). Solve each for quantity of the same product (ideally the one you are asked about). 3. Compare answers to step 2. Whichever reactant (A or B) produces the LEAST amount of product is the limiting reactant. 4. The smaller amount of product i ...
AlcoholsandEthersNote
... General Formula : R—OH (containing at least one hydroxyl functional group); Naming Alcohols : two commonly used methods are possible: ...
... General Formula : R—OH (containing at least one hydroxyl functional group); Naming Alcohols : two commonly used methods are possible: ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... • Become proficient in inorganic nomenclature: names and formulas of compounds (LAB) • Be able to name and write formulas for a few types of simple organic compounds. Daley/Larson ...
... • Become proficient in inorganic nomenclature: names and formulas of compounds (LAB) • Be able to name and write formulas for a few types of simple organic compounds. Daley/Larson ...
Describing Matter from Text
... Chemical Properties of Matter Unlike physical properties of matter, some properties can’t be observed just by looking at or touching a substance. A chemical property is a characteristic of a pure substance that describes its ability to change into different substances. To observe the chemical proper ...
... Chemical Properties of Matter Unlike physical properties of matter, some properties can’t be observed just by looking at or touching a substance. A chemical property is a characteristic of a pure substance that describes its ability to change into different substances. To observe the chemical proper ...
CHAPTER 2: ATOMS, MOLECULES AND IONS ULES AND IONS
... Mass of reactant is equal to mass of product. Law of Definite Proportion: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass. Law of Multiple Proportions: When chemical elements combine to form a compound, they do so in a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
... Mass of reactant is equal to mass of product. Law of Definite Proportion: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass. Law of Multiple Proportions: When chemical elements combine to form a compound, they do so in a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
1 Unit 4 – Conservation of Mass and Stoichiometry
... 1. Write the symbols for the ions side by side. ALWAYS write the cation first! 2. Cross over the charges by using the absolute value of each ion’s charge as the subscript for the other ion 3. Check that the subscripts are in smallest whole number ratio E. The Stock System of Nomenclature 1. Roman nu ...
... 1. Write the symbols for the ions side by side. ALWAYS write the cation first! 2. Cross over the charges by using the absolute value of each ion’s charge as the subscript for the other ion 3. Check that the subscripts are in smallest whole number ratio E. The Stock System of Nomenclature 1. Roman nu ...
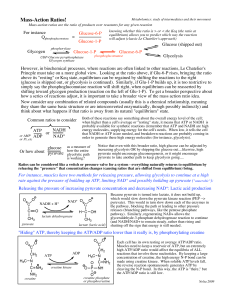
Mass-Action Ratios!
... simply say the phosphoglucomutase reaction will shift right, when equilibrium can be reasserted by shifting toward glycogen production (reaction on the left of Glu-1-P). To get a broader perspective about how a series of reactions adjust, it is important to take a broader view of the mass action rat ...
... simply say the phosphoglucomutase reaction will shift right, when equilibrium can be reasserted by shifting toward glycogen production (reaction on the left of Glu-1-P). To get a broader perspective about how a series of reactions adjust, it is important to take a broader view of the mass action rat ...
Chemical Reactions
... Bellringer, tell me what type of reaction is shown in each problem.Also, take 1 of the ten and work it out completely. ...
... Bellringer, tell me what type of reaction is shown in each problem.Also, take 1 of the ten and work it out completely. ...
CHEM 1405 Practice Exam #2 (2015)
... 10) How many valence electrons does the representative element with the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p5 possess? A) 5 B) 6 11) The compound Au2Se3 is classified as which of the following? A) binary ionic B) ternary ionic C) 7 D) 2 C) binary molecular D) binary acid 12) Which of the following ...
... 10) How many valence electrons does the representative element with the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p5 possess? A) 5 B) 6 11) The compound Au2Se3 is classified as which of the following? A) binary ionic B) ternary ionic C) 7 D) 2 C) binary molecular D) binary acid 12) Which of the following ...
atoms. - Unicam
... would have seemed if these predictions had been incorrect but fortunately for him three of these missing elements were discovered by others within 15 years (ie within his lifetime). The first of these Mendeleev had called eka-aluminium because it was the one after aluminium (eka = 1 in Sanskrit) and ...
... would have seemed if these predictions had been incorrect but fortunately for him three of these missing elements were discovered by others within 15 years (ie within his lifetime). The first of these Mendeleev had called eka-aluminium because it was the one after aluminium (eka = 1 in Sanskrit) and ...
Atoms - Peoria Public Schools
... The mass number of chlorine-37 is 37. Using the periodic table shows the atomic number of chlorine is 17. Atomic number = number of protons = number of electrons = 17 protons and electrons Number of neutrons = mass number – atomic number ...
... The mass number of chlorine-37 is 37. Using the periodic table shows the atomic number of chlorine is 17. Atomic number = number of protons = number of electrons = 17 protons and electrons Number of neutrons = mass number – atomic number ...
chemistry-2nd-edition-julia-burdge-solution
... Rubidium is an alkali metal. It only forms a 1 cation. The polyatomic ion nitrite, NO 2 , has a 1 charge. Because the charges on the cation and anion are numerically equal, the ions combine in a oneto-one ratio. The correct formula is RbNO2. Potassium is an alkali metal. It only forms a 1 cation ...
... Rubidium is an alkali metal. It only forms a 1 cation. The polyatomic ion nitrite, NO 2 , has a 1 charge. Because the charges on the cation and anion are numerically equal, the ions combine in a oneto-one ratio. The correct formula is RbNO2. Potassium is an alkali metal. It only forms a 1 cation ...
14 Chapter
... • Cholesterol is a complex lipid that is present in foods that come from animals, such as meat, butter, eggs, and cheese. • Even if you don’t eat foods containing cholesterol, your body makes its own supply. • Your body needs cholesterol for building cell ...
... • Cholesterol is a complex lipid that is present in foods that come from animals, such as meat, butter, eggs, and cheese. • Even if you don’t eat foods containing cholesterol, your body makes its own supply. • Your body needs cholesterol for building cell ...
Experiment 3: Dynamic NMR spectroscopy
... will be used to study molecular dynamics. NMR is the most widely applied magnetic spectroscopy method. It is an important tool for studying molecular structures and molecular dynamics of both organic and inorganic compounds. For example, for synthetic chemists it offers a great tool for identifying ...
... will be used to study molecular dynamics. NMR is the most widely applied magnetic spectroscopy method. It is an important tool for studying molecular structures and molecular dynamics of both organic and inorganic compounds. For example, for synthetic chemists it offers a great tool for identifying ...
Understanding Metabolic Regulation and Its
... 2010). Finally, small molecules can affect metabolic flux by allosteric effects on enzymes (Carminatti et al., 1971). The goal of these processes is to parse metabolites through pathways in the proportions needed to match the requirements of individual cells. Because metabolic needs can fluctuate on ...
... 2010). Finally, small molecules can affect metabolic flux by allosteric effects on enzymes (Carminatti et al., 1971). The goal of these processes is to parse metabolites through pathways in the proportions needed to match the requirements of individual cells. Because metabolic needs can fluctuate on ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.