Atoms, Elements and Compounds Home
... are several different types of nitrogen oxide. When this happens, the number of the type of atom that can be different is shown by using a prefix: ‘mono-’ (one), ‘di-’ (two) or ‘tri-’ (three). For example, the compound with the formula NO is called nitrogen monoxide and NO2 is nitrogen dioxide. If t ...
... are several different types of nitrogen oxide. When this happens, the number of the type of atom that can be different is shown by using a prefix: ‘mono-’ (one), ‘di-’ (two) or ‘tri-’ (three). For example, the compound with the formula NO is called nitrogen monoxide and NO2 is nitrogen dioxide. If t ...
AP Chem Stoichiometry Notes Table of Contents Atomic Masses
... isolate it as a pure compound. This and similar antibiotics have saved millions of lives that might have been lost to infections. Penicillin F has the formula C14H20N2SO4. Compute the mass percent of each element. Soln: Ans: C – 53.81%, H – 6.453%, N – 8.969%, S – 10.27%, O – 20.49% ...
... isolate it as a pure compound. This and similar antibiotics have saved millions of lives that might have been lost to infections. Penicillin F has the formula C14H20N2SO4. Compute the mass percent of each element. Soln: Ans: C – 53.81%, H – 6.453%, N – 8.969%, S – 10.27%, O – 20.49% ...
Organic Review Worksheet and Problem Set
... Cu2+ ions. Since the copper atoms lost electrons, the copper is oxidized. At the same time, the positively charged silver ions each gained a negatively charged electron and became insoluble, solid silver. Since the silver atoms gained electrons, the silver is reduced. In the above reaction, identify ...
... Cu2+ ions. Since the copper atoms lost electrons, the copper is oxidized. At the same time, the positively charged silver ions each gained a negatively charged electron and became insoluble, solid silver. Since the silver atoms gained electrons, the silver is reduced. In the above reaction, identify ...
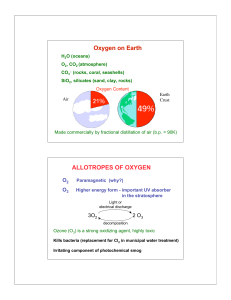
Symbols of Elements
... and electrons in one or more of the isotopes of an element; calculate the atomic mass of an element using the percent abundance and mass of its naturally occurring isotopes. ...
... and electrons in one or more of the isotopes of an element; calculate the atomic mass of an element using the percent abundance and mass of its naturally occurring isotopes. ...
06.1 - Chemical formulas and composition stoichiometry
... Each molecule of acetic acid, CH3COOH, contains 2 carbon atoms, 4 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygens. Writing it as CH3COOH (instead of C2H4O2) includes useful bonding and ...
... Each molecule of acetic acid, CH3COOH, contains 2 carbon atoms, 4 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygens. Writing it as CH3COOH (instead of C2H4O2) includes useful bonding and ...
Chemistry, Biomolecules, and Enzymes
... • Made up of amino acids, which all have an amino group, carboxyl group, and one of 20 possible different R groups • Joined together by peptide bonds between carboxyl and amino groups • Levels of Structure – Primary (1ー) - sequence and types of amino acids used in a protein – Secondary (2ー)- shape ( ...
... • Made up of amino acids, which all have an amino group, carboxyl group, and one of 20 possible different R groups • Joined together by peptide bonds between carboxyl and amino groups • Levels of Structure – Primary (1ー) - sequence and types of amino acids used in a protein – Secondary (2ー)- shape ( ...
Module 6 Chemical Reactions
... tracers to diagnose cancer and other diseases. • Radioactive tracers are also used in agriculture to measure the amount of fertilizer used by the plant. From these measurements, they can tell farmers just how much fertilizer to use on their crops. ...
... tracers to diagnose cancer and other diseases. • Radioactive tracers are also used in agriculture to measure the amount of fertilizer used by the plant. From these measurements, they can tell farmers just how much fertilizer to use on their crops. ...
Lecture_09_Metabolic_systems - Home | CISB-ECN
... Metabolomics is the scientific study of biochemical systems involving large numbers of metabolites at the same time. ...
... Metabolomics is the scientific study of biochemical systems involving large numbers of metabolites at the same time. ...
Atoms
... • Not exactly correct because binding energy is needed to hold the parts of an atom together • Some mass converted to this binding energy in a nuclear reaction so the calculation gives a value that is a little larger than reality • (E = mc2) ...
... • Not exactly correct because binding energy is needed to hold the parts of an atom together • Some mass converted to this binding energy in a nuclear reaction so the calculation gives a value that is a little larger than reality • (E = mc2) ...
CH100: Fundamentals for Chemistry
... Mixtures can be separated by physical means (and also by chemical methods, as well) There are 2 general methods of separation Physical separation Chemical separation ...
... Mixtures can be separated by physical means (and also by chemical methods, as well) There are 2 general methods of separation Physical separation Chemical separation ...
Structure of Molecules and Compounds | Principles of Biology from
... chemical reaction. The reactants in a cake may include flour, sugar, butter, and eggs. In a chemical reaction, the ingredients are elements or compounds. The reactants combine during the chemical reaction to form the product. In the cake analogy, the product is the cake. In a chemical reaction, the ...
... chemical reaction. The reactants in a cake may include flour, sugar, butter, and eggs. In a chemical reaction, the ingredients are elements or compounds. The reactants combine during the chemical reaction to form the product. In the cake analogy, the product is the cake. In a chemical reaction, the ...
Question - Bellingham High School
... When the quantities of reactants are available in the exact ratio described by the balanced equation, the chemists say that the reactants are in stoichiometric proportions. When this is the case, all the reactants will take part in the reaction and there will be no reactants left over one the react ...
... When the quantities of reactants are available in the exact ratio described by the balanced equation, the chemists say that the reactants are in stoichiometric proportions. When this is the case, all the reactants will take part in the reaction and there will be no reactants left over one the react ...
Stoichiometry
... • Stoichiometry is the study of the relationships between the masses of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction • If we know the amount of reactants (products), we can calculate the amount of products (reactants) that are ...
... • Stoichiometry is the study of the relationships between the masses of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction • If we know the amount of reactants (products), we can calculate the amount of products (reactants) that are ...
doc 3.5.2 respiration notes Student notes for section 3.5.2
... Glycolysis uses two molecules of ATP and produces four giving a net gain of ………… molecules of ATP for each glucose molecule. Glycolysis also produces two molecules of NADH (reduced NAD) which can go on to produce more ATP in oxidative phosphorylation. LINK REACTION If oxygen is available, the pyruva ...
... Glycolysis uses two molecules of ATP and produces four giving a net gain of ………… molecules of ATP for each glucose molecule. Glycolysis also produces two molecules of NADH (reduced NAD) which can go on to produce more ATP in oxidative phosphorylation. LINK REACTION If oxygen is available, the pyruva ...
Chapter 2
... The pH of the fluids within most cells in the human body must generally be kept between ______________ in order to maintain _________. If the pH is lower or higher, it will affect the chemical reactions that take place within the cells. One of the ways that organisms control pH is through dissolved ...
... The pH of the fluids within most cells in the human body must generally be kept between ______________ in order to maintain _________. If the pH is lower or higher, it will affect the chemical reactions that take place within the cells. One of the ways that organisms control pH is through dissolved ...
Help us improve Wikipedia by supporting it financially
... have either 6, 7, or 8 neutrons. Since the mass numbers of these are 12, 13 and 14 respectively, the three isotopes of carbon are known as carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14, often abbreviated to 12C, 13C, and 14C. Carbon in everyday life and in chemistry is a mixture of 12C, 13C, and 14C atoms. Ex ...
... have either 6, 7, or 8 neutrons. Since the mass numbers of these are 12, 13 and 14 respectively, the three isotopes of carbon are known as carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14, often abbreviated to 12C, 13C, and 14C. Carbon in everyday life and in chemistry is a mixture of 12C, 13C, and 14C atoms. Ex ...
Calculations and Chemical Equations Atomic mass: Mass of an
... Chemical Reaction: Interaction between substances that results in one or more new substances being produced ...
... Chemical Reaction: Interaction between substances that results in one or more new substances being produced ...
Utah - Wavefunction, Inc.
... matter how they are rearranged; the total mass stays the same. Although energy can be absorbed or released in a chemical reaction, the total amount of energy and matter in it remains constant. Many reactions attain a state of equilibrium. Many ordinary activities, such as baking, involve chemical re ...
... matter how they are rearranged; the total mass stays the same. Although energy can be absorbed or released in a chemical reaction, the total amount of energy and matter in it remains constant. Many reactions attain a state of equilibrium. Many ordinary activities, such as baking, involve chemical re ...
Molar Mass and Formulas
... • The relative weights of molecules can be calculated from atomic masses Water = H2O = 2(1.008 g) + 16.00 g = 18.02 g • 1 mole of H2O will weigh 18.02 g, therefore the molar mass of H2O is 18.02 g • 1 mole of H2O will contain 16.00 g of oxygen and 2.02 g of hydrogen ...
... • The relative weights of molecules can be calculated from atomic masses Water = H2O = 2(1.008 g) + 16.00 g = 18.02 g • 1 mole of H2O will weigh 18.02 g, therefore the molar mass of H2O is 18.02 g • 1 mole of H2O will contain 16.00 g of oxygen and 2.02 g of hydrogen ...
The Atom - cloudfront.net
... definite proportions and the law of multiple proportions. . Statement 4 implies that a compound is always formed using atoms in the same whole-number ratio. Because an atom has a fixed masE it also follows that using twice as many atoms of an element will result in a cornpound containing twice the m ...
... definite proportions and the law of multiple proportions. . Statement 4 implies that a compound is always formed using atoms in the same whole-number ratio. Because an atom has a fixed masE it also follows that using twice as many atoms of an element will result in a cornpound containing twice the m ...
Chemistry 201 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... There are six significant figures in this measured quantity There are five significant figures in this measured quantity There are four significant figures in this measured quantity There are three significant figures in this measured quantity There are two significant figures in this measured quant ...
... There are six significant figures in this measured quantity There are five significant figures in this measured quantity There are four significant figures in this measured quantity There are three significant figures in this measured quantity There are two significant figures in this measured quant ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.