
ATOMIC THEORY
... The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different. What makes atoms of different elements different? The fundamental characteristic that all atoms of the same element share is the number of protons . All atoms of hydrogen have on ...
... The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different. What makes atoms of different elements different? The fundamental characteristic that all atoms of the same element share is the number of protons . All atoms of hydrogen have on ...
Atomic Structure and Models
... Atoms of the same element are the same. Atoms of different elements are different. Atoms combine to make molecules of compounds. Atoms cannot be created or destroyed (by physical or chemical processes). ...
... Atoms of the same element are the same. Atoms of different elements are different. Atoms combine to make molecules of compounds. Atoms cannot be created or destroyed (by physical or chemical processes). ...
Do Now - Montville.net
... the element, but a different number of neutrons. Ex: Carbon-14 Contains 6 protons (still carbon) Also contains 8 neutrons, instead of 6 ...
... the element, but a different number of neutrons. Ex: Carbon-14 Contains 6 protons (still carbon) Also contains 8 neutrons, instead of 6 ...
atoms
... is an atom of the isotope carbon-12 Next the masses of the other atoms relative to carbon -12 are determined with a mass spectrometer ...
... is an atom of the isotope carbon-12 Next the masses of the other atoms relative to carbon -12 are determined with a mass spectrometer ...
atoms
... is an atom of the isotope carbon-12 Next the masses of the other atoms relative to carbon -12 are determined with a mass spectrometer ...
... is an atom of the isotope carbon-12 Next the masses of the other atoms relative to carbon -12 are determined with a mass spectrometer ...
1 The Nucleus Total number of nucleons: mass number Number of
... Cooling time for earth surface: 11.5 × 109 yr Age of earth at about: 4.04.5 × 109 yr Ex. ...
... Cooling time for earth surface: 11.5 × 109 yr Age of earth at about: 4.04.5 × 109 yr Ex. ...
Distinguishing Between Atoms
... •1 amu is equal to 1/12 the mass of the carbon-12 isotope. (roughly the mass of a neutron or proton) Notice, the mass of electrons is so much less than that of a neutron or proton that its mass is negligible. ...
... •1 amu is equal to 1/12 the mass of the carbon-12 isotope. (roughly the mass of a neutron or proton) Notice, the mass of electrons is so much less than that of a neutron or proton that its mass is negligible. ...
All you need to know about Additional Science
... 2NaOH + Cl2 NaOCl + NaCl + H2O If we have a solution containing 100 g of sodium hydroxide, how much chlorine gas should we pass through the solution to make bleach? Too much, and some chlorine will be wasted, too little and not all of the sodium hydroxide will react. ...
... 2NaOH + Cl2 NaOCl + NaCl + H2O If we have a solution containing 100 g of sodium hydroxide, how much chlorine gas should we pass through the solution to make bleach? Too much, and some chlorine will be wasted, too little and not all of the sodium hydroxide will react. ...
File
... The electronic charge of an atom All elements in order A unit of energy Positive or negative charge on an atom or group of atoms Atoms of the same element with different atomic mass A negatively charged particle A positively charged particle An atomic particle with no charge Used Boyle’s information ...
... The electronic charge of an atom All elements in order A unit of energy Positive or negative charge on an atom or group of atoms Atoms of the same element with different atomic mass A negatively charged particle A positively charged particle An atomic particle with no charge Used Boyle’s information ...
All you need to know about Additional Science
... 2NaOH + Cl2 NaOCl + NaCl + H2O If we have a solution containing 100 g of sodium hydroxide, how much chlorine gas should we pass through the solution to make bleach? Too much, and some chlorine will be wasted, too little and not all of the sodium hydroxide will react. ...
... 2NaOH + Cl2 NaOCl + NaCl + H2O If we have a solution containing 100 g of sodium hydroxide, how much chlorine gas should we pass through the solution to make bleach? Too much, and some chlorine will be wasted, too little and not all of the sodium hydroxide will react. ...
Combining and Choosing Analytical Techniques
... HPLC, infrared spectroscopy and NMR spectroscopy. Each technique will give different information. We can even combine some of the techniques. ...
... HPLC, infrared spectroscopy and NMR spectroscopy. Each technique will give different information. We can even combine some of the techniques. ...
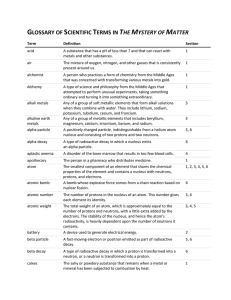
GLOSSARY OF SCIENTIFIC TERMS IN THE MYSTERY OF MATTER
... A unit that measures the effect of ionizing radiation upon a particular person. A group of two or more atoms linked together by sharing electrons in a chemical bond. A heavy, neutral particle in an atom’s nucleus that accounts for almost all of each atom’s mass, in addition to protons. Any of the si ...
... A unit that measures the effect of ionizing radiation upon a particular person. A group of two or more atoms linked together by sharing electrons in a chemical bond. A heavy, neutral particle in an atom’s nucleus that accounts for almost all of each atom’s mass, in addition to protons. Any of the si ...
Unit Description - Honors Chemistry
... Chapters 1 and 3 – Scientific Method and Matter Distinguish among hypothesis, theory and scientific law using examples. Identify the common steps of scientific methods. Distinguish between qualitative and quantitative data. Distinguish between independent and dependent variables, controls an ...
... Chapters 1 and 3 – Scientific Method and Matter Distinguish among hypothesis, theory and scientific law using examples. Identify the common steps of scientific methods. Distinguish between qualitative and quantitative data. Distinguish between independent and dependent variables, controls an ...
Unit 3 - Princeton High School
... 6. A long cherished dream of alchemists was to produce gold from cheaper and more abundant elements. This dream was finally realized when 198 80 Hg was converted into gold by neutron bombardment. What one other particle is produced? ...
... 6. A long cherished dream of alchemists was to produce gold from cheaper and more abundant elements. This dream was finally realized when 198 80 Hg was converted into gold by neutron bombardment. What one other particle is produced? ...
Chemistry is a material science
... Chemistry is a material science! How is chemistry defined? Chemistry is the _______ of ______ its ____________, the ______ matter undergoes, and the _______ associated with these changes. Matter is anything that has _______ and takes up _________. This fundamental definition of matter leads to a com ...
... Chemistry is a material science! How is chemistry defined? Chemistry is the _______ of ______ its ____________, the ______ matter undergoes, and the _______ associated with these changes. Matter is anything that has _______ and takes up _________. This fundamental definition of matter leads to a com ...
ppt-nuclear - SandersScienceStuff
... into different fragments. • This generally occurs with atoms that have a mass number heavier than 60. • The nuclei do not always split the same way. Scientists have found 200 different products from the fission reaction of Uranium-235. ...
... into different fragments. • This generally occurs with atoms that have a mass number heavier than 60. • The nuclei do not always split the same way. Scientists have found 200 different products from the fission reaction of Uranium-235. ...
AP Chemistry 2013 Semester 1 Final Exam Review Problems
... line (emission) spectra and Niels Bohr; the wave properties of the electron; quantum mechanical view of the atom; atomic orbital shapes; electron spin (para/dia magnetism); the Pauli exclusion principle; atomic subshell energies and electron assignments; atomic electron configurations; electron conf ...
... line (emission) spectra and Niels Bohr; the wave properties of the electron; quantum mechanical view of the atom; atomic orbital shapes; electron spin (para/dia magnetism); the Pauli exclusion principle; atomic subshell energies and electron assignments; atomic electron configurations; electron conf ...
Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts
... --Matter consists of tiny particles called atoms. --Atoms are indestructible. In chemical reactions, the atoms rearrange but they do not themselves break apart. --In any sample of a pure element, all the atoms are identical in mass and other properties. --The atoms of different elements differ in ma ...
... --Matter consists of tiny particles called atoms. --Atoms are indestructible. In chemical reactions, the atoms rearrange but they do not themselves break apart. --In any sample of a pure element, all the atoms are identical in mass and other properties. --The atoms of different elements differ in ma ...
希臘 - 中正大學化生系
... modern experimental scientific method. 2. He endorsed the view of elements as the undecomposable constituents of material bodies; and made the distinction between mixtures and compounds. ...
... modern experimental scientific method. 2. He endorsed the view of elements as the undecomposable constituents of material bodies; and made the distinction between mixtures and compounds. ...
Atomic Structure - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Protons have a charge of +1 and are located in the nucleus with neutrons. Both are 1,840 times larger than electrons. ...
... Protons have a charge of +1 and are located in the nucleus with neutrons. Both are 1,840 times larger than electrons. ...
Development of the Periodic Table
... ◦ Atom: the smallest particle of an element that keeps the properties of that element. (Greek: atomos = indivisible) ...
... ◦ Atom: the smallest particle of an element that keeps the properties of that element. (Greek: atomos = indivisible) ...
Protein - Peoria Public Schools
... All amino acids are structurally the same with the exception of ...
... All amino acids are structurally the same with the exception of ...
Word - The Chemistry Book
... 3. Marie and Pierre Curie (1898) a. Isolated two new elements, radium and polonium b. Marie Curie is the only scientist to win Nobel Prizes from two different sciences (1903 – physics; 1911 – chemistry) 4. Ernest Rutherford (1911) a. Radioactive elements undergo a process of decay over time b. First ...
... 3. Marie and Pierre Curie (1898) a. Isolated two new elements, radium and polonium b. Marie Curie is the only scientist to win Nobel Prizes from two different sciences (1903 – physics; 1911 – chemistry) 4. Ernest Rutherford (1911) a. Radioactive elements undergo a process of decay over time b. First ...
The atom: Isotopes (Grade 10) [NCS]
... The chemical properties of an element depend on the number of protons and electrons inside the atom. So if a neutron or two is added or removed from the nucleus, then the chemical properties will not change. This means that such an atom would remain in the same place in the Periodic Table. For examp ...
... The chemical properties of an element depend on the number of protons and electrons inside the atom. So if a neutron or two is added or removed from the nucleus, then the chemical properties will not change. This means that such an atom would remain in the same place in the Periodic Table. For examp ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.






















![The atom: Isotopes (Grade 10) [NCS]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016109524_1-1437871a54cd24e5ee13c27e98f0719d-300x300.png)