Atomic Structure (history of atom)
... ATOMS of any one ELEMENT are different from those of any other element Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine to form ...
... ATOMS of any one ELEMENT are different from those of any other element Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine to form ...
Section 3.1
... 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their physical and chemical properties. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole number ratios to form compounds. 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged but never created, destroyed, or changed. ...
... 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their physical and chemical properties. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole number ratios to form compounds. 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged but never created, destroyed, or changed. ...
Exam 2b Key Fall 2010
... c. That electrons exist in discrete energy levels. d. That electrons are very far from the nucleus. 10. In the modern model of the atom… a. the electron is treated as a wave. b. the electron’s mass is not counted c. the protons are in the nucleus. d. all of the above e. none of the above. ...
... c. That electrons exist in discrete energy levels. d. That electrons are very far from the nucleus. 10. In the modern model of the atom… a. the electron is treated as a wave. b. the electron’s mass is not counted c. the protons are in the nucleus. d. all of the above e. none of the above. ...
Document
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory - Summary 1. matter is composed, indivisible particles (atoms) 2. all atoms of a particular element are identical 3. different elements have different atoms 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new comp ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory - Summary 1. matter is composed, indivisible particles (atoms) 2. all atoms of a particular element are identical 3. different elements have different atoms 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new comp ...
Microbial alteration of stable nitrogen and carbon isotopic
... ammonia plus organic acids. The ammonia is fixed into glutamic acid, and this nitrogen is subsequently passed on to most of the protein amino acids, while the organic acid is metabolized via the Krebs cycle. These reactions occur in bacteria growing with alanine, serine and threonine. The cultures u ...
... ammonia plus organic acids. The ammonia is fixed into glutamic acid, and this nitrogen is subsequently passed on to most of the protein amino acids, while the organic acid is metabolized via the Krebs cycle. These reactions occur in bacteria growing with alanine, serine and threonine. The cultures u ...
Atoms, molecules and ions
... • Atomic number: The number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of a given element • Atomic mass: The total number of neutrons and protons contained in the nucleus of an atom • All atoms of an element have the same number of protons, but not necessarily the same number of neutrons • Atoms that ha ...
... • Atomic number: The number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of a given element • Atomic mass: The total number of neutrons and protons contained in the nucleus of an atom • All atoms of an element have the same number of protons, but not necessarily the same number of neutrons • Atoms that ha ...
Fundamentals Fall Final Review
... 16. In a flask, 50.3 grams of aluminum reacted with bromine to form 263.0 grams of aluminum bromide. How many grams of bromine were reacted? Aluminum + bromine aluminum bromide Percent by mass problems: 17. A 156 gram sample of an unknown compound contains 25 grams of hydrogen. What is the percent ...
... 16. In a flask, 50.3 grams of aluminum reacted with bromine to form 263.0 grams of aluminum bromide. How many grams of bromine were reacted? Aluminum + bromine aluminum bromide Percent by mass problems: 17. A 156 gram sample of an unknown compound contains 25 grams of hydrogen. What is the percent ...
Chapter 25.2 Nuclear Transformations
... After each half-life, half of the existing radioactive atoms have decayed into atoms of a new element. Half-lives can range from fractions of a second to billions of years ...
... After each half-life, half of the existing radioactive atoms have decayed into atoms of a new element. Half-lives can range from fractions of a second to billions of years ...
Physical Science –McDougal-Littell Name
... 3. What is it that determines whether particles attract or repel each other? 4. Define: attract and repel 5. Atoms are composed of what three types of particles? 6. Define: proton, neutron and electron 7. Where are protons and neutrons located? 8. What electrical charge is associated with the nucleu ...
... 3. What is it that determines whether particles attract or repel each other? 4. Define: attract and repel 5. Atoms are composed of what three types of particles? 6. Define: proton, neutron and electron 7. Where are protons and neutrons located? 8. What electrical charge is associated with the nucleu ...
Diapositiva 1 - UniFI
... The protein is produced by expression from bacteria which are grown on minimal medium supplemented with small amounts of 15NH4Cl and 13C-labelled glucose as well as labelled and unlabelled amino acids. The idea is that only those amino acids which are added in labelled form become labelled in the pr ...
... The protein is produced by expression from bacteria which are grown on minimal medium supplemented with small amounts of 15NH4Cl and 13C-labelled glucose as well as labelled and unlabelled amino acids. The idea is that only those amino acids which are added in labelled form become labelled in the pr ...
CHAPTER 25 - CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS
... Living or was once living Organic Chemistry - The chemistry of carbon compounds Carbon is well suited for life because it is the most versatile element in terms of bonding. ...
... Living or was once living Organic Chemistry - The chemistry of carbon compounds Carbon is well suited for life because it is the most versatile element in terms of bonding. ...
NAME REVIEW 1: JUST THE BASICS ___1) In which material are
... 20) 1) HI it is produced endothermically and that means more energy is absorbed by the breaking of bonds than is released as the new H-I polar covalent bond(s) is (are) produced. Thus HI is less stable than the reactants. 21) 3 an increase in temp favors the endo. rxn which in this case is the forwa ...
... 20) 1) HI it is produced endothermically and that means more energy is absorbed by the breaking of bonds than is released as the new H-I polar covalent bond(s) is (are) produced. Thus HI is less stable than the reactants. 21) 3 an increase in temp favors the endo. rxn which in this case is the forwa ...
CHAPTER 1 Practice Exercises 1.1 12.3 g Cd 1.3 26.9814 u 1.5
... A period in the periodic table is a horizontal row of elements. A group is one of the vertical columns of the periodic table. ...
... A period in the periodic table is a horizontal row of elements. A group is one of the vertical columns of the periodic table. ...
Atomic Number and Mass Number
... 22. Circle the letter of each statement that is true about the average atomic mass of an element and the relative abundance of its isotopes. a. In nature, most elements occur as a mixture of two or more isotopes. b. Isotopes of an element do not have a specific natural percent abundance. c. The aver ...
... 22. Circle the letter of each statement that is true about the average atomic mass of an element and the relative abundance of its isotopes. a. In nature, most elements occur as a mixture of two or more isotopes. b. Isotopes of an element do not have a specific natural percent abundance. c. The aver ...
Roland-Story Biology Class
... a substance made of the joined atoms of two or more different elements a large molecule formed by linked smaller molecules of amino acids are nonpolar molecules that are not soluble in water attraction between molecules of the same substance a long chain of smaller molecules made of only one type of ...
... a substance made of the joined atoms of two or more different elements a large molecule formed by linked smaller molecules of amino acids are nonpolar molecules that are not soluble in water attraction between molecules of the same substance a long chain of smaller molecules made of only one type of ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... Hg (mercury) can exist by itself...but, oxygen will need to bond with another oxygen to make O2 (diatomic) To balance the atoms we need to: Put the coefficient of 2 in front of reactant HgO. Put the coefficient of 2 in front the product Hg. ...
... Hg (mercury) can exist by itself...but, oxygen will need to bond with another oxygen to make O2 (diatomic) To balance the atoms we need to: Put the coefficient of 2 in front of reactant HgO. Put the coefficient of 2 in front the product Hg. ...
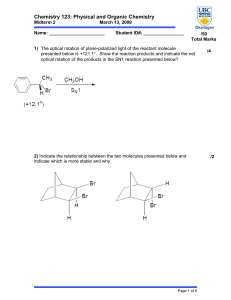
Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry
... 15) If a reaction has a half-life of one day and it is initiated on Monday, how much remains on Friday? (A) ~20% (B) ~5% (C) ~3% (D) ~12% 16) For the reaction, N2(g) + 3 H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g) , the rate would be; A) First order B) Second order with regard to [NH3] C) Third order D) not enough information ...
... 15) If a reaction has a half-life of one day and it is initiated on Monday, how much remains on Friday? (A) ~20% (B) ~5% (C) ~3% (D) ~12% 16) For the reaction, N2(g) + 3 H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g) , the rate would be; A) First order B) Second order with regard to [NH3] C) Third order D) not enough information ...
nuclear chemistry - Wood County Schools
... Fission: The splitting of an atomic nucleus into two or more smaller fragments. Fusion: The combining of two atoms to form an element of a larger atomic number. Releases more energy than fission. Chain Reaction: A self-sustaining fission process. Critical Mass: The minimum quantity of a radioactive ...
... Fission: The splitting of an atomic nucleus into two or more smaller fragments. Fusion: The combining of two atoms to form an element of a larger atomic number. Releases more energy than fission. Chain Reaction: A self-sustaining fission process. Critical Mass: The minimum quantity of a radioactive ...
Chemical Reactions
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
Regents Review Packet B2 Answer Key
... 4. Identify the physical property in the table that could be used to differentiate the samples of the three elements from each other. ...
... 4. Identify the physical property in the table that could be used to differentiate the samples of the three elements from each other. ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
class 2.pptx
... mass of Br+ ions and two masses are determined to be 78.91834 and 80.91629 amu. From analytical chemistry we can determine the molar mass of bromine to be 79.904(1) g/mol. What are the % abundances of each isotope? ...
... mass of Br+ ions and two masses are determined to be 78.91834 and 80.91629 amu. From analytical chemistry we can determine the molar mass of bromine to be 79.904(1) g/mol. What are the % abundances of each isotope? ...
class 2.pptx
... Bromine occurs as Br2 molecules. t A high-precision mass spectrometer measure the mass of Br+ ions and two masses are determined to be 78.91834 and 80.91629 amu. From analytical chemistry we can determine the molar mass of bromine to be 79.904(1) g/mol. t What are the % abundances of each isotope? ...
... Bromine occurs as Br2 molecules. t A high-precision mass spectrometer measure the mass of Br+ ions and two masses are determined to be 78.91834 and 80.91629 amu. From analytical chemistry we can determine the molar mass of bromine to be 79.904(1) g/mol. t What are the % abundances of each isotope? ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.