atomic mass and symb..
... electrons All the elements can be represented as symbols that are organized in the periodic table. Carbon is represented by ...
... electrons All the elements can be represented as symbols that are organized in the periodic table. Carbon is represented by ...
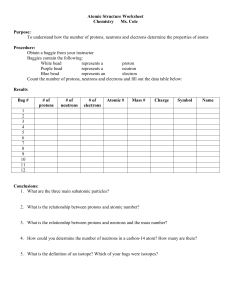
Atomic Structure Mini Lab
... To understand how the number of protons, neutrons and electrons determine the properties of atoms Procedure: Obtain a baggie from your instructor Baggies contain the following: White bead represents a proton Purple bead represents a neutron Blue bead represents an electron Count the number of proton ...
... To understand how the number of protons, neutrons and electrons determine the properties of atoms Procedure: Obtain a baggie from your instructor Baggies contain the following: White bead represents a proton Purple bead represents a neutron Blue bead represents an electron Count the number of proton ...
* Abundant! * Able to share 4 outer valence electrons! * Versatile
... • Would your body like to use a single enzyme for more than one reaction? Why or why not? • Will your body want to regulate (start and stop) chemical reactions at different times throughout your life? ...
... • Would your body like to use a single enzyme for more than one reaction? Why or why not? • Will your body want to regulate (start and stop) chemical reactions at different times throughout your life? ...
atomic number - Net Start Class
... •How many protons does helium have? •What element has 79 protons? •What is uranium’s atomic number? •How many electrons does a neutral atom of calcium have? ...
... •How many protons does helium have? •What element has 79 protons? •What is uranium’s atomic number? •How many electrons does a neutral atom of calcium have? ...
Atomic Structure - Mr. Cervantes Science Classes
... reasonable to think that the mass of an atom should be expressed as a whole number B. The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of all the isotopes of that element 1. When calculating the average atomic mass you must take into account the relative abundance of each isotope ...
... reasonable to think that the mass of an atom should be expressed as a whole number B. The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of all the isotopes of that element 1. When calculating the average atomic mass you must take into account the relative abundance of each isotope ...
Atoms/Atomic Theory PPT
... applies when 2 or more elements combine to make more than one type of compound the mass ratios of the second element simplify to small whole numbers ...
... applies when 2 or more elements combine to make more than one type of compound the mass ratios of the second element simplify to small whole numbers ...
2010 Physical Science Comprehensive Test REVIEW Ch 0.3 Sig
... 42. Many models have been developed to explain the nature of atoms. The model that helped scientists to understand energy levels of atoms was developed by: 43. An atom emits light when one of its electrons: 44. What 3 things are required for a bioluminescent reaction to occur? 45. Most of the elemen ...
... 42. Many models have been developed to explain the nature of atoms. The model that helped scientists to understand energy levels of atoms was developed by: 43. An atom emits light when one of its electrons: 44. What 3 things are required for a bioluminescent reaction to occur? 45. Most of the elemen ...
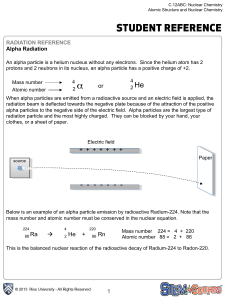
2 α
... The element phosphorus in found in many organic molecules. Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is your body’s main form of energy. Phosphorus also helps maintain cell structure in the form of phospholipids, keeping cells separate but permeable to compounds in your bloodstream. Phosphorus-32 is a radioacti ...
... The element phosphorus in found in many organic molecules. Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is your body’s main form of energy. Phosphorus also helps maintain cell structure in the form of phospholipids, keeping cells separate but permeable to compounds in your bloodstream. Phosphorus-32 is a radioacti ...
section_2_review_set
... 1. What is the claim to fame for the proton? determines the element 2. What is the claim to fame for the electron? creates the chemical bonds 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? stabilizes the nucleus 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton 1; neutron 1; electron 0. ...
... 1. What is the claim to fame for the proton? determines the element 2. What is the claim to fame for the electron? creates the chemical bonds 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? stabilizes the nucleus 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton 1; neutron 1; electron 0. ...
Chemical reactions
... • Occur through formation and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms • Involve changes in matter, creation of new materials and energy exchange • Chemical equations - concise representation of chemical reactions ...
... • Occur through formation and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms • Involve changes in matter, creation of new materials and energy exchange • Chemical equations - concise representation of chemical reactions ...
Structure of Atoms
... RADIOACTIVE ISOTOPE Unstable isotope in which the nucleus spontaneously decays, emitting subatomic particles and/or energy as radioactivity. Loss of nuclear particles may transform one element to another A radioactive isotope has a fixed half-life: HALF LIFE = Time for 50% of radioactive atoms i ...
... RADIOACTIVE ISOTOPE Unstable isotope in which the nucleus spontaneously decays, emitting subatomic particles and/or energy as radioactivity. Loss of nuclear particles may transform one element to another A radioactive isotope has a fixed half-life: HALF LIFE = Time for 50% of radioactive atoms i ...
Name: What are atoms? Atoms are the ______ building blocks of
... atom doesn't have 36 protons, it can't be an atom of ____________. Adding or removing protons from the nucleus of an atom creates a different ____________. For example, removing one proton from an atom of krypton creates an atom of _____________. The Number of Neutrons is... The __________ _________ ...
... atom doesn't have 36 protons, it can't be an atom of ____________. Adding or removing protons from the nucleus of an atom creates a different ____________. For example, removing one proton from an atom of krypton creates an atom of _____________. The Number of Neutrons is... The __________ _________ ...
The Structure of the Atom
... •His experimental results revealed something different. Most alpha particles paths were not affected by any charge when in contact with gold foil. (Red straight lines on left diagram). Just a few deflected back at large angles. Knew it had to be of the same charge, because repelled. ...
... •His experimental results revealed something different. Most alpha particles paths were not affected by any charge when in contact with gold foil. (Red straight lines on left diagram). Just a few deflected back at large angles. Knew it had to be of the same charge, because repelled. ...
H 2 and H 2 + O 2 g H 2 O and H 2 O Hydrogen + Oxygen g Water
... Balancing – A simple method Write down the word equation 2. Write the symbol equation 3. Choose one element and count how many atoms of that element there are on each side of the equation. 4. If the numbers do not match you will need more of one of the chemicals. You must write a 2 in front of the ...
... Balancing – A simple method Write down the word equation 2. Write the symbol equation 3. Choose one element and count how many atoms of that element there are on each side of the equation. 4. If the numbers do not match you will need more of one of the chemicals. You must write a 2 in front of the ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Continued
... or down (.0 - .49 round down; .5 - .99 round up): Example: Oxygen Atomic Mass = 15.9994 Mass Number = 16 ...
... or down (.0 - .49 round down; .5 - .99 round up): Example: Oxygen Atomic Mass = 15.9994 Mass Number = 16 ...
Unit 2 Review Game
... • During a chemical reaction, a group combines 5.00 grams of sodium and 7.72 grams of chlorine. The result of the reaction was 12.72 grams of sodium chloride. Which law does this support? ...
... • During a chemical reaction, a group combines 5.00 grams of sodium and 7.72 grams of chlorine. The result of the reaction was 12.72 grams of sodium chloride. Which law does this support? ...
Name___________________________________ Physical
... 8) A term that means "without water" is ________________________. 9) How can you drive the water out of a hydrate? By ________________________. _________ _________ 10) Which of the following correctly shows the formula for a hydrate? A) MgSO4 (H2 O)7 B) H2 O C) H2 O2 ...
... 8) A term that means "without water" is ________________________. 9) How can you drive the water out of a hydrate? By ________________________. _________ _________ 10) Which of the following correctly shows the formula for a hydrate? A) MgSO4 (H2 O)7 B) H2 O C) H2 O2 ...
Document
... – Actually, the ratio of the size of the nucleus to the diameter of the orbits of electrons can be compared with placing a marble in the middle of a ...
... – Actually, the ratio of the size of the nucleus to the diameter of the orbits of electrons can be compared with placing a marble in the middle of a ...
atoms-chemical
... unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that one atom strips an electron completely from the other becoming ions and form an ionic bond. • sodium with one valence electron • chlorine with 7 valence electrons ...
... unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that one atom strips an electron completely from the other becoming ions and form an ionic bond. • sodium with one valence electron • chlorine with 7 valence electrons ...
CHEM 1211K Test I MULTIPLE CHOICE. (3 points each) 1
... 18) __________ and __________ reside in the atomic nucleus. A) Protons, electrons B) Protons, neutrons C) Electrons, neutrons D) none of the above E) Neutrons, only neutrons 19) In the Rutherford nuclear-atom model, __________. A) the light subatomic particles, protons and neutrons, reside in the n ...
... 18) __________ and __________ reside in the atomic nucleus. A) Protons, electrons B) Protons, neutrons C) Electrons, neutrons D) none of the above E) Neutrons, only neutrons 19) In the Rutherford nuclear-atom model, __________. A) the light subatomic particles, protons and neutrons, reside in the n ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.