Notes - PowerPoint
... • Write the name of the cation. • If the anion is an element, change its ending to -ide; if the anion is a polyatomic ion, simply write the name of the polyatomic ion. • If the cation can have more than one possible charge, write the charge as a Roman numeral in parentheses. ...
... • Write the name of the cation. • If the anion is an element, change its ending to -ide; if the anion is a polyatomic ion, simply write the name of the polyatomic ion. • If the cation can have more than one possible charge, write the charge as a Roman numeral in parentheses. ...
Chapter 3 - Stoichiometry
... Treat % as grams and convert grams to moles using the mass from the PTE Find the smallest whole number ratio of atoms (multiply by an integer to make them whole numbers). A compound contains 63.5% Silver, 8.2% Nitrogen and 28.2% Oxygen. What is the empirical formula for this compound? ...
... Treat % as grams and convert grams to moles using the mass from the PTE Find the smallest whole number ratio of atoms (multiply by an integer to make them whole numbers). A compound contains 63.5% Silver, 8.2% Nitrogen and 28.2% Oxygen. What is the empirical formula for this compound? ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
Name: MACROMOLECULES Date: I. ELEMENTS AND
... and nucleic acids such as DNA & RNA). Carbohydrates and lipids are made of only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO). Proteins are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen (CHON). Nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus (CHON P).The body also ...
... and nucleic acids such as DNA & RNA). Carbohydrates and lipids are made of only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO). Proteins are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen (CHON). Nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus (CHON P).The body also ...
Chapter 5
... – “Functional groups have specific functions that they consistently do” – predictable way with other molecules – 4 Functional groups of carbon • Hydroxyl hydrophilic (attract water…molecules with this group will attract water) • Carbonyl • Carboxyl • Amino ...
... – “Functional groups have specific functions that they consistently do” – predictable way with other molecules – 4 Functional groups of carbon • Hydroxyl hydrophilic (attract water…molecules with this group will attract water) • Carbonyl • Carboxyl • Amino ...
nature of Matter
... Nitrogen-14 (7 protons & 7 neutrons) An isotope is when atoms of the same element have a different number of NEUTRONS. Isotopes are identified by their mass number. Since they still have the same number of electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. A compound is a sub ...
... Nitrogen-14 (7 protons & 7 neutrons) An isotope is when atoms of the same element have a different number of NEUTRONS. Isotopes are identified by their mass number. Since they still have the same number of electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. A compound is a sub ...
Atomic Structure - Miami East Schools
... philosophy • Matter was made of small invisible particles called atoms • No scientific evidence, but it was logical ...
... philosophy • Matter was made of small invisible particles called atoms • No scientific evidence, but it was logical ...
Chapter 18 Resource: Matter
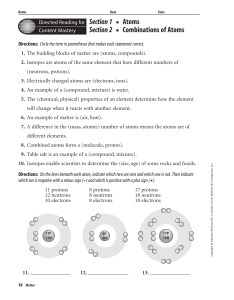
... 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an el ...
... 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an el ...
Intro To Atomic Theory
... The molar mass of Cl-35 is 34.968852g and Cl-37 is 36.965903. If 75.77% of chlorine is Cl-35 and 24.23% of chlorine is Cl-37, what is the average molar mass of the chlorine atom in such a mixture? Take the percent average Mass of Cl-35= 75.77% x 34.968852 = 26.4959 Mass of Cl-37= 24.23% x 36.965803 ...
... The molar mass of Cl-35 is 34.968852g and Cl-37 is 36.965903. If 75.77% of chlorine is Cl-35 and 24.23% of chlorine is Cl-37, what is the average molar mass of the chlorine atom in such a mixture? Take the percent average Mass of Cl-35= 75.77% x 34.968852 = 26.4959 Mass of Cl-37= 24.23% x 36.965803 ...
chapter_17_ppt - District 128 Moodle
... MASS NUMBER = total # of particles in the nucleus MASS NUMBER = total number of protons and neutrons Ex: Boron has mass number of 11 and atomic number of 5. So it has 5 protons and 6 neutrons. ...
... MASS NUMBER = total # of particles in the nucleus MASS NUMBER = total number of protons and neutrons Ex: Boron has mass number of 11 and atomic number of 5. So it has 5 protons and 6 neutrons. ...
Chapter 2 Notes - Waterford Public Schools
... in mass and in all other properties. Different chemical elements have different kinds of atoms, and such atoms have different masses. In an ordinary chemical reaction, atoms move from one substance to another, but no atom of element disappears or is changed into an atom of another element. The forma ...
... in mass and in all other properties. Different chemical elements have different kinds of atoms, and such atoms have different masses. In an ordinary chemical reaction, atoms move from one substance to another, but no atom of element disappears or is changed into an atom of another element. The forma ...
Chemical Reaction Basics
... Requirements for Chemical Equations 1. Must represent all known facts (states of reactants and products, etc.) *Assume reactions take place at room temperature unless noted otherwise* 2. Must contain correctly written formulas 3. Must satisfy the Law of Conservation of Mass (*Balanced*) ...
... Requirements for Chemical Equations 1. Must represent all known facts (states of reactants and products, etc.) *Assume reactions take place at room temperature unless noted otherwise* 2. Must contain correctly written formulas 3. Must satisfy the Law of Conservation of Mass (*Balanced*) ...
Note 1.1 Chemistry of Life
... Atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of the atom. It determines the particular atom identity. (Periodic Table) Atomic mass is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are not found within the nucleus and do not contribute to the ...
... Atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of the atom. It determines the particular atom identity. (Periodic Table) Atomic mass is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are not found within the nucleus and do not contribute to the ...
Humes Biology Chapter 3 Biochemistry Carbon Compounds
... Composed of 2 fatty acids joined to a glycerol molecule Found in cell membranes also called the phospholipid bi-layer because it is composed of 2 layers of phospholipids o Waxes Composed of a long fatty acid chain joined to a long alcohol chain Wax can be found on the outside of plants to pr ...
... Composed of 2 fatty acids joined to a glycerol molecule Found in cell membranes also called the phospholipid bi-layer because it is composed of 2 layers of phospholipids o Waxes Composed of a long fatty acid chain joined to a long alcohol chain Wax can be found on the outside of plants to pr ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... ____________________23. DNA and RNA belong to this category of biological molecules. ____________________ 24. Name for an electrically charged atom. ____________________ 25. When the pH equals 7, it is said to be this. ...
... ____________________23. DNA and RNA belong to this category of biological molecules. ____________________ 24. Name for an electrically charged atom. ____________________ 25. When the pH equals 7, it is said to be this. ...
Topic 3&4 Atoms and the per.table
... Q4. (a) The elements in group 1 react with water to form an ...
... Q4. (a) The elements in group 1 react with water to form an ...
Macromolecules Worksheet - High School Science Help
... ____________________23. DNA and RNA belong to this category of biological molecules. ____________________ 24. Name for an electrically charged atom. ____________________ 25. When the pH equals 7, it is said to be this. ...
... ____________________23. DNA and RNA belong to this category of biological molecules. ____________________ 24. Name for an electrically charged atom. ____________________ 25. When the pH equals 7, it is said to be this. ...
CH303 Spectroscopic Identification of Organic Compounds
... 1. Introduction. The spectroscopic approach to structure. Contribution of different forms of spectroscopy (NMR, IR, MS). 2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy. Principles of NMR. Instrumentation and sample handling. Routine proton magnetic resonance (1H NMR): Chemical shift ...
... 1. Introduction. The spectroscopic approach to structure. Contribution of different forms of spectroscopy (NMR, IR, MS). 2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy. Principles of NMR. Instrumentation and sample handling. Routine proton magnetic resonance (1H NMR): Chemical shift ...
Building Blocks of Life
... The valences of carbon and its most frequent partners (hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen) are the “building code” that governs the architecture of living molecules ...
... The valences of carbon and its most frequent partners (hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen) are the “building code” that governs the architecture of living molecules ...
Macromolecules Notes
... ____________________23. DNA and RNA belong to this category of biological molecules. ____________________ 24. Name for an electrically charged atom. ____________________ 25. When the pH equals 7, it is said to be this. ...
... ____________________23. DNA and RNA belong to this category of biological molecules. ____________________ 24. Name for an electrically charged atom. ____________________ 25. When the pH equals 7, it is said to be this. ...
Chapter 3 Power Point
... atom of every element is always the same – However, the number of neutrons can vary from one atom of the element to the next Atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are known as isotopes of that element ...
... atom of every element is always the same – However, the number of neutrons can vary from one atom of the element to the next Atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are known as isotopes of that element ...
Mass Spectroscopy
... field. • Amount of deflection depends on m/z. • The detector signal is proportional to the number of ions hitting it. • By varying the magnetic field, ions of all masses are collected and counted. => ...
... field. • Amount of deflection depends on m/z. • The detector signal is proportional to the number of ions hitting it. • By varying the magnetic field, ions of all masses are collected and counted. => ...
Atomic Structure Notes Blank
... III. How Atoms Differ: A. Atomic Number 1. Henry Moseley (1912) – discovered that atoms of 2 different elements contain different numbers of ____________________. 2. Atomic Number – The number of ________________ in an element a. How many protons does a gold atom have?_______ An aluminum atom?______ ...
... III. How Atoms Differ: A. Atomic Number 1. Henry Moseley (1912) – discovered that atoms of 2 different elements contain different numbers of ____________________. 2. Atomic Number – The number of ________________ in an element a. How many protons does a gold atom have?_______ An aluminum atom?______ ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.