Section 2–1 The Nature of Matter
... This section identifies the three particles that make up atoms. It also explains how atoms of the same element can have a different number of neutrons and describes the two main types of chemical bonds. ...
... This section identifies the three particles that make up atoms. It also explains how atoms of the same element can have a different number of neutrons and describes the two main types of chemical bonds. ...
AP Chem
... even number of neutrons. The least stable situation is when both numbers are odd. There are only four (or five) stable odd/odd nuclei. Nuclides with a mass number over 200 usually undergo alpha decay. They emit a particle consisting of two protons and two neutrons. Nuclides with too many neutrons un ...
... even number of neutrons. The least stable situation is when both numbers are odd. There are only four (or five) stable odd/odd nuclei. Nuclides with a mass number over 200 usually undergo alpha decay. They emit a particle consisting of two protons and two neutrons. Nuclides with too many neutrons un ...
Unit 5 Notes
... Many times in chemistry, you will need to express a measurement in a unit different from the one given or measured initially. C. A ___________________________ is a ratio of equivalent measurements used to convert from one unit to another. They are written in the form of a ___________________. ...
... Many times in chemistry, you will need to express a measurement in a unit different from the one given or measured initially. C. A ___________________________ is a ratio of equivalent measurements used to convert from one unit to another. They are written in the form of a ___________________. ...
Sec 3.1
... Law of Definite Proportions – Compounds are always composed of a fixed proportion of elements. ex. NaCl always contains 1 Na and 1 Cl or 39.34% by mass Na 60.66% by mass Cl Law of Multiple Proportions – the same element may combine to form more than one compound. ex. CO (Carbon monoxide) and CO2 (Ca ...
... Law of Definite Proportions – Compounds are always composed of a fixed proportion of elements. ex. NaCl always contains 1 Na and 1 Cl or 39.34% by mass Na 60.66% by mass Cl Law of Multiple Proportions – the same element may combine to form more than one compound. ex. CO (Carbon monoxide) and CO2 (Ca ...
CHAPTER 4: ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
... There are currently 91 naturally occurring elements and 20 man-made elements. 4.2 Indivisible: The Atomic Theory Greek philosophers were the first to propose explanations for what was observed in nature. – Surprisingly, some of these Greek ideas led to similar modern ideas. Democritus (462-370 B.C.) ...
... There are currently 91 naturally occurring elements and 20 man-made elements. 4.2 Indivisible: The Atomic Theory Greek philosophers were the first to propose explanations for what was observed in nature. – Surprisingly, some of these Greek ideas led to similar modern ideas. Democritus (462-370 B.C.) ...
The Atom
... protons • An isotope refers to atoms that have the same # of ___________, but they have a neutrons different # of ___________. mass • Because of this, they have different _________ #’s (or simply, different masses ___________.) • Isotopes are the same element, but the atoms weigh a different amount ...
... protons • An isotope refers to atoms that have the same # of ___________, but they have a neutrons different # of ___________. mass • Because of this, they have different _________ #’s (or simply, different masses ___________.) • Isotopes are the same element, but the atoms weigh a different amount ...
31.1 Nuclear Structure
... •In 1949, Willard Libby developed a method of using the radioactive isotope 14 C to determine the age of organic materials up to about 50,000 years old. Libby won a Nobel Prize for his work. •The concentration of 14 C in the is about 1 part per trillion (1 atom of 14 C for 8.3 x 1011 atoms of 12 C. ...
... •In 1949, Willard Libby developed a method of using the radioactive isotope 14 C to determine the age of organic materials up to about 50,000 years old. Libby won a Nobel Prize for his work. •The concentration of 14 C in the is about 1 part per trillion (1 atom of 14 C for 8.3 x 1011 atoms of 12 C. ...
Zn + HCl → ZnCl 2 + H2 NaOH + H3PO4 → Na3PO4 + H2O N2 +
... Now, never touch the subscripts in the formulas again. Different subscripts = different molecules 2) Balance the equation by trying different coefficients to make the number of atoms of each element the same on both sides of the equation. Remember to multiply by the subscript when adding up numb ...
... Now, never touch the subscripts in the formulas again. Different subscripts = different molecules 2) Balance the equation by trying different coefficients to make the number of atoms of each element the same on both sides of the equation. Remember to multiply by the subscript when adding up numb ...
AP Unit 0: Chemical Foundations
... Other wise they will accept answers that are ±1 sig fig. All most every question has 3 sig. fig. Therefore if you report with 3 sig fig always you’re most likely to get it correct. ...
... Other wise they will accept answers that are ±1 sig fig. All most every question has 3 sig. fig. Therefore if you report with 3 sig fig always you’re most likely to get it correct. ...
Counting atoms
... High-precision measurements of the Avogadro constant are important for being able to quantitatively connect the macroand microscales — obviously, knowing NA, one can switch between molar mass and particle mass. But in addition, metrologists are planning to define the kilogram and the mole via the Pl ...
... High-precision measurements of the Avogadro constant are important for being able to quantitatively connect the macroand microscales — obviously, knowing NA, one can switch between molar mass and particle mass. But in addition, metrologists are planning to define the kilogram and the mole via the Pl ...
PAP Chemistry - Fall Final Review
... 1. Be able to determine the number of significant figures present in a given number a. 0.00203 b. 123 c. 100 d. 100. e. 100.050 2. 7.65 * 2 = (with correct s.f.) 3. 2.30 + 3.225 = (with correct s.f.) Chapter 3 (Atoms) 4. Define atom, nucleus, electron, neutron, proton 5. What did Rutherford discover ...
... 1. Be able to determine the number of significant figures present in a given number a. 0.00203 b. 123 c. 100 d. 100. e. 100.050 2. 7.65 * 2 = (with correct s.f.) 3. 2.30 + 3.225 = (with correct s.f.) Chapter 3 (Atoms) 4. Define atom, nucleus, electron, neutron, proton 5. What did Rutherford discover ...
File
... or share electrons so as to have eight electrons in their outer electron shell. Atoms gain or lose electrons so that they have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas. Some metal atoms, depending on the nature of the chemical reaction, can form stable ions with more than one charge. Fo ...
... or share electrons so as to have eight electrons in their outer electron shell. Atoms gain or lose electrons so that they have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas. Some metal atoms, depending on the nature of the chemical reaction, can form stable ions with more than one charge. Fo ...
N.9 – Metabolic Changes of Drugs and Related
... Why Aflatoxin B1 is carcinogenic? This naturally occurring carcinogenic agent contains an olefinic (C2–C3) double bond adjacent to a cyclic ether oxygen. The hepatocarcinogenicity of aflatoxin B1 has been clearly linked to its metabolic oxidation to the corresponding 2,3-oxide, which is extremely ...
... Why Aflatoxin B1 is carcinogenic? This naturally occurring carcinogenic agent contains an olefinic (C2–C3) double bond adjacent to a cyclic ether oxygen. The hepatocarcinogenicity of aflatoxin B1 has been clearly linked to its metabolic oxidation to the corresponding 2,3-oxide, which is extremely ...
The Periodic table and subatomic particles
... Ionic compounds – metal and nonmetal – name metal and change ending of nonmetal to “ide” Molecular compounds – 2 nonmetals (use prefixes) Polyatomic compounds – metal and group of nonmetals – name metal followed by polyatomic ion ...
... Ionic compounds – metal and nonmetal – name metal and change ending of nonmetal to “ide” Molecular compounds – 2 nonmetals (use prefixes) Polyatomic compounds – metal and group of nonmetals – name metal followed by polyatomic ion ...
OH - H + - WordPress.com
... these are generally plant based and are better from a health standpoint. An unsaturated fatty acid has a carbon skeleton with at least one double bond (not fully saturated with hydrogen); these are generally animal based and are worse from a health standpoint. The double bonds of unsaturated fatty a ...
... these are generally plant based and are better from a health standpoint. An unsaturated fatty acid has a carbon skeleton with at least one double bond (not fully saturated with hydrogen); these are generally animal based and are worse from a health standpoint. The double bonds of unsaturated fatty a ...
Ch. 21.1 Nuclear Radiation
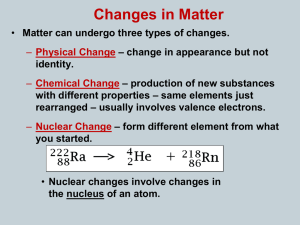
... • Matter can undergo three types of changes. – Physical Change – change in appearance but not identity. – Chemical Change – production of new substances with different properties – same elements just rearranged – usually involves valence electrons. – Nuclear Change – form different element from what ...
... • Matter can undergo three types of changes. – Physical Change – change in appearance but not identity. – Chemical Change – production of new substances with different properties – same elements just rearranged – usually involves valence electrons. – Nuclear Change – form different element from what ...
File
... Coefficients Interpretation of above example: 2 atoms of solid iron (metal) react with 3 molecules of chlorine gas to produce 2 formula units of solid iron (III) chloride. Coefficients can also be interpreted in a more useful way: MOLES! This is just as if we multiplied the whole equation by 6.02 x ...
... Coefficients Interpretation of above example: 2 atoms of solid iron (metal) react with 3 molecules of chlorine gas to produce 2 formula units of solid iron (III) chloride. Coefficients can also be interpreted in a more useful way: MOLES! This is just as if we multiplied the whole equation by 6.02 x ...
Carbohydrates, Lipids, and proteins
... Some are storage molecules, which cells break down as needed to obtain sugar ...
... Some are storage molecules, which cells break down as needed to obtain sugar ...
CHEM_Review - Kenston Local Schools
... Counting Atoms The formula for a compound indicates the elements that make up the compound and the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. These numbers of atoms are indicated by the use of small numbers called subscripts. Sometimes groups of atoms act as a single atom. Such a grou ...
... Counting Atoms The formula for a compound indicates the elements that make up the compound and the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. These numbers of atoms are indicated by the use of small numbers called subscripts. Sometimes groups of atoms act as a single atom. Such a grou ...
ΑΝΑΚΟΙΝΩΣΗ Υπάρχει δυνατότητα για Έλληνες διδακτορικούς
... The biophysicists active at ISOLDE presently pursue two paths. They produce relatively long‐lived isotopes of elements such as Cd, Pb, and Hg, and transport them to offline laboratories, where they perform experiments with the Perturbed Angular Correlation (PAC) method. In addition, within a VITO co ...
... The biophysicists active at ISOLDE presently pursue two paths. They produce relatively long‐lived isotopes of elements such as Cd, Pb, and Hg, and transport them to offline laboratories, where they perform experiments with the Perturbed Angular Correlation (PAC) method. In addition, within a VITO co ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.