Chapter 2
... All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: The atomic number (Z) Atomic Mass The mass of an atom in atomic mass units (amu) is the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom Isotopes: • Atoms of the same element with different masses. • Isotopes have different numbers of ne ...
... All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: The atomic number (Z) Atomic Mass The mass of an atom in atomic mass units (amu) is the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom Isotopes: • Atoms of the same element with different masses. • Isotopes have different numbers of ne ...
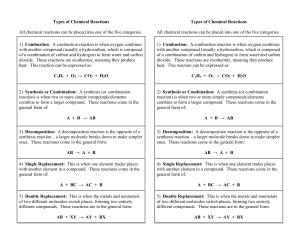
Types of Chemical Reactions
... general form of: A + BC → AC + B 5) Double Replacement: This is when the metals and nonmetals of two different molecules switch places, forming two entirely different compounds. These reactions are in the general form: ...
... general form of: A + BC → AC + B 5) Double Replacement: This is when the metals and nonmetals of two different molecules switch places, forming two entirely different compounds. These reactions are in the general form: ...
1 2.1 Atomic Structure and Subatomic Particles (p. 40) There are two
... The atom is electrically ____________. This means that the number of ____________ is equal to the number of ________________. The electrons, composing less than ______% of the atom’s mass, ________ ___________ the nucleus. In some atoms, the electrons are _________________ to move from one atom to a ...
... The atom is electrically ____________. This means that the number of ____________ is equal to the number of ________________. The electrons, composing less than ______% of the atom’s mass, ________ ___________ the nucleus. In some atoms, the electrons are _________________ to move from one atom to a ...
Chapter 4
... Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
AP Chem Stoichiometry Topic#4 Questions WS Name: Date: Per
... (1) Naturally occurring magnesium has isotopic abundances as shown. (a) What is the average atomic mass of Mg? (b) Sketch the mass spectrum of Mg. (2) Glycine, an amino acid used by organisms to make proteins, is represented by the molecular model. (a) Write its molecular formula. (b) Determine its ...
... (1) Naturally occurring magnesium has isotopic abundances as shown. (a) What is the average atomic mass of Mg? (b) Sketch the mass spectrum of Mg. (2) Glycine, an amino acid used by organisms to make proteins, is represented by the molecular model. (a) Write its molecular formula. (b) Determine its ...
Carbon Isotopes
... which the original parent nuclide forms an unstable daughter nuclide, which also decays... ...
... which the original parent nuclide forms an unstable daughter nuclide, which also decays... ...
Review Notes for Atomic Structure and Radioactivity Test on Friday
... 13. Atomic number - the number on the bottom before the element’s symbol - is unique to each element and is equal to the number of protons, which is equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom. 14. Mass number - equal to the total number of protons plus neutrons, and appears at the top before ...
... 13. Atomic number - the number on the bottom before the element’s symbol - is unique to each element and is equal to the number of protons, which is equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom. 14. Mass number - equal to the total number of protons plus neutrons, and appears at the top before ...
Chemical formula Chemistry Subscript Subscript
... 8U2 - 5(D) recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing subscripts; A way of describing the number of atoms Chemical formula that makes up one molecule of a compound ...
... 8U2 - 5(D) recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing subscripts; A way of describing the number of atoms Chemical formula that makes up one molecule of a compound ...
Final Preparation
... 4. Which of the following statements about isotopes is TRUE? A) Isotopes of the same element differ only in the number of electrons they contain. B) An isotope of an atom with a larger number of neutrons is larger than an isotope of the same atom that contains fewer neutrons. C) Isotopes of the same ...
... 4. Which of the following statements about isotopes is TRUE? A) Isotopes of the same element differ only in the number of electrons they contain. B) An isotope of an atom with a larger number of neutrons is larger than an isotope of the same atom that contains fewer neutrons. C) Isotopes of the same ...
Understanding the Atom
... Lavoisier conducted experiments that led to the Law of Conservation of Mass. It says that in any chemical reaction, the mass of the products of the reaction will always be equal to the mass of the materials at the beginning of the reaction. ...
... Lavoisier conducted experiments that led to the Law of Conservation of Mass. It says that in any chemical reaction, the mass of the products of the reaction will always be equal to the mass of the materials at the beginning of the reaction. ...
CHEMISTRY
... 2. Why do atoms form bonds? a. To change from a gaseous state b. To become more stable c. To build larger molecules d. To gather more electrons ...
... 2. Why do atoms form bonds? a. To change from a gaseous state b. To become more stable c. To build larger molecules d. To gather more electrons ...
AP Semester I Review: Free Response Questions
... The structures of a water molecule and a crystal of LiCl(s) are represented above. A student prepares a 1.0 M solution by dissolving 4.2 g of LiCl(s) in enough water to make 100 mL of solution. a. In the space provided below, show the interactions of the components of LiCl(aq) by making a drawing th ...
... The structures of a water molecule and a crystal of LiCl(s) are represented above. A student prepares a 1.0 M solution by dissolving 4.2 g of LiCl(s) in enough water to make 100 mL of solution. a. In the space provided below, show the interactions of the components of LiCl(aq) by making a drawing th ...
atoms
... • In a living organism, the amount of carbon-14 remains in constant balance with the levels of the isotope in the atmosphere or ocean. • This balance occurs because living organisms take in and release carbon. • Geologists examine the decay of uranium to age rocks. ...
... • In a living organism, the amount of carbon-14 remains in constant balance with the levels of the isotope in the atmosphere or ocean. • This balance occurs because living organisms take in and release carbon. • Geologists examine the decay of uranium to age rocks. ...
atoms - My CCSD
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
Balancing Equations
... the formulas of the reactants (on the left) are connected by an arrow with the formulas for the products (on the right). • Example: Reactants Products ...
... the formulas of the reactants (on the left) are connected by an arrow with the formulas for the products (on the right). • Example: Reactants Products ...
Atoms and Isotopes Worksheet
... 7. The # of protons in the nucleus of an atom is also known as the atomic _________ (mass/ number/ weight/ charge) 8. Which subatomic particles are found in the nucleus? ...
... 7. The # of protons in the nucleus of an atom is also known as the atomic _________ (mass/ number/ weight/ charge) 8. Which subatomic particles are found in the nucleus? ...
chapter-7-explore-page-248-protons-neutrons
... Any one of these three quantities can be determined if you know the value of the other two quantities. For example: to determine the mass number of an atom, you must know the number of neutrons and the number of protons in the atom. An isotope often is written with the element name followed by t ...
... Any one of these three quantities can be determined if you know the value of the other two quantities. For example: to determine the mass number of an atom, you must know the number of neutrons and the number of protons in the atom. An isotope often is written with the element name followed by t ...
Chapter 2 Biochemistry Goux Guided Notes
... - Some isotopes are radioactive, The radiation these isotopes give off can be dangerous, but radioactive isotopes have a number of important scientific and practical uses; geologists can determine the ages of rocks and fossils by analyzing the isotopes found in them. Radiation from certain isotopes ...
... - Some isotopes are radioactive, The radiation these isotopes give off can be dangerous, but radioactive isotopes have a number of important scientific and practical uses; geologists can determine the ages of rocks and fossils by analyzing the isotopes found in them. Radiation from certain isotopes ...
Chemistry I Honors
... • Since the actual mass (in grams) of atoms is such an obnoxious number, Chemistry decided to invent a new measurement to describe the mass of individual atoms. ...
... • Since the actual mass (in grams) of atoms is such an obnoxious number, Chemistry decided to invent a new measurement to describe the mass of individual atoms. ...
Chapter 14.1 The Structure of The Atom
... contains 99% of all the mass and ALL of the positive charge What do you think is found inside the nucleus? Protons, neutrons, or electrons Protons are found in the nucleus and have a positive charge (+e) EXACTLY opposite to the electron Electrons are found inside atoms, but OUTSIDE of the nucleus an ...
... contains 99% of all the mass and ALL of the positive charge What do you think is found inside the nucleus? Protons, neutrons, or electrons Protons are found in the nucleus and have a positive charge (+e) EXACTLY opposite to the electron Electrons are found inside atoms, but OUTSIDE of the nucleus an ...
atomic theory of matter
... PROPORTIONS • Some elements can form more than one compound when they react together (C & O: CO and CO2; N & O: N2O, NO, NO2, etc.). Dalton’s law predicted that the mass proportions should be proportional. Experiment confirmed this leading to this law. • Law of multiple proportions: when two element ...
... PROPORTIONS • Some elements can form more than one compound when they react together (C & O: CO and CO2; N & O: N2O, NO, NO2, etc.). Dalton’s law predicted that the mass proportions should be proportional. Experiment confirmed this leading to this law. • Law of multiple proportions: when two element ...
Unit 1 – Atomic Structure
... 1. The number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element 2. Atoms are identified by their atomic number 3. Because atoms are neutral, # protons = # electrons 4. Periodic Table is in order of increasing atomic number B. Mass Number 1. The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleu ...
... 1. The number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element 2. Atoms are identified by their atomic number 3. Because atoms are neutral, # protons = # electrons 4. Periodic Table is in order of increasing atomic number B. Mass Number 1. The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleu ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.