3. Biotechnological Importance of MO - Copy
... ethanol to acetic acid, sorbitol to sorbose, synthesis of steroid hormones and certain amino acids ...
... ethanol to acetic acid, sorbitol to sorbose, synthesis of steroid hormones and certain amino acids ...
Honors Chemistry
... phase state solid liquid gas melting / freezing evaporating / condensing mixture solution substance homogeneous heterogeneous element compound atom molecule formula unit diatomic elements nucleus isotope energy frequency wavelength light electromagnetic waves photons quantized subatomic charge neutr ...
... phase state solid liquid gas melting / freezing evaporating / condensing mixture solution substance homogeneous heterogeneous element compound atom molecule formula unit diatomic elements nucleus isotope energy frequency wavelength light electromagnetic waves photons quantized subatomic charge neutr ...
Chapter 2 Review
... W hat are the storage and quick energy forms of carbohydrates found in animals, and how are these structurally related to each other? (pp.45-46)__________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... W hat are the storage and quick energy forms of carbohydrates found in animals, and how are these structurally related to each other? (pp.45-46)__________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
The Atom: History and Structure
... electrons are just scattered around and orbit the nucleus like the planets orbit the sun Later found that nucleus contains protons (positive particles) and neutrons (particles with no charge) ...
... electrons are just scattered around and orbit the nucleus like the planets orbit the sun Later found that nucleus contains protons (positive particles) and neutrons (particles with no charge) ...
Chapter 4 Section 1
... chemical symbol for iron. 14. Stars consist of matter in the form of plasma, a gas-like mixture of free electrons and atomic nuclei. 15. Elements are created when the extreme high pressure inside the stars forces atomic nuclei to collide. 16. The process is called nuclear fusion. 17. Nuclear fusion, ...
... chemical symbol for iron. 14. Stars consist of matter in the form of plasma, a gas-like mixture of free electrons and atomic nuclei. 15. Elements are created when the extreme high pressure inside the stars forces atomic nuclei to collide. 16. The process is called nuclear fusion. 17. Nuclear fusion, ...
Discovery of Atomic Structure
... Isotopes have different numbers of neutrons. An atom of a specific isotope is called a nuclide. Nuclides of hydrogen include: 1H ...
... Isotopes have different numbers of neutrons. An atom of a specific isotope is called a nuclide. Nuclides of hydrogen include: 1H ...
An Introduction to Matter
... • Chemical Change: Sugar is a compound that can be easily decomposed to simpler substances by heating. One of the simpler substances is the black element carbon, which cannot be further decomposed by chemical or physical means. ...
... • Chemical Change: Sugar is a compound that can be easily decomposed to simpler substances by heating. One of the simpler substances is the black element carbon, which cannot be further decomposed by chemical or physical means. ...
- 5`d*
... potassium gains one electron --a-. q!,, the potassium ion simulates the electron con{iguration of argon fluoride ion simulates the electron configuration of neon i"c. td. ,the fluorine loses one electron e. all are incorrect statements 8. Which of the following a. e. ...
... potassium gains one electron --a-. q!,, the potassium ion simulates the electron con{iguration of argon fluoride ion simulates the electron configuration of neon i"c. td. ,the fluorine loses one electron e. all are incorrect statements 8. Which of the following a. e. ...
Kimya
... atomic structure was not fully understood until the discovery of the neutron in 1932. The history of the discovery of atomic structure is one of the most interesting and profound stories in science. In 1910 Rutherford was the first to propose what is accepted today as the basic structure of the atom ...
... atomic structure was not fully understood until the discovery of the neutron in 1932. The history of the discovery of atomic structure is one of the most interesting and profound stories in science. In 1910 Rutherford was the first to propose what is accepted today as the basic structure of the atom ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom Mass number = # protons + # neutrons or Mass number = atomic number + # neutrons • How do you determine the number of neutrons in an atom? # neutrons = mass number (A) - atomic number (Z) ...
... number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom Mass number = # protons + # neutrons or Mass number = atomic number + # neutrons • How do you determine the number of neutrons in an atom? # neutrons = mass number (A) - atomic number (Z) ...
Chapter 3—Time and Geology
... elsewhere in Europe that were higher (hence, younger according to superposition) than those described as Silurian in southern Wales by Murchison. FIGURE 3–7 (p. 39) The stratum beneath the ash must be older than 453.7 million years. FIGURE 3–10 (p. 40) If a graph were prepared showing how much sand ...
... elsewhere in Europe that were higher (hence, younger according to superposition) than those described as Silurian in southern Wales by Murchison. FIGURE 3–7 (p. 39) The stratum beneath the ash must be older than 453.7 million years. FIGURE 3–10 (p. 40) If a graph were prepared showing how much sand ...
Chemical Reactions
... 3. Determine where to place coefficients in front of formulas so that the left side has the same number of atoms as the right side for EACH element in order to balance the equation. 4. Check your answer to see if: • The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. • The coefficie ...
... 3. Determine where to place coefficients in front of formulas so that the left side has the same number of atoms as the right side for EACH element in order to balance the equation. 4. Check your answer to see if: • The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. • The coefficie ...
Attachment: Click to download
... One way of producing O2(g) involves the decomposition of potassium chlorate into potassium chloride and oxygen gas. A 25.5 g sample of Potassium chlorate is decomposed. How many moles of O2(g) are produced? How many grams of potassium chloride? How many grams of oxygen? ...
... One way of producing O2(g) involves the decomposition of potassium chlorate into potassium chloride and oxygen gas. A 25.5 g sample of Potassium chlorate is decomposed. How many moles of O2(g) are produced? How many grams of potassium chloride? How many grams of oxygen? ...
The Chemistry of Biology
... 31. Which of the following functional groups is mismatched to the organic compound? A. Phosphate-carbohydrates B. Sulfhydryl-proteins C. Amino-proteins D. Hydroxyl-alcohols E. Carboxyl-fatty acids 32. Organic chemicals always have a basic framework of the element _____ bonded to other atoms. A. Car ...
... 31. Which of the following functional groups is mismatched to the organic compound? A. Phosphate-carbohydrates B. Sulfhydryl-proteins C. Amino-proteins D. Hydroxyl-alcohols E. Carboxyl-fatty acids 32. Organic chemicals always have a basic framework of the element _____ bonded to other atoms. A. Car ...
6.1 Info Sheet The Nature of Chemical Reactions
... 9. Reactions that release energy are ______________ a) In the isooctane-oxygen reaction, more __________ is released as the products form than is absorbed to _______ the bonds in the ____________. b) Like all other ______________ reactions, this in an ______________ _____________. c) After an exothe ...
... 9. Reactions that release energy are ______________ a) In the isooctane-oxygen reaction, more __________ is released as the products form than is absorbed to _______ the bonds in the ____________. b) Like all other ______________ reactions, this in an ______________ _____________. c) After an exothe ...
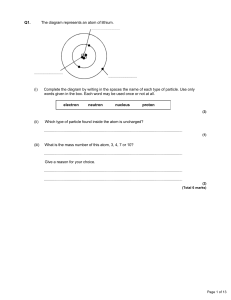
Atomic Structure Worksheet
... symbol charge location mass size (see below) Let’s make this more visual using information from the Chart of Fundamental Particles. If the proton were 10 cm in diameter… the size of an orange, how big would everything be? ...
... symbol charge location mass size (see below) Let’s make this more visual using information from the Chart of Fundamental Particles. If the proton were 10 cm in diameter… the size of an orange, how big would everything be? ...
Chem Ch4,25
... rather than a bunch of grapes. Some isotopes of some elements contain and unstable ratio of protons to neutrons. These Radioisotopes are radioactive because they have unstable nuclei. ...
... rather than a bunch of grapes. Some isotopes of some elements contain and unstable ratio of protons to neutrons. These Radioisotopes are radioactive because they have unstable nuclei. ...
Heine - MrZitarelli
... When you take a test, read the question slowly. Don’t look at the answer choices. Try to think of a possible answer for the question. Once you’ve thought of an answer, look at your choices. Do you see a match? Read the following question. Do not read the answer choices. Think of a possible answer. W ...
... When you take a test, read the question slowly. Don’t look at the answer choices. Try to think of a possible answer for the question. Once you’ve thought of an answer, look at your choices. Do you see a match? Read the following question. Do not read the answer choices. Think of a possible answer. W ...
673 lab three
... A) DISCUSS CHEMICAL REACTIONS: start with a definition and apply the law of conservation of mass in a chemical reaction to the reaction in this lab. Discuss balanced reactions and give three example reactions and SHOW that they are balanced. Clearly indicate the role of COEFFICIENTS., B) DISCUSS CHE ...
... A) DISCUSS CHEMICAL REACTIONS: start with a definition and apply the law of conservation of mass in a chemical reaction to the reaction in this lab. Discuss balanced reactions and give three example reactions and SHOW that they are balanced. Clearly indicate the role of COEFFICIENTS., B) DISCUSS CHE ...
Chemistry Standards Checklist
... SC5. Students will understand that the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs can be affected by changing concentration, temperature, or pressure and the addition of a ...
... SC5. Students will understand that the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs can be affected by changing concentration, temperature, or pressure and the addition of a ...
Chemistry of Life Review Sheet Key
... Metabolism- sum of the reactions that take place in the cell. atom- smallest single particle of matter. isotope- atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. ion- atom with + or - charge. Na+ or O2element- pure substance, one type of atom. molecule- any cluster of at ...
... Metabolism- sum of the reactions that take place in the cell. atom- smallest single particle of matter. isotope- atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. ion- atom with + or - charge. Na+ or O2element- pure substance, one type of atom. molecule- any cluster of at ...
Radiation Questions March 4th
... In 1991, some scientists compared the health of two groups of people: a control group and a group that had been exposed to the radiation from Chernobyl. What people would have been in the control group? ...
... In 1991, some scientists compared the health of two groups of people: a control group and a group that had been exposed to the radiation from Chernobyl. What people would have been in the control group? ...
know thy reference tables!
... disintegration of this radioisotope is the first in a series of spontaneous decays. The sixth decay in this series produces the radioisotope radon-222. The decay of radon-222 produces the radioisotope polonium-218 that has a half life of 3.04 minutes. Eventually, the stable isotope lead-206 is produ ...
... disintegration of this radioisotope is the first in a series of spontaneous decays. The sixth decay in this series produces the radioisotope radon-222. The decay of radon-222 produces the radioisotope polonium-218 that has a half life of 3.04 minutes. Eventually, the stable isotope lead-206 is produ ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.