know thy reference tables!
... disintegration of this radioisotope is the first in a series of spontaneous decays. The sixth decay in this series produces the radioisotope radon-222. The decay of radon-222 produces the radioisotope polonium-218 that has a half life of 3.04 minutes. Eventually, the stable isotope lead-206 is produ ...
... disintegration of this radioisotope is the first in a series of spontaneous decays. The sixth decay in this series produces the radioisotope radon-222. The decay of radon-222 produces the radioisotope polonium-218 that has a half life of 3.04 minutes. Eventually, the stable isotope lead-206 is produ ...
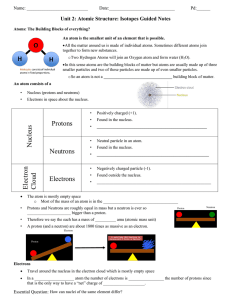
Nucleus Protons Neutrons Electron Cloud Electrons
... Isotope – atoms of the same element that have the same number of _______________but a different number of _________________________ Ions – atoms of the same element that have the same number of __________________ but different number of _________________________ ...
... Isotope – atoms of the same element that have the same number of _______________but a different number of _________________________ Ions – atoms of the same element that have the same number of __________________ but different number of _________________________ ...
CHEMICAL EQUATIONS, SYMBOLS, FORULAS 7
... There are two O atoms on the reactant side (coefficient 2 x (understood) subscript 1) and two O atoms on the product side (understood coefficient 1 x subscript 2). There are the same number of H atoms (4) and O atoms (2) on both sides of the equation; therefore, the equation is said to be balanced. ...
... There are two O atoms on the reactant side (coefficient 2 x (understood) subscript 1) and two O atoms on the product side (understood coefficient 1 x subscript 2). There are the same number of H atoms (4) and O atoms (2) on both sides of the equation; therefore, the equation is said to be balanced. ...
atom
... Two samples of carbon dioxide are decomposed into their constituent elements. One sample produces 25.6 g of oxygen and 9.60 g of carbon, and the other produces 21.6 g of oxygen and 8.10 g of carbon. Show that these results are consistent with the law of definite ...
... Two samples of carbon dioxide are decomposed into their constituent elements. One sample produces 25.6 g of oxygen and 9.60 g of carbon, and the other produces 21.6 g of oxygen and 8.10 g of carbon. Show that these results are consistent with the law of definite ...
10th Grade Chemistry X (TJ) GRADE(S)/LEVELS SUBJECT Power
... Solutions are mixtures in which particles of one substance are evenly distributed through another substance. Liquids are limited in the amount of dissolved solid or gas that they can contain. Aqueous solutions can be described by relative quantities of the dissolved substances and acidity or alkalin ...
... Solutions are mixtures in which particles of one substance are evenly distributed through another substance. Liquids are limited in the amount of dissolved solid or gas that they can contain. Aqueous solutions can be described by relative quantities of the dissolved substances and acidity or alkalin ...
Atomic Structure Notepacket
... Atomic and Molecular Structure 1a. Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. 1b. Students know how to use the periodic table to identify metals, semi-metals {metalloids}, non-metals, and halogens 1e. Students know the nucleus o ...
... Atomic and Molecular Structure 1a. Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. 1b. Students know how to use the periodic table to identify metals, semi-metals {metalloids}, non-metals, and halogens 1e. Students know the nucleus o ...
Chapter 14 section 2
... What are the uses of radioactive isotopes? Scientists have made many useful isotopes. These isotopes, called tracer elements, can be placed in the body or released into the air. Then, scientists can use instruments to look for radiation while the tracer elements decay. Tracer elements have been used ...
... What are the uses of radioactive isotopes? Scientists have made many useful isotopes. These isotopes, called tracer elements, can be placed in the body or released into the air. Then, scientists can use instruments to look for radiation while the tracer elements decay. Tracer elements have been used ...
Natural Carbon Isotope Abundance of Plasma
... behind the difference in δ13C signature is complex when multiple compartments are modelled [9], we can then assume that isotope discrimination can occur at various steps between the plasma and the different tissues, including 1) isotope fractionation associated with the uptake and utilization of sub ...
... behind the difference in δ13C signature is complex when multiple compartments are modelled [9], we can then assume that isotope discrimination can occur at various steps between the plasma and the different tissues, including 1) isotope fractionation associated with the uptake and utilization of sub ...
The atom CP and H ONLINE
... If something has 5 protons, 5 neutrons, and 5 electrons, what is the mass number? 5 P + 5 N= 10 amu total Remember, mass number= P + N ...
... If something has 5 protons, 5 neutrons, and 5 electrons, what is the mass number? 5 P + 5 N= 10 amu total Remember, mass number= P + N ...
Physics 102, Class 25 The Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity
... – If + charges are emitted, the atomic number goes down by the number of + charges – If – charges are emitted, the atomic number goes up by the number of – charges – If neutrons are emitted, the atomic mass goes down by the number of neutrons – If gamma rays are emitted, atomic number and atomic mas ...
... – If + charges are emitted, the atomic number goes down by the number of + charges – If – charges are emitted, the atomic number goes up by the number of – charges – If neutrons are emitted, the atomic mass goes down by the number of neutrons – If gamma rays are emitted, atomic number and atomic mas ...
Notes matter energy
... A molecule is made up of two or more nonmetal atoms. A chemical formula tells the number and type of atoms in a molecule. For example, H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) is the formula for a molecule because it consists of only nonmetals. The molecule is made up of 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 sulfur atom, and 4 oxygen a ...
... A molecule is made up of two or more nonmetal atoms. A chemical formula tells the number and type of atoms in a molecule. For example, H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) is the formula for a molecule because it consists of only nonmetals. The molecule is made up of 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 sulfur atom, and 4 oxygen a ...
ChemCh4and6of2011
... • After more elements were discovered, order of atomic mass wasn’t working • 1913: Discovered atoms have unique number or protons in nucleus and rearranged table in order of atomic number • Periodic Law: The statement that there is a periodic repetition of chemical and physical properties of element ...
... • After more elements were discovered, order of atomic mass wasn’t working • 1913: Discovered atoms have unique number or protons in nucleus and rearranged table in order of atomic number • Periodic Law: The statement that there is a periodic repetition of chemical and physical properties of element ...
Packet 2 - Organic Chemistry
... A. large amount of stored information B. ability to catalyze biochemical reactions C. efficient storage of usable chemical energy D. tendency to make cell membranes hydrophobic 4. Substance A is converted to substance B in a metabolic reaction. Which statement best describes the role of an enzyme du ...
... A. large amount of stored information B. ability to catalyze biochemical reactions C. efficient storage of usable chemical energy D. tendency to make cell membranes hydrophobic 4. Substance A is converted to substance B in a metabolic reaction. Which statement best describes the role of an enzyme du ...
File
... Law of Conservation of Matter • Mass is not created (gained) nor destroyed (lost) during ordinary physical and chemical reactions. • Proven by Antoine Lavoisier 200 years ago ...
... Law of Conservation of Matter • Mass is not created (gained) nor destroyed (lost) during ordinary physical and chemical reactions. • Proven by Antoine Lavoisier 200 years ago ...
Tentative Chapter Three Assignments and Schedule
... Here is a list of quiz problems (partner, in-class, take-home or just "put them on the ch3 quiz" problems): 87,93 (if need more stoich),99 (if need more limiter), 107 (I usually give this one as a partner quiz...death by cyanide problem (kids like the name, but then they find it hard), but good revi ...
... Here is a list of quiz problems (partner, in-class, take-home or just "put them on the ch3 quiz" problems): 87,93 (if need more stoich),99 (if need more limiter), 107 (I usually give this one as a partner quiz...death by cyanide problem (kids like the name, but then they find it hard), but good revi ...
Worksheet 4.1 File
... c. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together, or can chemically combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds. d. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged; however, atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another element by a chem ...
... c. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together, or can chemically combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds. d. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged; however, atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another element by a chem ...
Name
... c. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together, or can chemically combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds. d. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged; however, atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another element by a chem ...
... c. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together, or can chemically combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds. d. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged; however, atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another element by a chem ...
Review Chemistry KEY - cms16-17
... 30. What happens when substances react chemically to produce new substances? The substances will have a new identity and new and different chemical and physical properties will form. 31. Explain the difference between reactants and products. Include where in the equation they would be found. Reactan ...
... 30. What happens when substances react chemically to produce new substances? The substances will have a new identity and new and different chemical and physical properties will form. 31. Explain the difference between reactants and products. Include where in the equation they would be found. Reactan ...
Document
... • One way of producing O2(g) involves the decomposition of potassium chlorate into potassium chloride and oxygen gas. A 25.5 g sample of Potassium chlorate is decomposed. How many moles of O2(g) are produced? • How many grams of potassium chloride? • How many grams of oxygen? ...
... • One way of producing O2(g) involves the decomposition of potassium chlorate into potassium chloride and oxygen gas. A 25.5 g sample of Potassium chlorate is decomposed. How many moles of O2(g) are produced? • How many grams of potassium chloride? • How many grams of oxygen? ...
S90 Notes U2 Topic 6 Chemical Compounds
... Naming ionic compounds: Ex. NaCl, LiF, CaCl2 Rules are from IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) 1. Name the metallic element 1st as it is written on the periodic table. 2. Name the nonmetallic element second, changing its ending to “ide.” 3. Positive and negative charges must e ...
... Naming ionic compounds: Ex. NaCl, LiF, CaCl2 Rules are from IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) 1. Name the metallic element 1st as it is written on the periodic table. 2. Name the nonmetallic element second, changing its ending to “ide.” 3. Positive and negative charges must e ...
Notes Unit 5-4
... • 1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 particles • Mole = amount of a substance “mol” • Avogadro’s Number • Based on the weight of carbon-12 atoms. ...
... • 1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 particles • Mole = amount of a substance “mol” • Avogadro’s Number • Based on the weight of carbon-12 atoms. ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.