B - eko.olunet.org
... Purity Grade of Compounds 3. In chemical experiments, the purity of the starting material and the composition of impurities/additives are of great importance. For his experiments, Thomas needed KBr with at least 95.0% purity. In order to determine the purity of an available inorganic compound, he w ...
... Purity Grade of Compounds 3. In chemical experiments, the purity of the starting material and the composition of impurities/additives are of great importance. For his experiments, Thomas needed KBr with at least 95.0% purity. In order to determine the purity of an available inorganic compound, he w ...
CH100: Fundamentals for Chemistry
... component substances by physical means only by a chemical process The breakdown of a pure substance results in formation of new substances (i.e. chemical change) For a pure substance there is nothing to separate (its only 1 substance to begin with) ...
... component substances by physical means only by a chemical process The breakdown of a pure substance results in formation of new substances (i.e. chemical change) For a pure substance there is nothing to separate (its only 1 substance to begin with) ...
CHEM 101 Final (Term 141)
... C) The pressure at the triple point for substance A is higher than that of substance B, but the normal boiling and normal melting point for substance A are lower than those of substance B. D) The pressure at the triple point, normal boiling and normal melting point for substance B and for substance ...
... C) The pressure at the triple point for substance A is higher than that of substance B, but the normal boiling and normal melting point for substance A are lower than those of substance B. D) The pressure at the triple point, normal boiling and normal melting point for substance B and for substance ...
Gas-Phase Reactions of Fe (CH2O)+ and Fe (CH2S)+ with Small
... bonding differences between Fe(CH2O)+ and Fe(CH2S)+. To do this, product ion structures were probed by collision-induced dissociation, specific ion-molecule reactions, and use of labeled compounds, and experimental bond energies were obtained by using ion-molecule bracketing and competitive collisio ...
... bonding differences between Fe(CH2O)+ and Fe(CH2S)+. To do this, product ion structures were probed by collision-induced dissociation, specific ion-molecule reactions, and use of labeled compounds, and experimental bond energies were obtained by using ion-molecule bracketing and competitive collisio ...
AP Chemistry Review Preparing for the AP
... Review your incorrect MC from the Practice Exam and understand the concepts. Know the 6 strong acids HCl, HI, HBr, H2SO4, HClO4, HNO3 and the one weak by formula acetic acid CH3COOH, everything else is weak. Remember that strong acids/bases don’t make buffers!!! You should be 100% confident what ion ...
... Review your incorrect MC from the Practice Exam and understand the concepts. Know the 6 strong acids HCl, HI, HBr, H2SO4, HClO4, HNO3 and the one weak by formula acetic acid CH3COOH, everything else is weak. Remember that strong acids/bases don’t make buffers!!! You should be 100% confident what ion ...
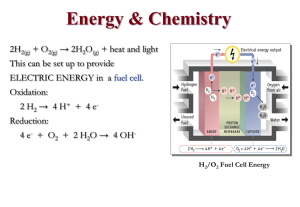
2H 2 O(g)
... pure form at one atmosphere and the temperature of interest. Standard enthalpy (ΔH°) is when all reactants and products are in their standard states. Standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf°) is the change in enthalpy that forms one mol of the compound from its elements. ...
... pure form at one atmosphere and the temperature of interest. Standard enthalpy (ΔH°) is when all reactants and products are in their standard states. Standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf°) is the change in enthalpy that forms one mol of the compound from its elements. ...
Exam 2 Key
... decreases, KE decreases. As KE drops, the average velocity of a gas decreases, resulting in fewer collisions with the walls of the container (and the collisions have less force). Fewer collisions mean lower pressure inside the balloon than outside the balloon. Since the balloon is elastic, the large ...
... decreases, KE decreases. As KE drops, the average velocity of a gas decreases, resulting in fewer collisions with the walls of the container (and the collisions have less force). Fewer collisions mean lower pressure inside the balloon than outside the balloon. Since the balloon is elastic, the large ...
Exames anteriores a 1994
... a function of the spatial coordinates. The maxima found in these maps coincide with the locations of the atoms and the values are approximately proportional to the number of electrons in the atom in question. a) Show where the maxima lie by drawing the contour curves around the maxima, connecting po ...
... a function of the spatial coordinates. The maxima found in these maps coincide with the locations of the atoms and the values are approximately proportional to the number of electrons in the atom in question. a) Show where the maxima lie by drawing the contour curves around the maxima, connecting po ...
19_Worked_Examples
... Analyze In part (a) we must predict the value for ΔG° relative to that for ΔH° on the basis of the balanced equation for the reaction. In part (b) we must calculate the value for ΔG° and compare this value with our qualitative prediction. Plan The free-energy change incorporates both the change in e ...
... Analyze In part (a) we must predict the value for ΔG° relative to that for ΔH° on the basis of the balanced equation for the reaction. In part (b) we must calculate the value for ΔG° and compare this value with our qualitative prediction. Plan The free-energy change incorporates both the change in e ...
Stoichiometry - Norbraten
... Your body deals with excess nitrogen by excreting it in the form of urea, NH2CONH2. The reaction producing it is the combination of arginine (C6H14N4O2) with water to give urea and ornithine (C5H12N2O2). C6H14N4O2 + H2O NH2CONH2 + C5H12N2O2 [Molar masses: ...
... Your body deals with excess nitrogen by excreting it in the form of urea, NH2CONH2. The reaction producing it is the combination of arginine (C6H14N4O2) with water to give urea and ornithine (C5H12N2O2). C6H14N4O2 + H2O NH2CONH2 + C5H12N2O2 [Molar masses: ...
AP - 04 - Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
... (d) Sodium, an alkali metal, always has an oxidation number of +1 in its compounds (rule 2). Oxygen has a common oxidation state of −2 (rule 3a). Letting x equal the oxidation number of S, we have 2(+1) + x + 3(−2) = 0. Therefore, the oxidation number of S in this compound is +4. (e) The oxidation s ...
... (d) Sodium, an alkali metal, always has an oxidation number of +1 in its compounds (rule 2). Oxygen has a common oxidation state of −2 (rule 3a). Letting x equal the oxidation number of S, we have 2(+1) + x + 3(−2) = 0. Therefore, the oxidation number of S in this compound is +4. (e) The oxidation s ...
hong kong diploma of secondary education examination
... Which of the following statements about the fuel cell are correct? (1) Electrode X acts as the anode of the cell. (2) Electrons flow from electrode X to electrode Y through the acidic electrolyte. (3) A higher concentration of ethanol produces a larger current. A ...
... Which of the following statements about the fuel cell are correct? (1) Electrode X acts as the anode of the cell. (2) Electrons flow from electrode X to electrode Y through the acidic electrolyte. (3) A higher concentration of ethanol produces a larger current. A ...
Chemistry Final Exam Practice Test
... 43. The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom can be calculated by ____. a) adding together the number of electrons and protons b) subtracting the number of electrons from the number of protons c) subtracting the atomic number from the mass number d) adding the mass number to the number of e ...
... 43. The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom can be calculated by ____. a) adding together the number of electrons and protons b) subtracting the number of electrons from the number of protons c) subtracting the atomic number from the mass number d) adding the mass number to the number of e ...
THERMOCHEMISTRY or Thermodynamics
... Energy of the universes (system + surroundings) is constant. Any energy transferred from a system must be transferred to the surroundings (and vice versa). From the first law of thermodynamics: When a system undergoes a physical or chemical change, the change in internal energy is given by the h ...
... Energy of the universes (system + surroundings) is constant. Any energy transferred from a system must be transferred to the surroundings (and vice versa). From the first law of thermodynamics: When a system undergoes a physical or chemical change, the change in internal energy is given by the h ...
Chapter 5
... Energy of the universes (system + surroundings) is constant. Any energy transferred from a system must be transferred to the surroundings (and vice versa). From the first law of thermodynamics: When a system undergoes a physical or chemical change, the change in internal energy is given by the h ...
... Energy of the universes (system + surroundings) is constant. Any energy transferred from a system must be transferred to the surroundings (and vice versa). From the first law of thermodynamics: When a system undergoes a physical or chemical change, the change in internal energy is given by the h ...
Theoretical Study of Gas-Phase Reactions of Fe(CO)5 with OH
... different basis sets (II and II++) have been used in this study. Basis set II uses a small-core effective core potential (ECP) with a (441/2111/41) split-valence basis set for Fe, which is derived from the (55/5/5) minimal basis set optimized by Hay and Wadt,22 and 6-31G(d,p) all-electron basis sets ...
... different basis sets (II and II++) have been used in this study. Basis set II uses a small-core effective core potential (ECP) with a (441/2111/41) split-valence basis set for Fe, which is derived from the (55/5/5) minimal basis set optimized by Hay and Wadt,22 and 6-31G(d,p) all-electron basis sets ...
Chapter 4 - Colby College Wiki
... concentration. If it takes 17.8 mL of the potassium hydroxide solution to turn the indicator (phenolphthalein) slightly pink, what is the concentration of the hydrobromic acid solution? • The above process is known as a titration – the careful addition of one solution to another until one component ...
... concentration. If it takes 17.8 mL of the potassium hydroxide solution to turn the indicator (phenolphthalein) slightly pink, what is the concentration of the hydrobromic acid solution? • The above process is known as a titration – the careful addition of one solution to another until one component ...
A Voyage through Equations
... decomposition (D), combustion(C), single displacement (SD) or double displacement (DD). ...
... decomposition (D), combustion(C), single displacement (SD) or double displacement (DD). ...
THERMOCHEMISTRY or Thermodynamics
... • The slope of the plot of V versus T varies for the same gas at different pressures, but the intercept remains constant at –273.15ºC. • Significance of the invariant T intercept in plots of V versus T was recognized by Thomson (Lord Kelvin), who postulated that –273.15ºC was the lowest possible tem ...
... • The slope of the plot of V versus T varies for the same gas at different pressures, but the intercept remains constant at –273.15ºC. • Significance of the invariant T intercept in plots of V versus T was recognized by Thomson (Lord Kelvin), who postulated that –273.15ºC was the lowest possible tem ...
revised Chemical Kinetics
... This is because molecules must collide in order to react. The more concentrated the reactants, the greater the number of molecules in any given volume, and therefore, the greater the number of molecular collisions. Not every molecular collision between reactant molecules will lead to reaction, but s ...
... This is because molecules must collide in order to react. The more concentrated the reactants, the greater the number of molecules in any given volume, and therefore, the greater the number of molecular collisions. Not every molecular collision between reactant molecules will lead to reaction, but s ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.