AP Reactions - Georgetown ISD
... say K° forms at the negative electrode (cathode) and immediately undergoes reaction with water: 2K° + 2H2O ...
... say K° forms at the negative electrode (cathode) and immediately undergoes reaction with water: 2K° + 2H2O ...
electrical energy and capacitance
... What is the molecular formula of this compound? 1A. (1) C = 12.01 amu (2) H = 1.01 amu (3) C2 + H5 (4) C2H5 = 2(12.01 amu) + 5(1.01 amu) (5) EF = C2H5 = 29.07 g/mol (6) MF = 58.12 g/mol (7) MF = n(EF) (8) n = MF / EF (9) n = 58.12 / 29.07 (10) n = 2 (11) MF = (2)(C2H5) (12) MF = C4H10 MOLE TO MOLE C ...
... What is the molecular formula of this compound? 1A. (1) C = 12.01 amu (2) H = 1.01 amu (3) C2 + H5 (4) C2H5 = 2(12.01 amu) + 5(1.01 amu) (5) EF = C2H5 = 29.07 g/mol (6) MF = 58.12 g/mol (7) MF = n(EF) (8) n = MF / EF (9) n = 58.12 / 29.07 (10) n = 2 (11) MF = (2)(C2H5) (12) MF = C4H10 MOLE TO MOLE C ...
AS CHECKLISTS File
... covalently-bonded atoms have different electronegativities, resulting in a polar bond. Describe intermolecular forces based on permanent dipoles, as in hydrogen chloride, and instantaneous dipoles (van der Waals’ forces), as in the noble gases. Describe hydrogen bonding, including the role of a lone ...
... covalently-bonded atoms have different electronegativities, resulting in a polar bond. Describe intermolecular forces based on permanent dipoles, as in hydrogen chloride, and instantaneous dipoles (van der Waals’ forces), as in the noble gases. Describe hydrogen bonding, including the role of a lone ...
Notes
... Does the composition of the substance that undergoes a change in temperature matter, matter if so why? Is the same thermodynamic quantity measured in all calorimetry experiments? Why or why not? Since we can’t measure every reactions enthalpy directly, what methods can we use to figure out the entha ...
... Does the composition of the substance that undergoes a change in temperature matter, matter if so why? Is the same thermodynamic quantity measured in all calorimetry experiments? Why or why not? Since we can’t measure every reactions enthalpy directly, what methods can we use to figure out the entha ...
CHAPTER 3 STOICHIOMETRY:
... relative numbers of moles in the reaction. A mole ratio is the ratio of the coefficients of two substances in a chemical equation. You must use the mole ratio to convert from one substance to another. C2H5OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O ...
... relative numbers of moles in the reaction. A mole ratio is the ratio of the coefficients of two substances in a chemical equation. You must use the mole ratio to convert from one substance to another. C2H5OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O ...
High School Knowledge Exam – Study Guide
... -A physical change is a change in which no new substance is formed (no new molecules formed) -A chemical change results in the formation of one or more new substances (new molecules) Physical Change examples: Phase change, physically altering something (cutting it up, etc.), dissolving salt in water ...
... -A physical change is a change in which no new substance is formed (no new molecules formed) -A chemical change results in the formation of one or more new substances (new molecules) Physical Change examples: Phase change, physically altering something (cutting it up, etc.), dissolving salt in water ...
pdf - Mattson Creighton
... provided — Write: “See PT” in the answer box and then hand the periodic table in with your exam. On your desk you are allowed only pencils (but no pencil pouch), an eraser, and a non-programmable calculator without a slipcover. Backpacks and purses must be closed and stored on the floor under the ta ...
... provided — Write: “See PT” in the answer box and then hand the periodic table in with your exam. On your desk you are allowed only pencils (but no pencil pouch), an eraser, and a non-programmable calculator without a slipcover. Backpacks and purses must be closed and stored on the floor under the ta ...
IChO 2012
... Boron-nitrogen chemistry has attracted significant attention in part because a B–N unit is isoelectronic with C–C. Furthermore, the radius of carbon and its electronegativity are roughly the average of those properties for B and N. One of the simplest boron-nitrogen compounds is H3N–BH3, the ammonia ...
... Boron-nitrogen chemistry has attracted significant attention in part because a B–N unit is isoelectronic with C–C. Furthermore, the radius of carbon and its electronegativity are roughly the average of those properties for B and N. One of the simplest boron-nitrogen compounds is H3N–BH3, the ammonia ...
Chapter 17: Reaction Energy and Reaction Kinetics
... compound has a high negative heat of formation. Such compounds are very stable. Once they start, the reactions forming them usually proceed vigorously and without outside assistance. Elements in their standard states are defined as having ∆H 0f = 0. The ∆H 0f of carbon dioxide is −393.5 kJ/mol of ga ...
... compound has a high negative heat of formation. Such compounds are very stable. Once they start, the reactions forming them usually proceed vigorously and without outside assistance. Elements in their standard states are defined as having ∆H 0f = 0. The ∆H 0f of carbon dioxide is −393.5 kJ/mol of ga ...
Thermochemistry - thelapierres.com
... change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps. (Enthalpy is a state function. It doesn’t matter how you get there, only where you start and end.) ...
... change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps. (Enthalpy is a state function. It doesn’t matter how you get there, only where you start and end.) ...
Program Review - Austin Community College
... We envision improved safety measures within our labs. Standard safety and emergency procedures that are used by staff, instructors, and students at all campuses are major priorities. We hope to have functional safety equipment such as eyewashes, showers, and hoods at all campuses. We will keep our c ...
... We envision improved safety measures within our labs. Standard safety and emergency procedures that are used by staff, instructors, and students at all campuses are major priorities. We hope to have functional safety equipment such as eyewashes, showers, and hoods at all campuses. We will keep our c ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... logarithms, quadratics, and algebraic equations, is essential to success in this course (calculus is not required). You should not be taking remedial algebra concurrently with this course. Topics included are atomic structure, electronic structure and chemical bonding, descriptive solution chemistry ...
... logarithms, quadratics, and algebraic equations, is essential to success in this course (calculus is not required). You should not be taking remedial algebra concurrently with this course. Topics included are atomic structure, electronic structure and chemical bonding, descriptive solution chemistry ...
ch17
... 17.1 The Equilibrium State and the Equilibrium Constant 17.2 The Reaction Quotient and the Equilibrium Constant 17.3 Expressing Equilibria with Pressure Terms: Relation between Kc and Kp 17.4 Comparing Q and K to Determine Reaction Direction 17.5 How to Solve Equilibrium Problems 17.6 Reaction Condi ...
... 17.1 The Equilibrium State and the Equilibrium Constant 17.2 The Reaction Quotient and the Equilibrium Constant 17.3 Expressing Equilibria with Pressure Terms: Relation between Kc and Kp 17.4 Comparing Q and K to Determine Reaction Direction 17.5 How to Solve Equilibrium Problems 17.6 Reaction Condi ...
Chemical Equations
... This equation tells us that two formula units of ammonium chloride react with one formula unit of sodium carbonate to produce two formula units of sodium chloride and one unit of ammonium carbonate. Those same ratios apply to moles of the substances. Two moles of ammonium chloride react with one mol ...
... This equation tells us that two formula units of ammonium chloride react with one formula unit of sodium carbonate to produce two formula units of sodium chloride and one unit of ammonium carbonate. Those same ratios apply to moles of the substances. Two moles of ammonium chloride react with one mol ...
FINAL EXAM REVIEW PROBLEMS
... 5. An antifreeze solution in a car’s radiator boils at 239F. What is the temperature on the Celsius scale? a. 22oC b. -16 oC c. 115 oC d. 458 oC 6. Write the formula for each of the following compounds, list the elements in order given: a. A molecule contains four phosphorus atoms and ten oxygen at ...
... 5. An antifreeze solution in a car’s radiator boils at 239F. What is the temperature on the Celsius scale? a. 22oC b. -16 oC c. 115 oC d. 458 oC 6. Write the formula for each of the following compounds, list the elements in order given: a. A molecule contains four phosphorus atoms and ten oxygen at ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
... re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
AP Chemistry Second Semester Notes
... 2B. Electron Arrangements in Atoms and Ions (6.7 to 6.9) 2. ions with the same # of e: isoelectronic 1. electrons fill from low to high energy (same for all atoms) b. transition metal ions a. n: 1 < 2 < 3 < 4 < 5 < 6 < 7 1. transition metal lose s electrons first b. l: s < p < next energy level < d ...
... 2B. Electron Arrangements in Atoms and Ions (6.7 to 6.9) 2. ions with the same # of e: isoelectronic 1. electrons fill from low to high energy (same for all atoms) b. transition metal ions a. n: 1 < 2 < 3 < 4 < 5 < 6 < 7 1. transition metal lose s electrons first b. l: s < p < next energy level < d ...
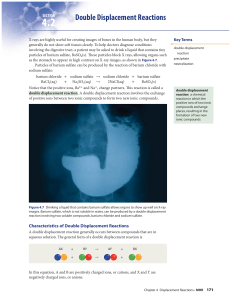
Double Displacement Reactions
... Reactions between acids and bases are also important for optimizing soil conditions. For example, lettuce and celery grow better in neutral to basic soil, but strawberries and tomatoes grow better in acidic soil. Figure 4.11 shows soil being tested to determine whether it is acidic, neutral, or basi ...
... Reactions between acids and bases are also important for optimizing soil conditions. For example, lettuce and celery grow better in neutral to basic soil, but strawberries and tomatoes grow better in acidic soil. Figure 4.11 shows soil being tested to determine whether it is acidic, neutral, or basi ...
Answers - U of L Class Index
... 2) If you use the “overflow” page, indicate this next to the question and clearly number your work on the “overflow” page. 3) If your work is not legible, it will be given a mark of zero. 4) Marks will be deducted for incorrect information added to an otherwise correct answer. 5) Marks will be deduc ...
... 2) If you use the “overflow” page, indicate this next to the question and clearly number your work on the “overflow” page. 3) If your work is not legible, it will be given a mark of zero. 4) Marks will be deducted for incorrect information added to an otherwise correct answer. 5) Marks will be deduc ...
9701/04 - StudyGuide.PK
... (b) Going down Group IV there is a variation in the relative stabilities of the higher and lower oxidation states of the elements in their oxides. Illustrating your answers with balanced chemical equations, in each of the following cases suggest one piece of chemical evidence to show that (i) CO is ...
... (b) Going down Group IV there is a variation in the relative stabilities of the higher and lower oxidation states of the elements in their oxides. Illustrating your answers with balanced chemical equations, in each of the following cases suggest one piece of chemical evidence to show that (i) CO is ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... nature as a diatomic molecule? b. 3 a. Nitrogen c. 4 b. Helium d. 2 c. Hydrogen 11. In the correct Lewis structure for the methane d. oxygen molecule, how many unshared electron pairs 2. Ionic compounds generally form: surround the carbon? a. Liquids a. 2 b. Gases b. 0 c. Crystals c. 8 d. molecules ...
... nature as a diatomic molecule? b. 3 a. Nitrogen c. 4 b. Helium d. 2 c. Hydrogen 11. In the correct Lewis structure for the methane d. oxygen molecule, how many unshared electron pairs 2. Ionic compounds generally form: surround the carbon? a. Liquids a. 2 b. Gases b. 0 c. Crystals c. 8 d. molecules ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.