Equilibrium and Pressure
... C. How does this value of Kp compare to the value you found before? ______________ ___________________________________________________________________ D. As the experiment reached equilibrium again, did the reactants or products increase? _____________________________________________________________ ...
... C. How does this value of Kp compare to the value you found before? ______________ ___________________________________________________________________ D. As the experiment reached equilibrium again, did the reactants or products increase? _____________________________________________________________ ...
File
... The halide ion is the 1 charged ion that halogens form when in ionic compounds. As can be seen from the positive standard reduction potentials in Table 20.6, the halogens energetically favor the X form over the X2 form. Because the reduction potentials are so large, this give an indication of the ...
... The halide ion is the 1 charged ion that halogens form when in ionic compounds. As can be seen from the positive standard reduction potentials in Table 20.6, the halogens energetically favor the X form over the X2 form. Because the reduction potentials are so large, this give an indication of the ...
Chemical Engineering Principles of CVD Processes
... The walls of the reactor are cold - usually no deposition occurs on them - with a low wall temp : the risk of contamination from vapor/wall reactions is reduced - Homogeneous reaction is suppressed (CH4 can not be used to reach acceptable deposition rates) Advantage: Flexibility, high cleanliness, h ...
... The walls of the reactor are cold - usually no deposition occurs on them - with a low wall temp : the risk of contamination from vapor/wall reactions is reduced - Homogeneous reaction is suppressed (CH4 can not be used to reach acceptable deposition rates) Advantage: Flexibility, high cleanliness, h ...
How many grams of NH4OH (ammonium hydroxide) are in 3.47
... Which of the following statements is a postulate of kinetic molecular theory? ✓A. The size of a gas particle is negligibly small. B. The average kinetic energy of a gas particle is inversely proportional to the temperature in ...
... Which of the following statements is a postulate of kinetic molecular theory? ✓A. The size of a gas particle is negligibly small. B. The average kinetic energy of a gas particle is inversely proportional to the temperature in ...
Synthesis of esterified solid fat from fractionated
... determined by employing least squares technique to predict quadratic polynomial models for SFC at different temperature (10 and 30 °C, respectively) is shown in Table 2. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) of response surface for SFC showed that this design was adequate and reproducible due to satisfactory ...
... determined by employing least squares technique to predict quadratic polynomial models for SFC at different temperature (10 and 30 °C, respectively) is shown in Table 2. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) of response surface for SFC showed that this design was adequate and reproducible due to satisfactory ...
____ 1. The energy required to convert a ground
... combustion produced liquid water H2O(g) ? (H for the phase change H2O(g) H2O(l) is -44 kJ mol-1.) a. -1,235 kJ d. -1,367 kJ b. -1,279 kJ e. -1,411 kJ c. -1,323 kJ ...
... combustion produced liquid water H2O(g) ? (H for the phase change H2O(g) H2O(l) is -44 kJ mol-1.) a. -1,235 kJ d. -1,367 kJ b. -1,279 kJ e. -1,411 kJ c. -1,323 kJ ...
Part One: Ions in Aqueous Solution A. Electrolytes and Non
... Titration = process in which a solution of one reactant (the titrant) is carefully added to a solution of another reactant. Volume of titrant required for complete reaction is ...
... Titration = process in which a solution of one reactant (the titrant) is carefully added to a solution of another reactant. Volume of titrant required for complete reaction is ...
Aqueous Solutions
... aluminum oxide Na3P sodium phosphide Mg3N2 magnesium nitride Notice that binary ionic compounds with metals having one oxidation state (representative metals) do not use prefixes or Roman numerals. ...
... aluminum oxide Na3P sodium phosphide Mg3N2 magnesium nitride Notice that binary ionic compounds with metals having one oxidation state (representative metals) do not use prefixes or Roman numerals. ...
m5zn_1ed95c16cede0b1
... 3. Pressure Factor i) Solids/Liquids - Very little effect Solids and Liquids are already close together, extra pressure will not increase solubility. ii) gas - Solubility increases with Pressure. Increase pressure squeezes gas solute into solvent. ...
... 3. Pressure Factor i) Solids/Liquids - Very little effect Solids and Liquids are already close together, extra pressure will not increase solubility. ii) gas - Solubility increases with Pressure. Increase pressure squeezes gas solute into solvent. ...
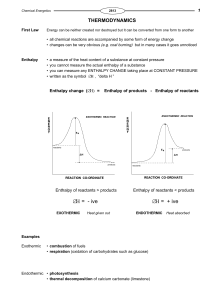
Chemical Thermodynamics - Winona State University
... temperature: Ice turning to water is spontaneous at T > 0C, Water turning to ice is spontaneous at T < 0C. Reversible and Irreversible Processes • A reversible process is one that can go back and forth between states along the same path. ...
... temperature: Ice turning to water is spontaneous at T > 0C, Water turning to ice is spontaneous at T < 0C. Reversible and Irreversible Processes • A reversible process is one that can go back and forth between states along the same path. ...
Stoichiometry1
... which reactant is the limiting one. The lower amount of a product is the correct answer. The reactant that makes the least amount of product is the limiting reactant. Once you determine the limiting reactant, you should ALWAYS start with it! Be sure to pick a product! You can’t compare to see ...
... which reactant is the limiting one. The lower amount of a product is the correct answer. The reactant that makes the least amount of product is the limiting reactant. Once you determine the limiting reactant, you should ALWAYS start with it! Be sure to pick a product! You can’t compare to see ...
Chapter 14 (Kinetics) – Slides and Practice
... Practice – If 2.4 x 102 g of NOBr (MM 109.91 g) decomposes in a 2.0 x 102 mL flask in 5.0 minutes, find the average rate of Br2 production in M/s 2 NOBr(g) 2 NO(g) + Br2(l) ...
... Practice – If 2.4 x 102 g of NOBr (MM 109.91 g) decomposes in a 2.0 x 102 mL flask in 5.0 minutes, find the average rate of Br2 production in M/s 2 NOBr(g) 2 NO(g) + Br2(l) ...
physical setting chemistry
... Setting/Chemistry, and your knowledge of chemistry. In the 1920s, paint used to inscribe the numbers on watch dials was composed of a luminescent (glow-in-the-dark) mixture. The powdered-paint base was a mixture of radium salts and zinc sulfide. As the paint was mixed, the powdered base became airbo ...
... Setting/Chemistry, and your knowledge of chemistry. In the 1920s, paint used to inscribe the numbers on watch dials was composed of a luminescent (glow-in-the-dark) mixture. The powdered-paint base was a mixture of radium salts and zinc sulfide. As the paint was mixed, the powdered base became airbo ...
Document
... Practice – If 2.4 x 102 g of NOBr (MM 109.91 g) decomposes in a 2.0 x 102 mL flask in 5.0 minutes, find the average rate of Br2 production in M/s 2 NOBr(g) 2 NO(g) + Br2(l) ...
... Practice – If 2.4 x 102 g of NOBr (MM 109.91 g) decomposes in a 2.0 x 102 mL flask in 5.0 minutes, find the average rate of Br2 production in M/s 2 NOBr(g) 2 NO(g) + Br2(l) ...
Chapter
... Practice – If 2.4 x 102 g of NOBr (MM 109.91 g) decomposes in a 2.0 x 102 mL flask in 5.0 minutes, find the average rate of Br2 production in M/s 2 NOBr(g) 2 NO(g) + Br2(l) ...
... Practice – If 2.4 x 102 g of NOBr (MM 109.91 g) decomposes in a 2.0 x 102 mL flask in 5.0 minutes, find the average rate of Br2 production in M/s 2 NOBr(g) 2 NO(g) + Br2(l) ...
Stoichiometery
... I have 1.6 mol of hydrogen. How much water can I make? A. 1.6 mol H2O B. 0.8 mol etc. C. 3.2 mol D. 4.8 mol E. None of the above ...
... I have 1.6 mol of hydrogen. How much water can I make? A. 1.6 mol H2O B. 0.8 mol etc. C. 3.2 mol D. 4.8 mol E. None of the above ...
Line 4: Equation
... 6. Write the given information on the appropriate line above the equation. Lines 1 through 3 are your givens. Later, we will call these theoretical lines. In this example, we were given 2.50 mol of magnesium. Moles go on line 2. Write 2.50 above magnesium on line 2. See violet text in chart. 7. Calc ...
... 6. Write the given information on the appropriate line above the equation. Lines 1 through 3 are your givens. Later, we will call these theoretical lines. In this example, we were given 2.50 mol of magnesium. Moles go on line 2. Write 2.50 above magnesium on line 2. See violet text in chart. 7. Calc ...
California Standards Practice - Student Edition
... 10. The bonding characteristics of carbon allow the formation of many different organic molecules of varied sizes, shapes, and chemical properties and provide the biochemicalbasis of life. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know large molecules (polymers), such as proteins, nucle ...
... 10. The bonding characteristics of carbon allow the formation of many different organic molecules of varied sizes, shapes, and chemical properties and provide the biochemicalbasis of life. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know large molecules (polymers), such as proteins, nucle ...
H2-rich fluids from serpentinization: Geochemical and biotic
... recharge ocean and atmosphere with CO2. Reaction 1 supports extant biota and abiotic processes. Methanogens in rocks can thrive at H2 concentrations of ⬇13 nM (19, 20), orders of magnitude below the concentration in equilibrium with serpentinite presented below. Magnetite and awaruite (FeNi3, a comm ...
... recharge ocean and atmosphere with CO2. Reaction 1 supports extant biota and abiotic processes. Methanogens in rocks can thrive at H2 concentrations of ⬇13 nM (19, 20), orders of magnitude below the concentration in equilibrium with serpentinite presented below. Magnetite and awaruite (FeNi3, a comm ...
Document
... you are given one dozen loaves of bread, a gallon of mustard, and three pieces of bologna, how many bologna sandwiches can you make? The limiting reagent is the reactant you run out of first. The excess reagent is the one you have left over. The limiting reagent determines how much product you ...
... you are given one dozen loaves of bread, a gallon of mustard, and three pieces of bologna, how many bologna sandwiches can you make? The limiting reagent is the reactant you run out of first. The excess reagent is the one you have left over. The limiting reagent determines how much product you ...
Module 2 - chem534
... Heat of Dissolution (ΔHd): The amount of energy absorbed/released when a solute dissolves. Heat of Neutralization (ΔHn): The amount of energy absorbed/released when a solute dissolves. Heat of Combustion (ΔHcombustion): amount of energy released when a material burns. Heat of Fusion (melting) or Sol ...
... Heat of Dissolution (ΔHd): The amount of energy absorbed/released when a solute dissolves. Heat of Neutralization (ΔHn): The amount of energy absorbed/released when a solute dissolves. Heat of Combustion (ΔHcombustion): amount of energy released when a material burns. Heat of Fusion (melting) or Sol ...
CHM 22 Test 2Take-homeKey Student Name
... 3. Let Z represent atomic number, A represent mass number, and N represent the number of neutrons in an atom. Which of the following is correct? A. N = A + Z B. Z = A + N C. N = A - Z D. A = N - Z Answer: C; Difficulty: easy; Reference: Section 5.8 4. The elements in group 6A form ions with a charge ...
... 3. Let Z represent atomic number, A represent mass number, and N represent the number of neutrons in an atom. Which of the following is correct? A. N = A + Z B. Z = A + N C. N = A - Z D. A = N - Z Answer: C; Difficulty: easy; Reference: Section 5.8 4. The elements in group 6A form ions with a charge ...
Chemistry (SPA)
... 440 BC, the Greek Leucippus and his pupil Democritus coined the term atomos to describe the smallest particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique at ...
... 440 BC, the Greek Leucippus and his pupil Democritus coined the term atomos to describe the smallest particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique at ...
Redox - edl.io
... an oxidation state of +1. Metal hydrides are an exception; H is at the end of the chemical formula since it has an oxidation state of 1-. 7. The sum of the oxidation states must be zero for an electrically neutral compound. For a polyatomic ion, the sum of the oxidation states must equal the charge ...
... an oxidation state of +1. Metal hydrides are an exception; H is at the end of the chemical formula since it has an oxidation state of 1-. 7. The sum of the oxidation states must be zero for an electrically neutral compound. For a polyatomic ion, the sum of the oxidation states must equal the charge ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.