The Major Classes of Chemical Reactions
... Many reactions take place in an aqueous environment, and our first step toward comprehending them is to understand how water acts as a solvent. The role a solvent plays in a reaction depends on its chemical nature. Some solvents play a passive role. They disperse the substances into individual molec ...
... Many reactions take place in an aqueous environment, and our first step toward comprehending them is to understand how water acts as a solvent. The role a solvent plays in a reaction depends on its chemical nature. Some solvents play a passive role. They disperse the substances into individual molec ...
PRACTICE EXAM 1-C
... to completion, and determine the molar concentration of all ions in the resulting solution. (Note: Assuming that the reaction goes to completion, some of the concentrations may be effectively zero.) (12 pts) ...
... to completion, and determine the molar concentration of all ions in the resulting solution. (Note: Assuming that the reaction goes to completion, some of the concentrations may be effectively zero.) (12 pts) ...
Organic Reactions in Organised Media
... containing the nonpolar reactant, the reaction may occur at the oil-water interface, i.e. the pore openings. The approach offers possibilities for reuse of the material since the particles can easily be removed from the reaction mixture by filtration or by centrifugation. Another potential use of me ...
... containing the nonpolar reactant, the reaction may occur at the oil-water interface, i.e. the pore openings. The approach offers possibilities for reuse of the material since the particles can easily be removed from the reaction mixture by filtration or by centrifugation. Another potential use of me ...
mark scheme - A-Level Chemistry
... Do not allow ‘to improve accuracy’ without qualification. Do not allow ‘water is a product of the reaction’. Do not allow ‘mass of crucible incorrect / too high’. ...
... Do not allow ‘to improve accuracy’ without qualification. Do not allow ‘water is a product of the reaction’. Do not allow ‘mass of crucible incorrect / too high’. ...
Worked solutions to textbook questions 1 Chapter 14 From organic
... the stomach walls. Its structure was modified by reaction salicylic acid (aspirin) with ethanoic acid to form the ester, acetylsalicylic acid which while an effective pain killer did not have this side effect. A soluble form of aspirin was developed by converting the carboxylic acid functional group ...
... the stomach walls. Its structure was modified by reaction salicylic acid (aspirin) with ethanoic acid to form the ester, acetylsalicylic acid which while an effective pain killer did not have this side effect. A soluble form of aspirin was developed by converting the carboxylic acid functional group ...
15.0 EquilibriumIHS2014
... Gaseous NOCl decomposes to form NO(g) and Cl2(g). At 35oC the equilibrium constant Keq = 1.60 X 10-5. If 1.00 mol of NOCl(g) is placed in a 1.0 L flask, what are the equilibrium concentrations of each species ...
... Gaseous NOCl decomposes to form NO(g) and Cl2(g). At 35oC the equilibrium constant Keq = 1.60 X 10-5. If 1.00 mol of NOCl(g) is placed in a 1.0 L flask, what are the equilibrium concentrations of each species ...
Equilibrium 5
... 9. Gaseous phosphorus pentachloride decomposes to gaseous phosphorus trichloride and chlorine at a temperature where K = 1.0 x 10-3. Suppose 2.0 moles of PCl5 in a 2.0-L vessel is allowed to come to equilibrium. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of all species. PCl5 ...
... 9. Gaseous phosphorus pentachloride decomposes to gaseous phosphorus trichloride and chlorine at a temperature where K = 1.0 x 10-3. Suppose 2.0 moles of PCl5 in a 2.0-L vessel is allowed to come to equilibrium. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of all species. PCl5 ...
Ch16
... The volume of the container was increased at constant temperature and a new equilbrium was established. Predict how each of the following quantities would change at the new equilibrium compared with the initial equilibrium: a concentration of NO2 b mass of NO2 A12. An increase in volume will cause a ...
... The volume of the container was increased at constant temperature and a new equilbrium was established. Predict how each of the following quantities would change at the new equilibrium compared with the initial equilibrium: a concentration of NO2 b mass of NO2 A12. An increase in volume will cause a ...
Chem 105 Final Exam
... Your answer:______________ 39. The correct order of increasing electronegativity is ______________ . a) As < Ga < K < Cs b) Cs < K < Ga < As c) Ga < As < K < Cs d) K < Ga < As < Cs Your answer:______________ 40. List the following atoms and ions in an order of increasing atomic size: K+, Cl-, Ar, Ca ...
... Your answer:______________ 39. The correct order of increasing electronegativity is ______________ . a) As < Ga < K < Cs b) Cs < K < Ga < As c) Ga < As < K < Cs d) K < Ga < As < Cs Your answer:______________ 40. List the following atoms and ions in an order of increasing atomic size: K+, Cl-, Ar, Ca ...
Nickel(II) cis- and trans-Dimethyl Complexes of
... addition of excess tBuCCeth, as shown in Table 3. Fitting of the rate data gave ∆Hq ) 24.0(6) kcal mol-1 and ∆Sq ) -4.7(1) cal K-1 mol-1 (cf. [Ni(dppe)Me2], with ∆Hq ) 26.8 and ∆Sq ) 1.9, and [Ni(dppp)Me2], with ∆Hq ) 25.1 kcal mol-1 and ∆Sq ) 4.8 cal K-1 mol-1).19 The low activation entropy and ind ...
... addition of excess tBuCCeth, as shown in Table 3. Fitting of the rate data gave ∆Hq ) 24.0(6) kcal mol-1 and ∆Sq ) -4.7(1) cal K-1 mol-1 (cf. [Ni(dppe)Me2], with ∆Hq ) 26.8 and ∆Sq ) 1.9, and [Ni(dppp)Me2], with ∆Hq ) 25.1 kcal mol-1 and ∆Sq ) 4.8 cal K-1 mol-1).19 The low activation entropy and ind ...
chemical change
... which is different from the original reactant or reactant, this is often accompanied by changes in energy, which are measured as temperature changes. Thus for the reaction of the silver metal sodium with the green/yellow gas chlorine, the product is a white crystalline solid, which looks very differ ...
... which is different from the original reactant or reactant, this is often accompanied by changes in energy, which are measured as temperature changes. Thus for the reaction of the silver metal sodium with the green/yellow gas chlorine, the product is a white crystalline solid, which looks very differ ...
Major 01 - KFUPM Faculty List
... (3.125 - 0.7024) mol O2 = 2.4226 mol O2 are left over (in excess). This is 2.4226 mol x 32 g O2/mol = 77.5 g O2 are left over (choice A). 15. 1.00 mL of a 3.50 x 10-4 M solution of oleic acid is diluted with 9.00 mL of ether, forming solution A. 2.00 mL of solution A is diluted with 8.00 mL of ether ...
... (3.125 - 0.7024) mol O2 = 2.4226 mol O2 are left over (in excess). This is 2.4226 mol x 32 g O2/mol = 77.5 g O2 are left over (choice A). 15. 1.00 mL of a 3.50 x 10-4 M solution of oleic acid is diluted with 9.00 mL of ether, forming solution A. 2.00 mL of solution A is diluted with 8.00 mL of ether ...
([Cu(NH3)4](MnO4)2)
... The appearance of IR-inactive Cu N stretching modes in the IR spectrum of 1 shows the symmetry-lowering due to distortion of the regular square-planar CuN4 geometry. The splittings of nÄs , ds, and 1r N H bands or the nÄas Cu N band confirm the symmetry-lowering of the complex cation. The presence o ...
... The appearance of IR-inactive Cu N stretching modes in the IR spectrum of 1 shows the symmetry-lowering due to distortion of the regular square-planar CuN4 geometry. The splittings of nÄs , ds, and 1r N H bands or the nÄas Cu N band confirm the symmetry-lowering of the complex cation. The presence o ...
Chapter 8 Quantities in Chemical Reactions
... was the additive of choice by the oil companies. • MTBE is a compound that does not biodegrade readily. • MTBE made its way into drinking water through gasoline spills at gas stations, from boat motors, and from leaking underground storage tanks. • Ethanol (C2H5OH), made from the fermentation of gra ...
... was the additive of choice by the oil companies. • MTBE is a compound that does not biodegrade readily. • MTBE made its way into drinking water through gasoline spills at gas stations, from boat motors, and from leaking underground storage tanks. • Ethanol (C2H5OH), made from the fermentation of gra ...
Chemistry Entrance Material for Grade 11 to 12
... Variation of molar heat of vaporization 10. Which of the following liquids has the lowest molar heat of vaporization? Which one has the highest molar heat of vaporization? Which one has the highest vapour pressure at its boiling point? ...
... Variation of molar heat of vaporization 10. Which of the following liquids has the lowest molar heat of vaporization? Which one has the highest molar heat of vaporization? Which one has the highest vapour pressure at its boiling point? ...
19—Principles of Reactivity: Entropy and Free Energy
... these two quanta of energy over the four atoms. In only 4 of the 10 cases [1, 1; 2, 2; 3, 3; and 4,4], is the energy concentrated on a single particle. In the majority of the cases, 6 out of 10, the energy is distributed to two different particles. Thus, even in a simple example with only two packet ...
... these two quanta of energy over the four atoms. In only 4 of the 10 cases [1, 1; 2, 2; 3, 3; and 4,4], is the energy concentrated on a single particle. In the majority of the cases, 6 out of 10, the energy is distributed to two different particles. Thus, even in a simple example with only two packet ...
4U Chemistry Practice Exam - Coristines
... 4. What is the difference between an amine and an amide? a. There is no carbon-oxygen bond in an amine, but there is in an amide. b. Amines are non-polar molecules. c. Amines always have a larger molecular weight than amides. d. Amines always have a nitrogen atom attached to two carbon atoms. e. Ami ...
... 4. What is the difference between an amine and an amide? a. There is no carbon-oxygen bond in an amine, but there is in an amide. b. Amines are non-polar molecules. c. Amines always have a larger molecular weight than amides. d. Amines always have a nitrogen atom attached to two carbon atoms. e. Ami ...
AS Specification pdf | AS/A level
... This specification provides a suitable foundation for the study of chemistry at A level. In addition, the specification provides a coherent, satisfying and worthwhile course of study for learners who do not progress to further study in this subject. This specification is not age specific and, as suc ...
... This specification provides a suitable foundation for the study of chemistry at A level. In addition, the specification provides a coherent, satisfying and worthwhile course of study for learners who do not progress to further study in this subject. This specification is not age specific and, as suc ...
2014 VCE Chemistry written examination report
... The choice of alternative C, which was six times the correct amount of energy, indicates that many students misinterpreted the formula CH4.6H2O and assumed that n(CH4) = 6 × n(CH4.6H2O), which was incorrect. The choice of alternative D was consistent with misintepreting the sample size as 1.00 kg of ...
... The choice of alternative C, which was six times the correct amount of energy, indicates that many students misinterpreted the formula CH4.6H2O and assumed that n(CH4) = 6 × n(CH4.6H2O), which was incorrect. The choice of alternative D was consistent with misintepreting the sample size as 1.00 kg of ...
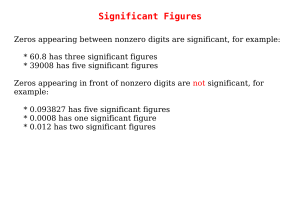
Significant Figures
... Significant Figures Zeros at the end of a number and to the right of a decimal are significant, for example: * 35.00 has four significant figures * 8,000.000000 has ten significant figures Zeros at the end of a number without a decimal point may or may not be significant, and are therefore ambiguou ...
... Significant Figures Zeros at the end of a number and to the right of a decimal are significant, for example: * 35.00 has four significant figures * 8,000.000000 has ten significant figures Zeros at the end of a number without a decimal point may or may not be significant, and are therefore ambiguou ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.















2)](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015968611_1-56df287e8435abc2be6b0a2948d2417f-300x300.png)