N5 Chemistry 2014
... 1. The answer to each question is either A, B, C or D. Decide what your answer is, then fill in the appropriate bubble (see sample question below). 2. There is only one correct answer to each question. 3. Any rough work must be written in the additional space for answers and rough work at t ...
... 1. The answer to each question is either A, B, C or D. Decide what your answer is, then fill in the appropriate bubble (see sample question below). 2. There is only one correct answer to each question. 3. Any rough work must be written in the additional space for answers and rough work at t ...
CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure
... Collisions and concentration Look at the illustrations showing the result of collisions between two different concentrations of hydrochloric acid and calcium carbonate, both after 10 seconds of reaction. The hydrochloric acid is represented as a large sphere and the calcium carbonate as a small sphe ...
... Collisions and concentration Look at the illustrations showing the result of collisions between two different concentrations of hydrochloric acid and calcium carbonate, both after 10 seconds of reaction. The hydrochloric acid is represented as a large sphere and the calcium carbonate as a small sphe ...
File
... f) Exothermic reaction and endothermic reaction: On the basis of energy changes during chemical reaction, they can be classified as i) Exothermic reaction: A chemical reaction in which heat energy is produced. C + O2 CO2 (g) + heat ii) Endothermic reaction: A chemical reaction in which heat energy ...
... f) Exothermic reaction and endothermic reaction: On the basis of energy changes during chemical reaction, they can be classified as i) Exothermic reaction: A chemical reaction in which heat energy is produced. C + O2 CO2 (g) + heat ii) Endothermic reaction: A chemical reaction in which heat energy ...
1994 AP Chemistry Multiple Choice
... Reproductions of these examination questions by classroom teachers is permitted for face-to-face teaching purposes only. ...
... Reproductions of these examination questions by classroom teachers is permitted for face-to-face teaching purposes only. ...
Chapter 6: Moles, Molar Mass, Percent Composition and Formulas
... ii) It’s impossible to count atoms with your hands. iii) Numbers of moles are smaller and easier to do math with than big numbers of atoms and molecules. 6) Convert moles of an atom to grams a) I need 2.0 moles of copper (Cu) for an experiment. How many grams is that? b) Atomic mass of Cu = 63.55 g/ ...
... ii) It’s impossible to count atoms with your hands. iii) Numbers of moles are smaller and easier to do math with than big numbers of atoms and molecules. 6) Convert moles of an atom to grams a) I need 2.0 moles of copper (Cu) for an experiment. How many grams is that? b) Atomic mass of Cu = 63.55 g/ ...
Slides
... Increases the rate of chemical reaction / biological process Remains unchanged Biomolecules that catalyze chemical reactions Usually proteins ...
... Increases the rate of chemical reaction / biological process Remains unchanged Biomolecules that catalyze chemical reactions Usually proteins ...
Chemistry HSC - The Bored of Studies Community
... Ethylene is the most versatile, but not found in large quantities in feedstock. Produced from other hydrocarbons in ‘cracking’ (a process where hydrocarbons of higher mol mass are converted to lower mol mass via breaking of chemical bonds). There is greater demand for some fractions than others (e.g ...
... Ethylene is the most versatile, but not found in large quantities in feedstock. Produced from other hydrocarbons in ‘cracking’ (a process where hydrocarbons of higher mol mass are converted to lower mol mass via breaking of chemical bonds). There is greater demand for some fractions than others (e.g ...
CHEM 121 Chp 5 Spaulding
... Actual yield is determined experimentally, it is the mass of the product that is measured Theoretical yield is the calculated mass of the products based on the initial mass or number of moles of the reactants ...
... Actual yield is determined experimentally, it is the mass of the product that is measured Theoretical yield is the calculated mass of the products based on the initial mass or number of moles of the reactants ...
1412e3 - studylib.net
... atoms present to decay (decreased or reduced ) by 6.25% of the initial value? 26. One of the hopes for solving the world’s energy problem is to make use of the fusion reaction: H + 31 H 42 He + 10 n + energy ...
... atoms present to decay (decreased or reduced ) by 6.25% of the initial value? 26. One of the hopes for solving the world’s energy problem is to make use of the fusion reaction: H + 31 H 42 He + 10 n + energy ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... A 1.034-g sample of impure oxalic acid (H2C2O4) is dissolved in water and an acidbase indicator is added. The sample required 34.47 mL of 0.485 M NaOH to reach the equivalence point. What is the mass of oxalic acid and what is its mass percent in the ...
... A 1.034-g sample of impure oxalic acid (H2C2O4) is dissolved in water and an acidbase indicator is added. The sample required 34.47 mL of 0.485 M NaOH to reach the equivalence point. What is the mass of oxalic acid and what is its mass percent in the ...
Electrochemistry
... with the zinc to acquire a net positive charge, while a net negative charge would build up in the solution on the copper side of the cell. These violations of electroneutrality would make it more difficult (require more work) to introduce additional Zn2+ ions into the positivelycharged electrolyte o ...
... with the zinc to acquire a net positive charge, while a net negative charge would build up in the solution on the copper side of the cell. These violations of electroneutrality would make it more difficult (require more work) to introduce additional Zn2+ ions into the positivelycharged electrolyte o ...
13.0 Redox Reactions PowerPoint
... transferred between entities • The total number of electrons gained in the reduction equals the total number of electrons lost in the oxidation • Reduction is a process in which electrons are gained by an entity • Oxidation is a process in which electrons are lost by an entity • Both reduction and o ...
... transferred between entities • The total number of electrons gained in the reduction equals the total number of electrons lost in the oxidation • Reduction is a process in which electrons are gained by an entity • Oxidation is a process in which electrons are lost by an entity • Both reduction and o ...
Development of paper-based color test
... of the silane reagent, while the former is more complex but involves conventional and successful chemistry (the oxidation of hydroxyl to carboxylic groups, their activation by EDAC/NHS chemistry and subsequent amine binding). The later made use of APTES reagent while the former was tried out by usin ...
... of the silane reagent, while the former is more complex but involves conventional and successful chemistry (the oxidation of hydroxyl to carboxylic groups, their activation by EDAC/NHS chemistry and subsequent amine binding). The later made use of APTES reagent while the former was tried out by usin ...
SQA CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure
... area (particle size), temperature and collision geometry on reaction rates; • calculate the relative rate of a reaction using the formula Rate = 1/t. ...
... area (particle size), temperature and collision geometry on reaction rates; • calculate the relative rate of a reaction using the formula Rate = 1/t. ...
General Chemistry Discretes Test
... Before you decide whether polarity has an effect on the boiling point of a substance, you should be able to eliminate this choice by realizing that water is not more polar that HF. Hydrogen fluoride has a greater charge separation between its constituent atoms and thus has a more polar bond. Choice ...
... Before you decide whether polarity has an effect on the boiling point of a substance, you should be able to eliminate this choice by realizing that water is not more polar that HF. Hydrogen fluoride has a greater charge separation between its constituent atoms and thus has a more polar bond. Choice ...
Chemistry - Separation techniques
... Further details are available in the specifications (Practical Skills Topics), and in these videos. ...
... Further details are available in the specifications (Practical Skills Topics), and in these videos. ...
Tro Chemistry a Molecular Approach, 3E
... chemical reactions. In Chapter 3, you learned how to write balanced chemical equations for chemical reactions. Here we will examine more closely the meaning of those balanced equations. In the second half of this chapter, we turn to describing chemical reactions that occur in water. You have probabl ...
... chemical reactions. In Chapter 3, you learned how to write balanced chemical equations for chemical reactions. Here we will examine more closely the meaning of those balanced equations. In the second half of this chapter, we turn to describing chemical reactions that occur in water. You have probabl ...
Section 2 Types of Chemical Reactions
... • List three observations that suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. • List three requirements for a correctly written chemical equation. • Write a word equation and a formula equation for a given chemical reaction. • Balance a formula equation by inspection. ...
... • List three observations that suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. • List three requirements for a correctly written chemical equation. • Write a word equation and a formula equation for a given chemical reaction. • Balance a formula equation by inspection. ...
Descriptive Chemistry for Midterm Exam #2
... Occurrence: found in more compounds than any other element on earth. It is the most abundant element in universe. Oxidation states: 0 in H2, +1 in compounds with other non-metals, −1 in metal hydrides. Industrial Preparation of H2: This is carried out through the reduction of +1 oxidation state in H ...
... Occurrence: found in more compounds than any other element on earth. It is the most abundant element in universe. Oxidation states: 0 in H2, +1 in compounds with other non-metals, −1 in metal hydrides. Industrial Preparation of H2: This is carried out through the reduction of +1 oxidation state in H ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... • The limiting reactant is the reactant present in the smallest stoichiometric amount. – In other words, it’s the reactant you’ll run out of first (in this case, the H2). ...
... • The limiting reactant is the reactant present in the smallest stoichiometric amount. – In other words, it’s the reactant you’ll run out of first (in this case, the H2). ...
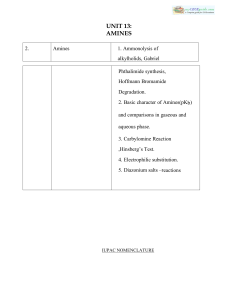
12_chemistry_impq_CH13_amines_02
... The azo products obtained have an extended conjugate system having both the aromatic rings joined through the –N=N– bond. These compounds are often coloured and are used as dyes. Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol in which the phenol molecule at its para position is coupled with the diazo ...
... The azo products obtained have an extended conjugate system having both the aromatic rings joined through the –N=N– bond. These compounds are often coloured and are used as dyes. Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol in which the phenol molecule at its para position is coupled with the diazo ...
CHE 1031 Lab Manual
... LAB 15: Ideal gas law determination of the molecular weight of Mg ..................................... 65 Pre-‐lab Quiz: Ideal gas law determination of MW of Mg ................................................................ ...
... LAB 15: Ideal gas law determination of the molecular weight of Mg ..................................... 65 Pre-‐lab Quiz: Ideal gas law determination of MW of Mg ................................................................ ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.