Many Chemistries Could Be Used to Build Living Systems
... on a cosmic scale. We know that at least one body in the Solar System has a large volume of liquid water on it. At least two and possibly three others have large bodies of very cold water/ammonia mixtures on or in them. The existence of surface oceans of ethane and methane on Titan has been postulat ...
... on a cosmic scale. We know that at least one body in the Solar System has a large volume of liquid water on it. At least two and possibly three others have large bodies of very cold water/ammonia mixtures on or in them. The existence of surface oceans of ethane and methane on Titan has been postulat ...
Chapter 6 - Sites @ Suffolk University
... 6 x 1023 hydrogen atoms to make up a single gram! Chemists have chosen a very simple way to deal with the masses of the elements and their compounds by expressing the atomic masses in grams. The gram atomic mass of hydrogen, for instance, is about one gram, and the gram atomic mass of oxygen is abou ...
... 6 x 1023 hydrogen atoms to make up a single gram! Chemists have chosen a very simple way to deal with the masses of the elements and their compounds by expressing the atomic masses in grams. The gram atomic mass of hydrogen, for instance, is about one gram, and the gram atomic mass of oxygen is abou ...
Step 2
... number to each element wherever it appears in the equation. If the reaction is a redox reaction, identify the element that undergoes an increase in oxidation number and the elements the undergoes a decrease. Find the numerical values of the increase and decrease. Determine the smallest whole-number ...
... number to each element wherever it appears in the equation. If the reaction is a redox reaction, identify the element that undergoes an increase in oxidation number and the elements the undergoes a decrease. Find the numerical values of the increase and decrease. Determine the smallest whole-number ...
BS Chemistry - Government College University Faisalabad
... Relation of entropy and energy with equilibrium constant and their dependence on temperature. Clausius-Clapeyron equation. Chemical potential. Partial molar quantities. Laws of thermodynamics and their applications. Thermodynamic functions internal energy, enthalpy, entropy and free energy. Relation ...
... Relation of entropy and energy with equilibrium constant and their dependence on temperature. Clausius-Clapeyron equation. Chemical potential. Partial molar quantities. Laws of thermodynamics and their applications. Thermodynamic functions internal energy, enthalpy, entropy and free energy. Relation ...
Chapter 4: Solution Chemistry: The Hydrosphere
... OXIDATION NUMBER: the actual or hypothetical charge of an atom in a compound if it (or OXIDATION STATE) existed as a monatomic ion – used to track changes in electron distribution in compounds and to determine electron transfer Guidelines for Assigning Oxidation Numbers 1. The oxidation number of a ...
... OXIDATION NUMBER: the actual or hypothetical charge of an atom in a compound if it (or OXIDATION STATE) existed as a monatomic ion – used to track changes in electron distribution in compounds and to determine electron transfer Guidelines for Assigning Oxidation Numbers 1. The oxidation number of a ...
VCE Chemistry Study Design
... Chemistry is a key science in explaining the workings of our universe through an understanding of the properties and interaction of substances that make up matter. Most processes, from the formation of molecules in outer space to the complex biological interactions occurring in cells, can be describ ...
... Chemistry is a key science in explaining the workings of our universe through an understanding of the properties and interaction of substances that make up matter. Most processes, from the formation of molecules in outer space to the complex biological interactions occurring in cells, can be describ ...
48th CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD CHEMISTRY
... most important buffer system is a carbonate buffer, which is prepared by a salt (HCO3−) and acid (H2CO3) in molar ratio 20:1 (precisely). The exhaled CO2 is released out from a metacarbonic acid, which participates in equilibrium in a blood. a) For the I and II dissociation stages of metacarbonic ac ...
... most important buffer system is a carbonate buffer, which is prepared by a salt (HCO3−) and acid (H2CO3) in molar ratio 20:1 (precisely). The exhaled CO2 is released out from a metacarbonic acid, which participates in equilibrium in a blood. a) For the I and II dissociation stages of metacarbonic ac ...
Chapter 3: Calculations with Chemical Formulas
... A 3.87 mg of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) gives 5.80mg of CO2 and 1.58mg of H2O on combustion. What is the % composition of this compound? First convert the mass of CO2 to moles of CO2. Next, convert this to moles of C (1 mol CO2 is equivalent to 1 mol C). Finally, convert to mass of C, changing millig ...
... A 3.87 mg of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) gives 5.80mg of CO2 and 1.58mg of H2O on combustion. What is the % composition of this compound? First convert the mass of CO2 to moles of CO2. Next, convert this to moles of C (1 mol CO2 is equivalent to 1 mol C). Finally, convert to mass of C, changing millig ...
Slide 1
... I. Oxidation & Reduction -a substance which ________ oxidizes another substance by ________ accepting its ________ electrons is called an ________ oxidizing _____, agent which is also reduced the substance that is _______ -a substance which _______ reduces another substance by ______ losing ________ ...
... I. Oxidation & Reduction -a substance which ________ oxidizes another substance by ________ accepting its ________ electrons is called an ________ oxidizing _____, agent which is also reduced the substance that is _______ -a substance which _______ reduces another substance by ______ losing ________ ...
ch 7.1 - PickIntSci
... by manipulating coefficients. Convert between moles and mass of a substance using molar mass. Calculate amounts of reactants or products by using molar mass, mole ratios, and balanced chemical equations. ...
... by manipulating coefficients. Convert between moles and mass of a substance using molar mass. Calculate amounts of reactants or products by using molar mass, mole ratios, and balanced chemical equations. ...
Chapter 14: Chemical Equilibrium
... as being in a state of dynamic equilibrium? What are the characteristics and requirements of dynamic equilibrium? ...
... as being in a state of dynamic equilibrium? What are the characteristics and requirements of dynamic equilibrium? ...
Chapter 7 - NordoniaHonorsChemistry
... that Takes Place when an Aqueous Solution of ammonium sulfate is Mixed with an Aqueous Solution of lead (II) acetate. ...
... that Takes Place when an Aqueous Solution of ammonium sulfate is Mixed with an Aqueous Solution of lead (II) acetate. ...
Dr David`s Chemistry Test Answers
... 2. Many familiar inorganic reactions like the reaction of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide are not reversible. Similarly, the reaction of silver nitrate solution with sodium chloride solution is a reaction which only goes one way (ie, left to right). This produces a white precipitate of silve ...
... 2. Many familiar inorganic reactions like the reaction of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide are not reversible. Similarly, the reaction of silver nitrate solution with sodium chloride solution is a reaction which only goes one way (ie, left to right). This produces a white precipitate of silve ...
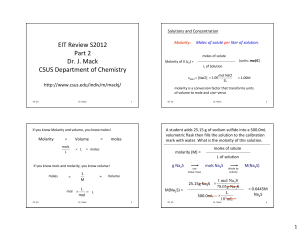
EIT Review S2012 Part 2 Dr. J. Mack CSUS Department of Chemistry
... • Concentration data can be used to calculate equilibrium constants for both aqueous and gaseous systems. • In these cases, the symbol K is sometimes given the subscript “c” for “concentration,” as in Kc. • For gases, however, equilibrium constant expressions can be written in another way: in ...
... • Concentration data can be used to calculate equilibrium constants for both aqueous and gaseous systems. • In these cases, the symbol K is sometimes given the subscript “c” for “concentration,” as in Kc. • For gases, however, equilibrium constant expressions can be written in another way: in ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... Mannich type condensation involving aromatic aldehydes, ammonium acetate and ketones having two active methylene groups, resulting in the formation of 2,6-diarylpiperidin-4-ones, was first reported by Noller and Baliah [5] . The extensive studies undertaken in the past on 4-piperidones have their re ...
... Mannich type condensation involving aromatic aldehydes, ammonium acetate and ketones having two active methylene groups, resulting in the formation of 2,6-diarylpiperidin-4-ones, was first reported by Noller and Baliah [5] . The extensive studies undertaken in the past on 4-piperidones have their re ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.