Fall 2008 Blank Exam 1 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State
... This exam consists of 25 multiple-choice questions. Each question has four points associated with it. Select the best multiple-choice answer by filling in the corresponding circle on the rear page of the answer sheet. If you have any questions before the exam, please ask. If you have any questions d ...
... This exam consists of 25 multiple-choice questions. Each question has four points associated with it. Select the best multiple-choice answer by filling in the corresponding circle on the rear page of the answer sheet. If you have any questions before the exam, please ask. If you have any questions d ...
S.O.L. Review
... A. It has a different number of protons and two less neutrons than C-12 B. It has the same number of protons and two more electrons than C-12 C. It has the same number of protons but two more neutrons than C-12 D. It has a different number of protons and two more neutrons than C-12 ...
... A. It has a different number of protons and two less neutrons than C-12 B. It has the same number of protons and two more electrons than C-12 C. It has the same number of protons but two more neutrons than C-12 D. It has a different number of protons and two more neutrons than C-12 ...
Packet #7- Chemical Reactions
... Conservation of mass [E] No atoms are lost or made during a chemical reaction. This means that the mass is always conserved. In other words, the total mass of products after the reaction is the same as the total mass of the reactants at the start. This fact allows you to work out the mass of one sub ...
... Conservation of mass [E] No atoms are lost or made during a chemical reaction. This means that the mass is always conserved. In other words, the total mass of products after the reaction is the same as the total mass of the reactants at the start. This fact allows you to work out the mass of one sub ...
AP CHEMISTRY – Source: 1999 AP Exam CHAPTER 8 TEST
... (A) Activation energy (D) Kinetic energy (B) Free energy (E) Lattice energy (C) Ionization energy 5.The energy required to convert a ground-state atom in the gas phase to a gaseous positive ion: C 6.The energy change that occurs in the conversion of an ionic solid to widely separated gaseous ions: E ...
... (A) Activation energy (D) Kinetic energy (B) Free energy (E) Lattice energy (C) Ionization energy 5.The energy required to convert a ground-state atom in the gas phase to a gaseous positive ion: C 6.The energy change that occurs in the conversion of an ionic solid to widely separated gaseous ions: E ...
Catalyst Notes - University of Idaho
... thermodynamics, by lowering the activation energy. Hence the reaction proceeds much faster. Catalysts: ...
... thermodynamics, by lowering the activation energy. Hence the reaction proceeds much faster. Catalysts: ...
Part II - KFUPM Faculty List
... Thermodynamics of Living Systems Thermodynamics have a great effect in biological sciences, such as processes taking place inside our bodies. such as processes taking place inside our bodies. Many chemical reactions carried out inside the body (such as DNA and protein formation) are not sponta ...
... Thermodynamics of Living Systems Thermodynamics have a great effect in biological sciences, such as processes taking place inside our bodies. such as processes taking place inside our bodies. Many chemical reactions carried out inside the body (such as DNA and protein formation) are not sponta ...
Spring Benchmark Exam
... A scientist observed changes in the gas pressure of one mole of a gas in a sealed chamber with a fixed volume. To identify the source of the changes, the scientist should check for variations in the A B C D ...
... A scientist observed changes in the gas pressure of one mole of a gas in a sealed chamber with a fixed volume. To identify the source of the changes, the scientist should check for variations in the A B C D ...
9182747 Chemistry Ja02
... 61 Which temperature change would cause the volume of a sample of an ideal gas to double when the pressure of the sample remains the same? (1) from 200°C to 400°C (2) from 400°C to 200°C (3) from 200 K to 400 K (4) from 400 K to 200 K ...
... 61 Which temperature change would cause the volume of a sample of an ideal gas to double when the pressure of the sample remains the same? (1) from 200°C to 400°C (2) from 400°C to 200°C (3) from 200 K to 400 K (4) from 400 K to 200 K ...
Powerpoints - Holy Cross Collegiate
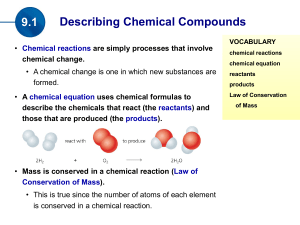
... • Every chemical reaction involves the rearrangement of atoms into different combinations. However, during these reactions, the total number of atoms of each type of element is the same after the reaction as it was before the reaction. • Chemical reactions have to be properly balanced in order to cl ...
... • Every chemical reaction involves the rearrangement of atoms into different combinations. However, during these reactions, the total number of atoms of each type of element is the same after the reaction as it was before the reaction. • Chemical reactions have to be properly balanced in order to cl ...
Organic Chemical Reactions
... A favorable thermodynamics is a necessary but not sufficient condition for a reaction to take place. In fact, the equilibrium can be reached in a relatively fast or low manner. If the rate is very low (for instance, months or even years or centuries) the net result is that the reaction basically doe ...
... A favorable thermodynamics is a necessary but not sufficient condition for a reaction to take place. In fact, the equilibrium can be reached in a relatively fast or low manner. If the rate is very low (for instance, months or even years or centuries) the net result is that the reaction basically doe ...
chemical reactions
... In these reactions one of the products formed is an insoluble solid called a precipitate. For example, when solutions of potassium chromate,K2CrO4 , and barium nitrate, Ba(NO3)2 , are combined an insoluble salt barium chromate, BaCrO4 , is formed. ...
... In these reactions one of the products formed is an insoluble solid called a precipitate. For example, when solutions of potassium chromate,K2CrO4 , and barium nitrate, Ba(NO3)2 , are combined an insoluble salt barium chromate, BaCrO4 , is formed. ...
2014MSC(ORGANIC(CHEMISTRY!
... ! Polar!covalent!bonds!are!formed!through!the!sharing!of!electrons!between!neutral!atoms!–! it!is!polar!where!the!electrons!are!attracted!stronger!to!one!atom!over!the!other.!! ! Therefore,!the!electron!distribution!between!the!atoms!is!not!symmetrical,!and!atoms!have! a!partial!negative!or!positive ...
... ! Polar!covalent!bonds!are!formed!through!the!sharing!of!electrons!between!neutral!atoms!–! it!is!polar!where!the!electrons!are!attracted!stronger!to!one!atom!over!the!other.!! ! Therefore,!the!electron!distribution!between!the!atoms!is!not!symmetrical,!and!atoms!have! a!partial!negative!or!positive ...
(the products). Mass is conserved in a chemical reaction
... coefficients as required throughout the equation so that atoms are conserved. Subscripts are never changed. • For example when the number of atoms of the reactant element(s) are the same as the number of atoms of the product element(s), the equation is balanced. ...
... coefficients as required throughout the equation so that atoms are conserved. Subscripts are never changed. • For example when the number of atoms of the reactant element(s) are the same as the number of atoms of the product element(s), the equation is balanced. ...
Dr. Baxley`s Equilibrium Worksheet
... 12. At 450°C, ammonia gas will decompose according to the following equation: 2 NH3 (g) ⇌ N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) At 450.˚C, Kc = 6.30. An unknown quantity of NH3 is placed in a reaction flask (with no N2 or H2) and is allowed to come to equilibrium at 450. °C. The equilibrium concentration of H2 is then ...
... 12. At 450°C, ammonia gas will decompose according to the following equation: 2 NH3 (g) ⇌ N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) At 450.˚C, Kc = 6.30. An unknown quantity of NH3 is placed in a reaction flask (with no N2 or H2) and is allowed to come to equilibrium at 450. °C. The equilibrium concentration of H2 is then ...
[Mg] +2[ S ]-2
... 11. Adding ice cubes to hot chocolate so it cools down faster not a chemical reaction 12. The smell that is given off from a stink bomb chemical reaction Using the 5 indicators of chemical reactions explain how you can determine whether a chemical reaction has taken place or not in the scenario belo ...
... 11. Adding ice cubes to hot chocolate so it cools down faster not a chemical reaction 12. The smell that is given off from a stink bomb chemical reaction Using the 5 indicators of chemical reactions explain how you can determine whether a chemical reaction has taken place or not in the scenario belo ...
Ch 06
... initial speed (kinetic energy). We could call this situation an effective trip. The minimum kinetic energy required is analogous to the activation energy for a reaction. If the ball does not have enough kinetic energy it will not reach the top of the track and will just roll back to point A. This is ...
... initial speed (kinetic energy). We could call this situation an effective trip. The minimum kinetic energy required is analogous to the activation energy for a reaction. If the ball does not have enough kinetic energy it will not reach the top of the track and will just roll back to point A. This is ...
Stoichiometry intro
... Remember that the coefficients from a balanced reaction represent the ratio of the moles of substances that react and form during a chemical reaction. These numbers are fixed - they do not change We can use these ratios to predict the amounts of substances that react and form in a reaction when ...
... Remember that the coefficients from a balanced reaction represent the ratio of the moles of substances that react and form during a chemical reaction. These numbers are fixed - they do not change We can use these ratios to predict the amounts of substances that react and form in a reaction when ...
Physical Science Semester 2 Final Exam 2013 –STUDY GUIDE
... 17. Increasing the speed of an object ____ its potential energy. 18. The SI (metric) unit for energy is the ____. 19. You can calculate kinetic energy by using the equation ____. 20. You can calculate gravitational potential energy by using the equation ____. 21. According to the law of conservatio ...
... 17. Increasing the speed of an object ____ its potential energy. 18. The SI (metric) unit for energy is the ____. 19. You can calculate kinetic energy by using the equation ____. 20. You can calculate gravitational potential energy by using the equation ____. 21. According to the law of conservatio ...
C:\exams\June\June_06\chemistry\final\Chemistry 3202 June 2006
... 51.(c) At 1000 K, sulfur dioxide is converted into sulfur trioxide, as shown below. 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) ...
... 51.(c) At 1000 K, sulfur dioxide is converted into sulfur trioxide, as shown below. 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) ...
Chapter 4 - U of L Class Index
... e.g. Propane (C3H8) burns in oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water. Calculate the mass of carbon dioxide produced if the reaction of 45.0 g of propane and sufficient oxygen has a 60.0% yield. ...
... e.g. Propane (C3H8) burns in oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water. Calculate the mass of carbon dioxide produced if the reaction of 45.0 g of propane and sufficient oxygen has a 60.0% yield. ...
chemistry — released form
... Light is emitted when relaxation occurs. Relaxation is when an electron goes from a high energy level to a lower energy level. Energy is absorbed when excitation occurs. Excitation is when an electron goes from a low energy level to a higher energy level. ...
... Light is emitted when relaxation occurs. Relaxation is when an electron goes from a high energy level to a lower energy level. Energy is absorbed when excitation occurs. Excitation is when an electron goes from a low energy level to a higher energy level. ...
Specification
... The format will be the same for each achievement standard. Within each paper all questions will provide opportunity for all grades of performance – achievement, achievement with merit, and achievement with excellence; there are no stand-alone questions for lower achievement grades. There will be thr ...
... The format will be the same for each achievement standard. Within each paper all questions will provide opportunity for all grades of performance – achievement, achievement with merit, and achievement with excellence; there are no stand-alone questions for lower achievement grades. There will be thr ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.













![[Mg] +2[ S ]-2](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014450548_1-468f3af464a09baae245d79fadf97d41-300x300.png)








