Unit_4_Notes_
... 14.1 Factors That Affect Reaction Rates Chemical kinetics is the art of chemistry that deals with the speeds, or rates, of reactions. Reaction rates can range from microseconds to millions of years. There are 5 main factors that affect reaction rates – the book leaves out the first to be underst ...
... 14.1 Factors That Affect Reaction Rates Chemical kinetics is the art of chemistry that deals with the speeds, or rates, of reactions. Reaction rates can range from microseconds to millions of years. There are 5 main factors that affect reaction rates – the book leaves out the first to be underst ...
Honors Chemistry Semester 1 Exam Review
... 14. Select all the phrases in the parenthesis that make the statement true: Solid X is placed in contact with solid Y. Heat will flow spontaneously from X to Y when (X is 20°C and Y is 20°C / X is 10°C and Y is 5°C / X is -25°C and Y is -10°C / X is 25°C and Y is 30°C). 15. What is the total number ...
... 14. Select all the phrases in the parenthesis that make the statement true: Solid X is placed in contact with solid Y. Heat will flow spontaneously from X to Y when (X is 20°C and Y is 20°C / X is 10°C and Y is 5°C / X is -25°C and Y is -10°C / X is 25°C and Y is 30°C). 15. What is the total number ...
Chem Regents 2015 A Few Things
... Temperature reprents (NOT: is equal to) the average molecular kinetic energy. Heat is the amount of total molecular kinetic energy. Objects with the same temperature but different mass or heat capacity have different amounts of total energy. ...
... Temperature reprents (NOT: is equal to) the average molecular kinetic energy. Heat is the amount of total molecular kinetic energy. Objects with the same temperature but different mass or heat capacity have different amounts of total energy. ...
Practice Questions
... Molecules of different gases having the same volume, the same pressure, and the same temperature will have an average speed that is in proportion to their molecular mass. A balloon containing 22.4 liters of hydrogen gas at zero degrees Celsius and a pressure of one atmosphere will contain the same n ...
... Molecules of different gases having the same volume, the same pressure, and the same temperature will have an average speed that is in proportion to their molecular mass. A balloon containing 22.4 liters of hydrogen gas at zero degrees Celsius and a pressure of one atmosphere will contain the same n ...
Just a Few Things 2012
... In BOTH types of cell the same types of reaction occur at the same electrode: ANode — OXidation ...
... In BOTH types of cell the same types of reaction occur at the same electrode: ANode — OXidation ...
de Caux - Combustion of Methane Demonstration
... The combustion of methane is an example of an exothermic reaction. More energy is released when the bonds in the products are formed than is used to break the bonds of the reactants. As the gas burns, it gives off energy and raises the temperature of its surroundings. Water has a high specific heat ...
... The combustion of methane is an example of an exothermic reaction. More energy is released when the bonds in the products are formed than is used to break the bonds of the reactants. As the gas burns, it gives off energy and raises the temperature of its surroundings. Water has a high specific heat ...
Resource for Final Exam Prep
... So, E = hc/ 1 nm = 1 10-9 m Photoelectric effect kinetic energy of ejected electron Uncertainty principle you can estimate accurately the position and the momentum of an electron at the same time Quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms), what do they each define? Value of l for s, p, d and f orbitals E ...
... So, E = hc/ 1 nm = 1 10-9 m Photoelectric effect kinetic energy of ejected electron Uncertainty principle you can estimate accurately the position and the momentum of an electron at the same time Quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms), what do they each define? Value of l for s, p, d and f orbitals E ...
Chemical Equations
... solid state. Placed after the formula of a substance Alternative to (s) but used ONLY for a solid PRODUCT, not reactants indicates a liquid reactant or product indicates an aqueous solution (where some solute has been dissolved in water) indicates a gaseous reactant or product alternative to (g), bu ...
... solid state. Placed after the formula of a substance Alternative to (s) but used ONLY for a solid PRODUCT, not reactants indicates a liquid reactant or product indicates an aqueous solution (where some solute has been dissolved in water) indicates a gaseous reactant or product alternative to (g), bu ...
From (2)
... K depends on different chemical potential between the specieses which are diffused in boundary layer and also depends on the geometry of powder particles. ...
... K depends on different chemical potential between the specieses which are diffused in boundary layer and also depends on the geometry of powder particles. ...
AP Chemistry Syllabus - Tuloso
... limiting reactants C. Equilibrium Concept of dynamic equilibrium, physical and chemical; Le Chatelier's principle; equilibrium constants A. Quantitative treatment . Equilibrium constants for gaseous reactions: Kp, Kc a. Equilibrium constants for reactions in solution 1. Constants for acids and bases ...
... limiting reactants C. Equilibrium Concept of dynamic equilibrium, physical and chemical; Le Chatelier's principle; equilibrium constants A. Quantitative treatment . Equilibrium constants for gaseous reactions: Kp, Kc a. Equilibrium constants for reactions in solution 1. Constants for acids and bases ...
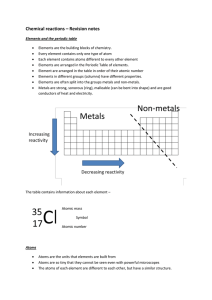
Chemical reactions revision
... Elements are the building blocks of chemistry. Every element contains only one type of atom Each element contains atoms different to every other element Elements are arranged in the Periodic Table of elements. Element are arranged in the table in order of their atomic number Elements in different gr ...
... Elements are the building blocks of chemistry. Every element contains only one type of atom Each element contains atoms different to every other element Elements are arranged in the Periodic Table of elements. Element are arranged in the table in order of their atomic number Elements in different gr ...
Welcome to 3FF3! Bio
... Evolution of Life • Life did not suddenly crop up in its element form of complex structures (DNA, proteins) in one sudden reaction from monofunctional simple molecules In this course, we will follow some of the ideas of how life may ...
... Evolution of Life • Life did not suddenly crop up in its element form of complex structures (DNA, proteins) in one sudden reaction from monofunctional simple molecules In this course, we will follow some of the ideas of how life may ...
Lecture 1 and 2a - Thermochemistry
... A measure of energy is the calorie, where 1 Calorie = 4.184 J. One calorie is the energy required to raise 1g of water 1°C Heat capacity is the heat required to raise an object by a number one degree Celsius. Larger objects have more heat capacity than smaller objects of the same composition. The un ...
... A measure of energy is the calorie, where 1 Calorie = 4.184 J. One calorie is the energy required to raise 1g of water 1°C Heat capacity is the heat required to raise an object by a number one degree Celsius. Larger objects have more heat capacity than smaller objects of the same composition. The un ...
Johnny Xie Period 5 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry 6.1 The Nature of
... 10. Nature tends to favor states that have lower energy rather than those that have higher energy. 11. First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy of the universe is constant. 12. Internal energy: sum of kinetic and potential energies of all the particles in the system. The internal energy of a system can b ...
... 10. Nature tends to favor states that have lower energy rather than those that have higher energy. 11. First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy of the universe is constant. 12. Internal energy: sum of kinetic and potential energies of all the particles in the system. The internal energy of a system can b ...
Thermodynamics - Ian Dalgleish
... In ALL of these reactions however, ∆H is negative - heat is given out. The surroundings heat up. The molecules of the surroundings move faster and become more disordered. The overall entropy therefore does increase. Free Energy Consider again the molecules doing work against the piston. Due to their ...
... In ALL of these reactions however, ∆H is negative - heat is given out. The surroundings heat up. The molecules of the surroundings move faster and become more disordered. The overall entropy therefore does increase. Free Energy Consider again the molecules doing work against the piston. Due to their ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... The active ingredient in the pain reliever aspirin is acetylsalicylic acid. This compound can be produced by reacting salicylic acid with acetic acid. The label of one aspirin bottle indicates that the accepted mass of acetylsalicylic acid in each tablet is 325 milligrams. In a laboratory, an aspiri ...
... The active ingredient in the pain reliever aspirin is acetylsalicylic acid. This compound can be produced by reacting salicylic acid with acetic acid. The label of one aspirin bottle indicates that the accepted mass of acetylsalicylic acid in each tablet is 325 milligrams. In a laboratory, an aspiri ...
The bombardier beetle uses an explosive discharge as a defensive
... 2. A hot air balloon is being inflated to its full extent by heating the air inside it. In the final stages of this process, the volume of the balloon changes from 3.5 x 106 L to 4.50 x 106 L by the addition of 160 MJ of energy as heat. Assuming that the balloon expands against a constant pressure o ...
... 2. A hot air balloon is being inflated to its full extent by heating the air inside it. In the final stages of this process, the volume of the balloon changes from 3.5 x 106 L to 4.50 x 106 L by the addition of 160 MJ of energy as heat. Assuming that the balloon expands against a constant pressure o ...
Paper
... (g) What observation is made when a sample of ethanal is heated with Fehling’s reagent? (h) The concentration of an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is 0.2 g per litre. Calculate its pH. (i) Under what circumstances can ionic compounds conduct electricity? (j) Which class of organic compo ...
... (g) What observation is made when a sample of ethanal is heated with Fehling’s reagent? (h) The concentration of an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is 0.2 g per litre. Calculate its pH. (i) Under what circumstances can ionic compounds conduct electricity? (j) Which class of organic compo ...
AP Syllabus
... Course Description: AP Chemistry is designed to be a freshmen level college course equivalent to a year of general chemistry suited for science majors. The pre-requisites for enrolling in AP Chemistry are APP Chemistry and Algebra II. Students taking AP Chemistry are usually juniors, however an occa ...
... Course Description: AP Chemistry is designed to be a freshmen level college course equivalent to a year of general chemistry suited for science majors. The pre-requisites for enrolling in AP Chemistry are APP Chemistry and Algebra II. Students taking AP Chemistry are usually juniors, however an occa ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.